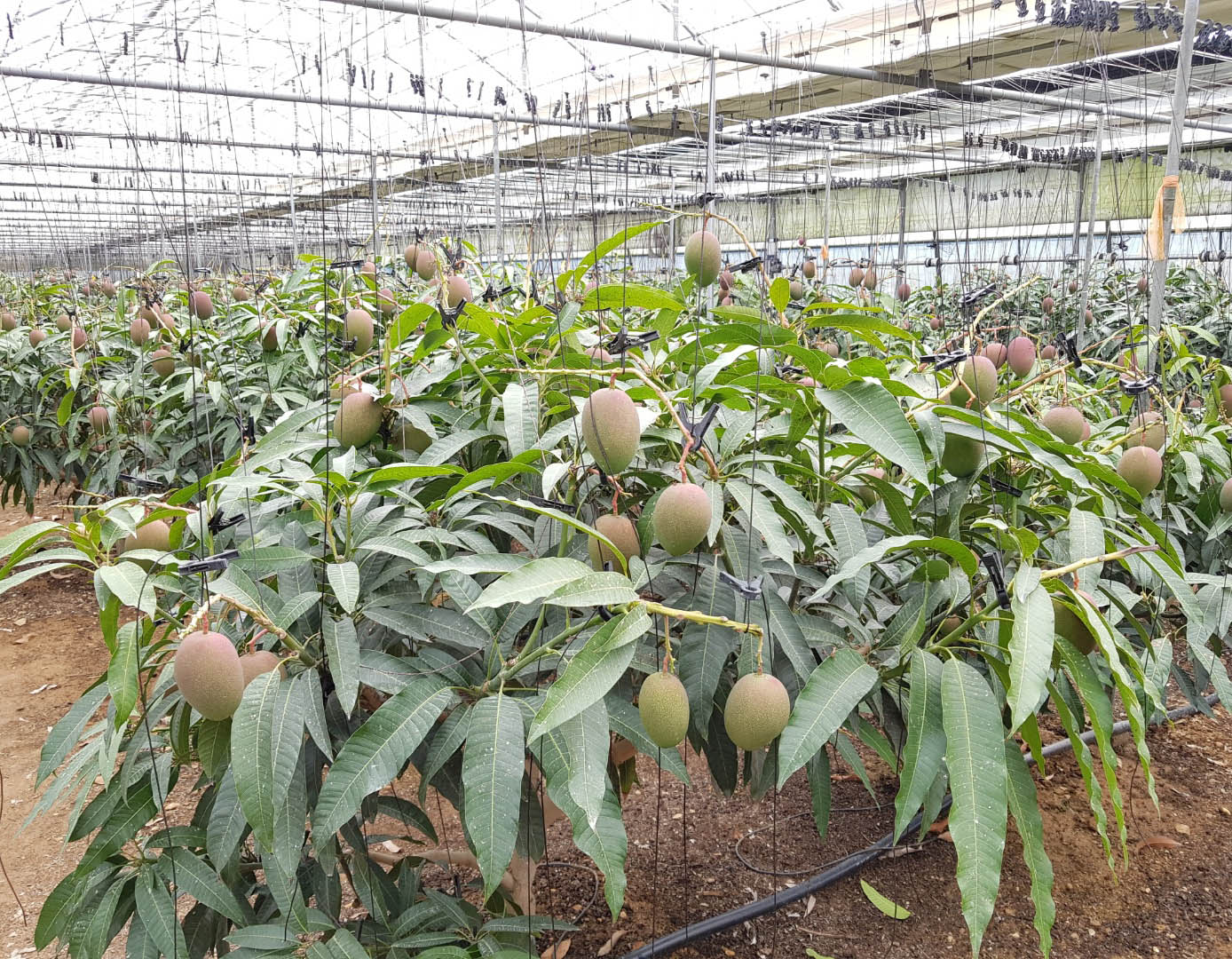
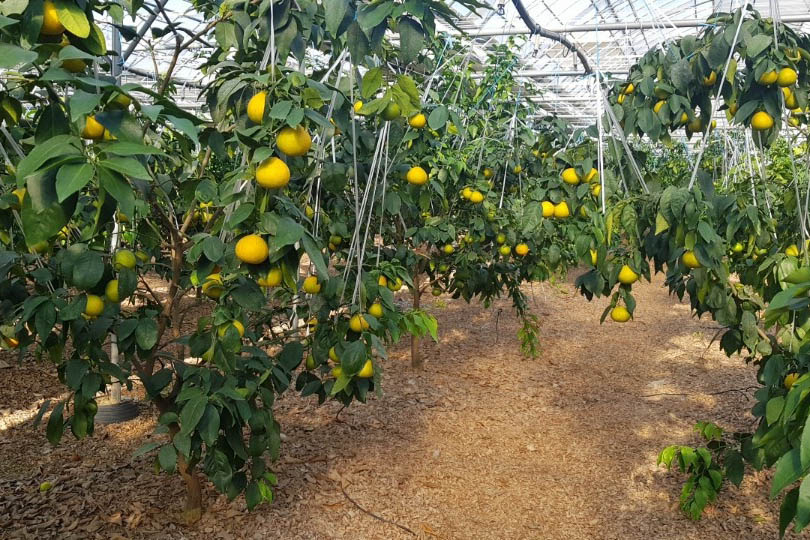
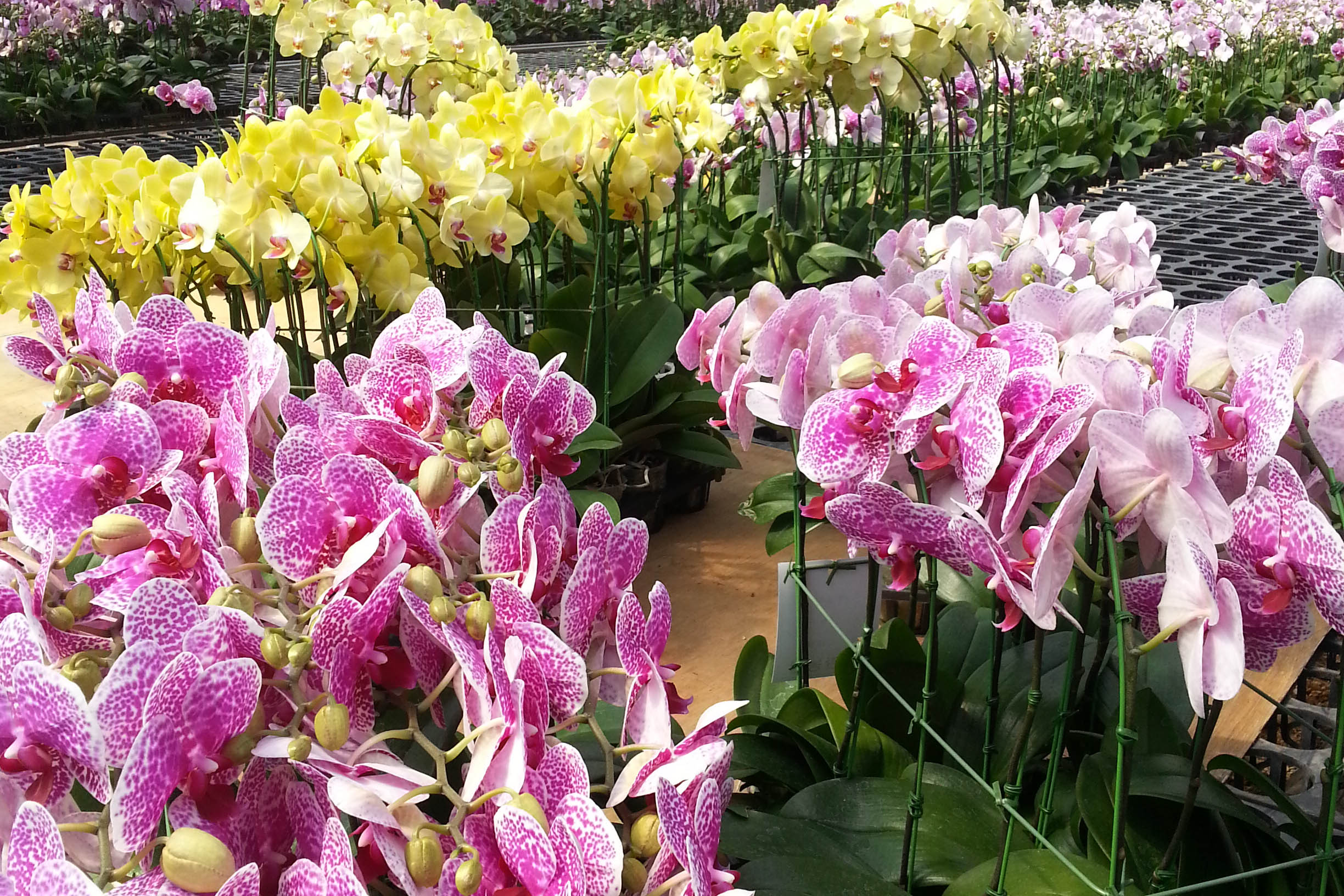
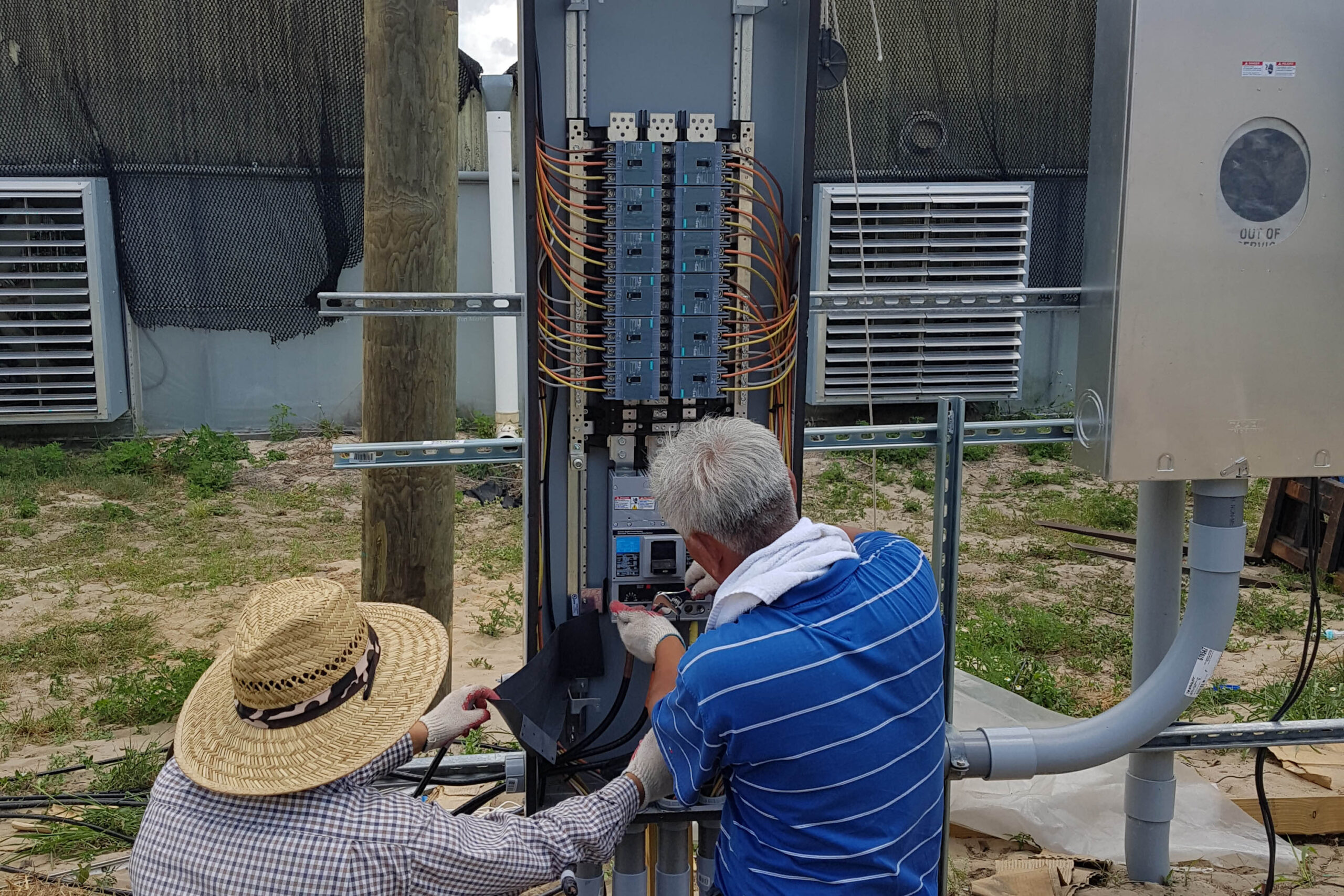
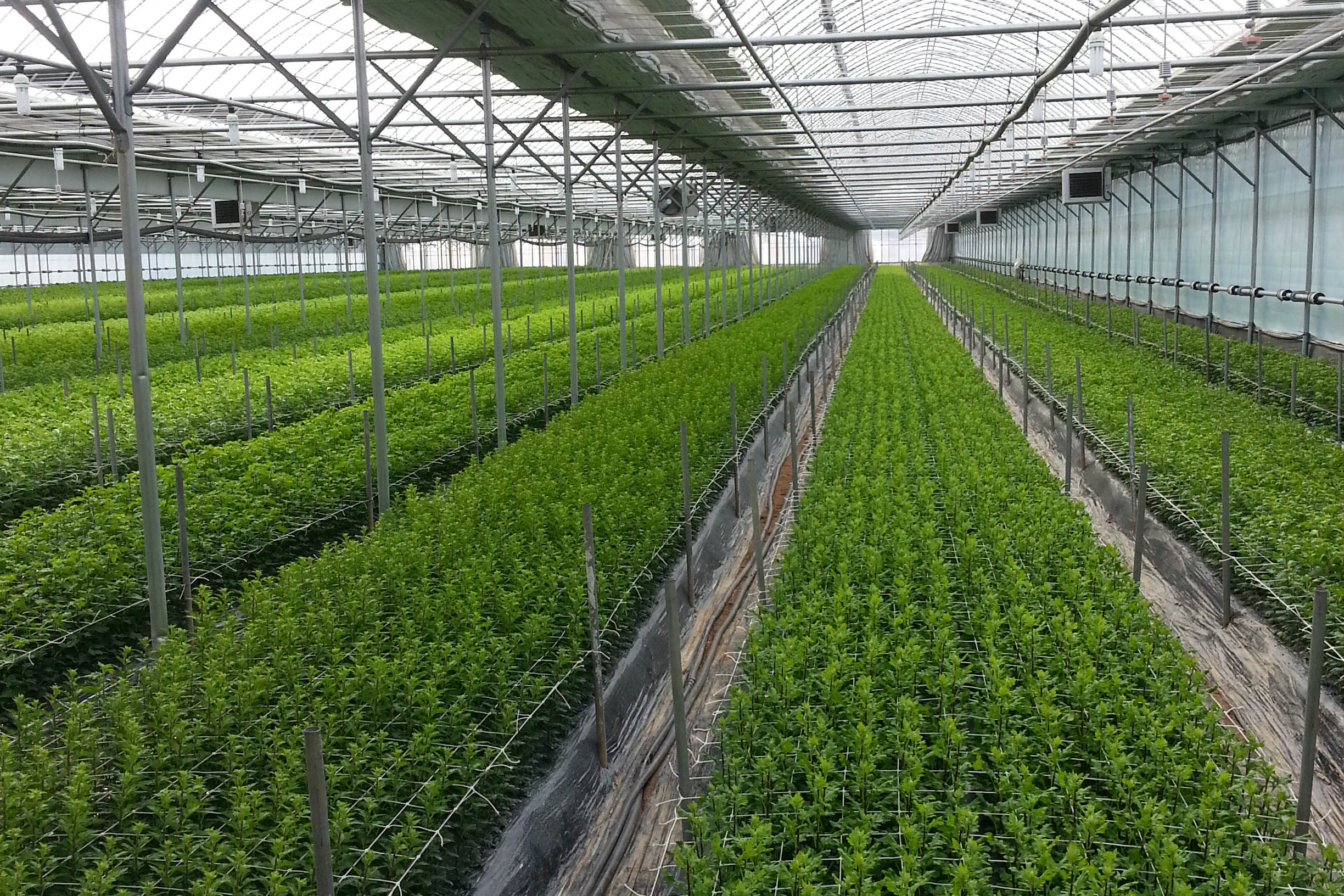
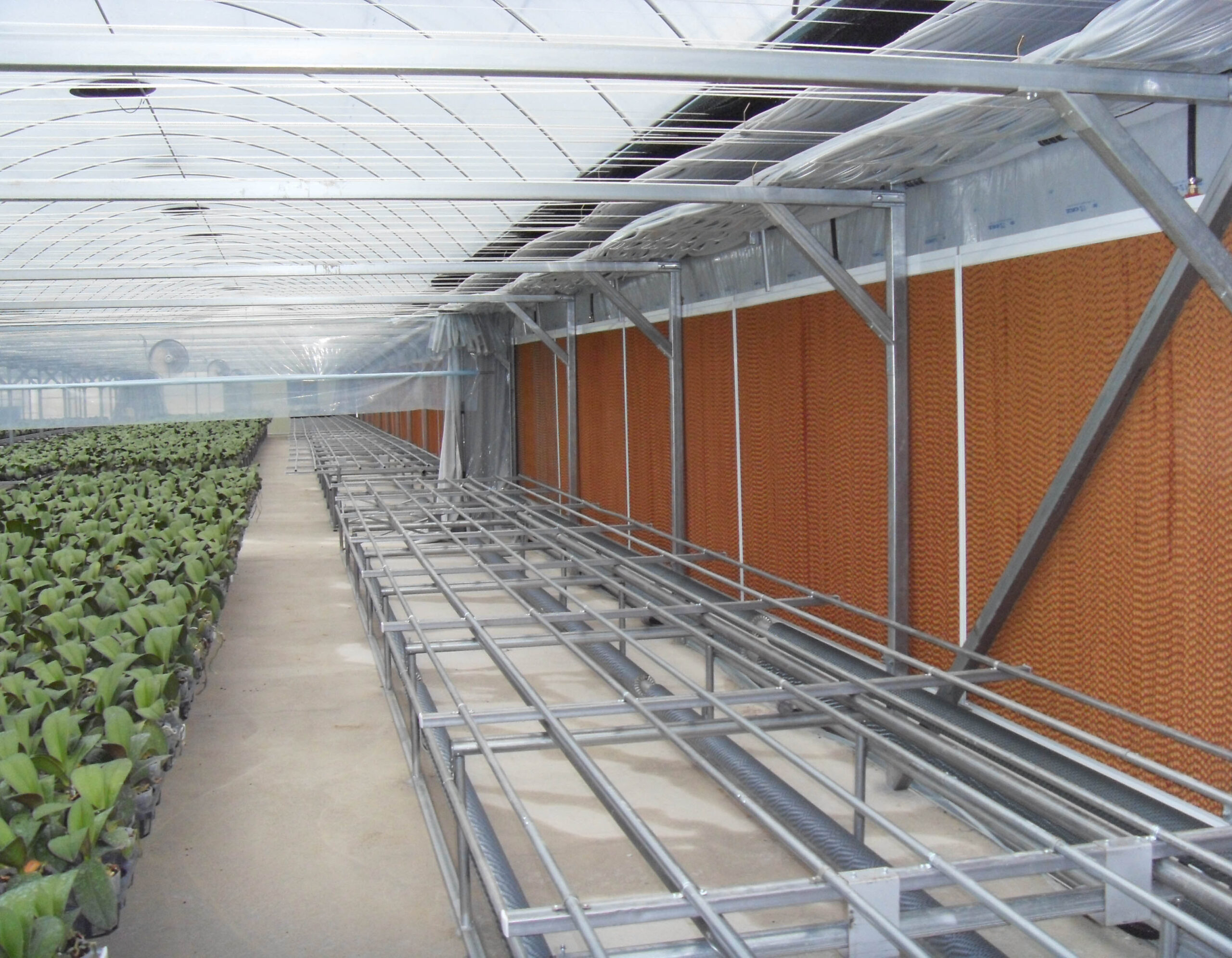
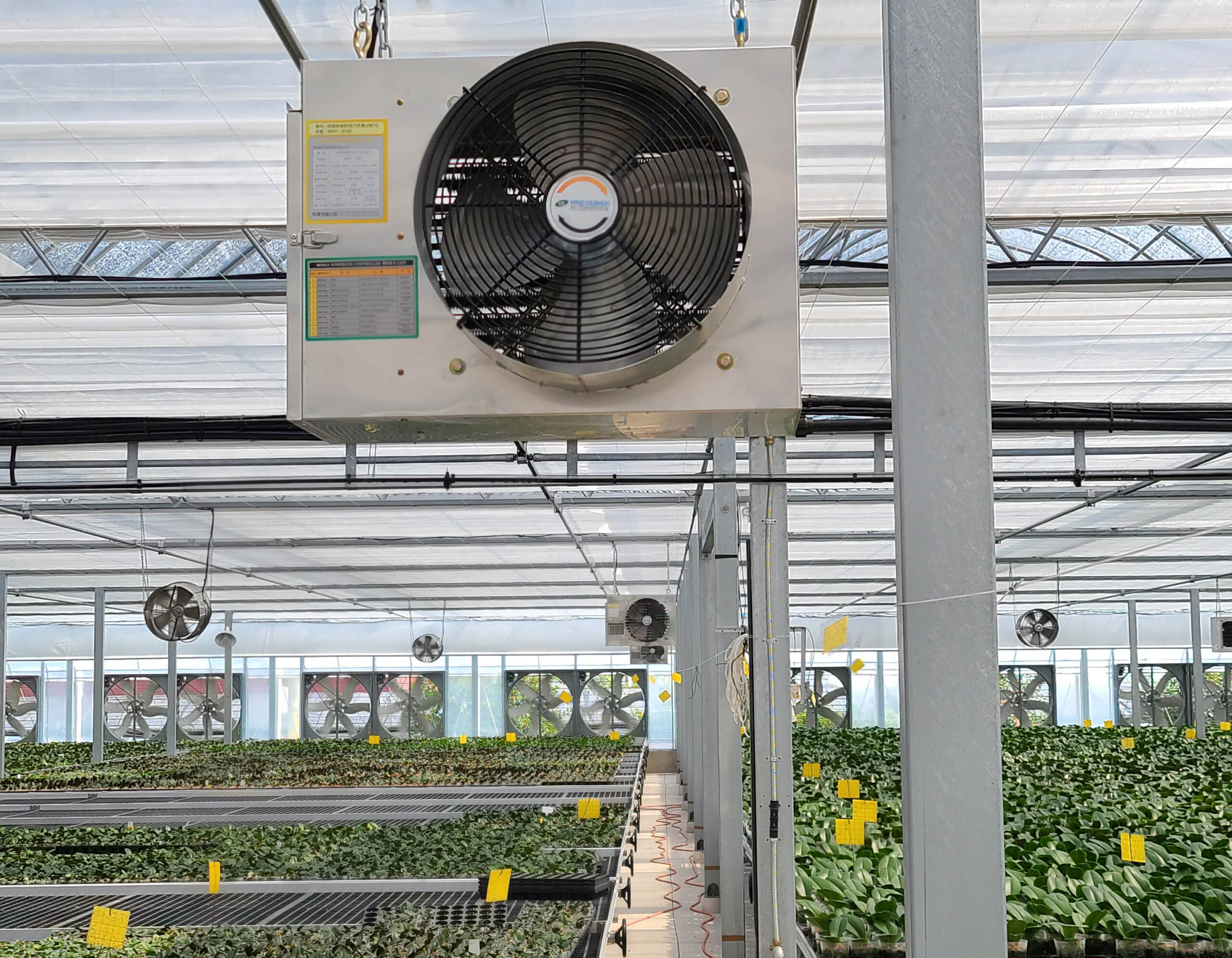
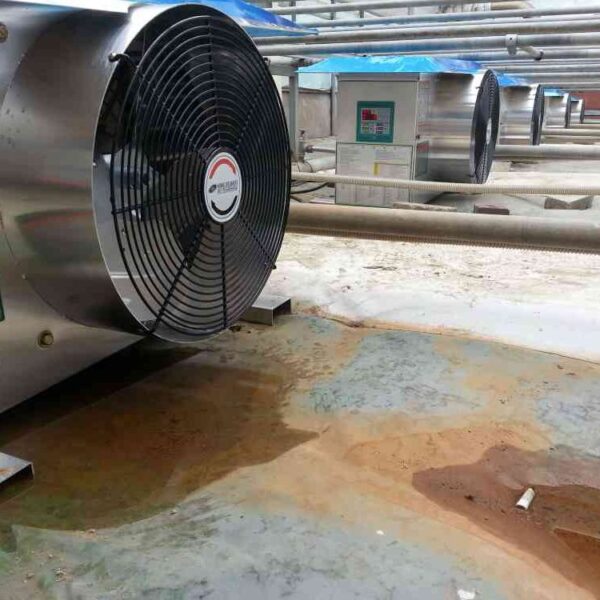
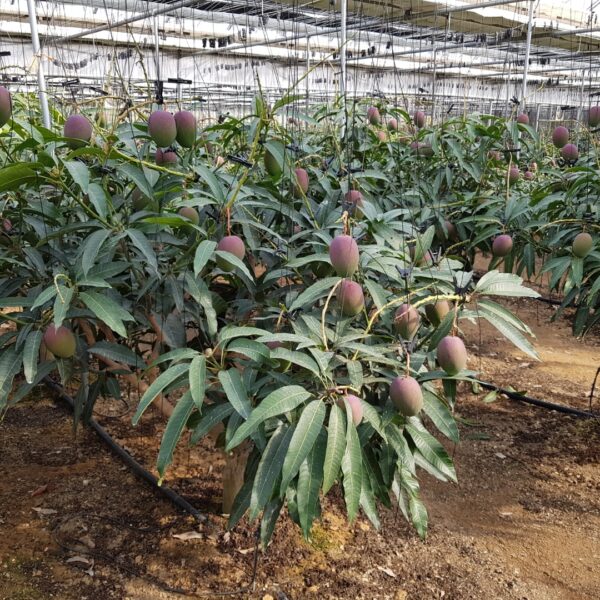
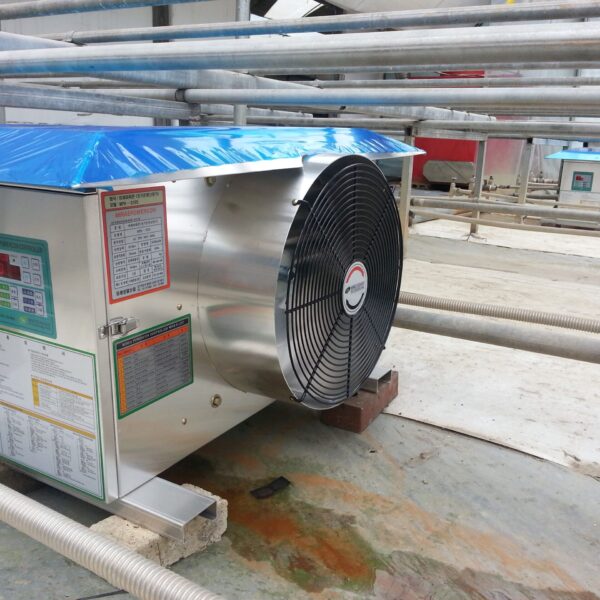
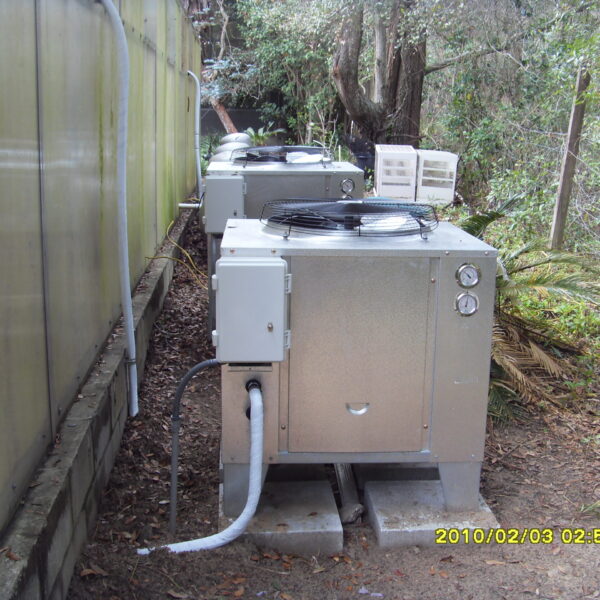
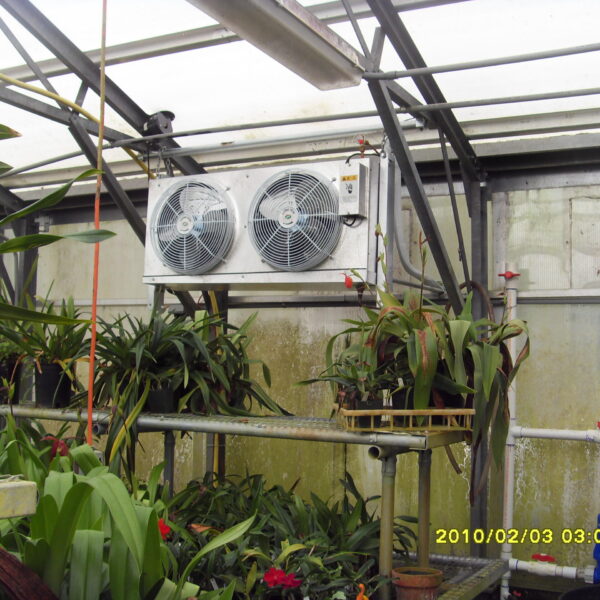
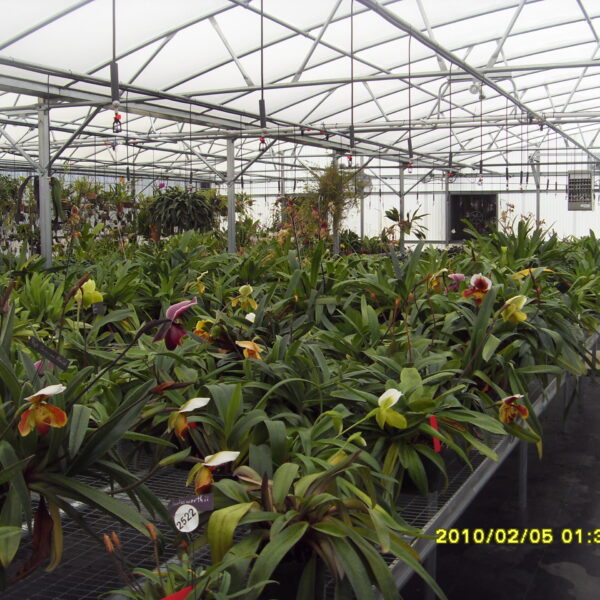
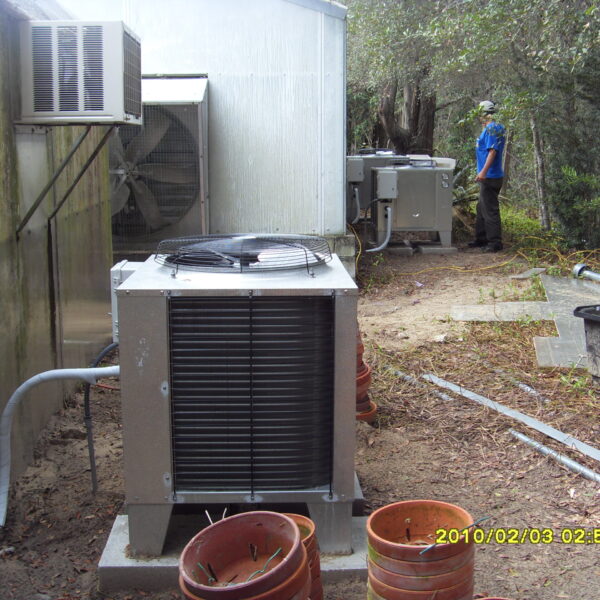
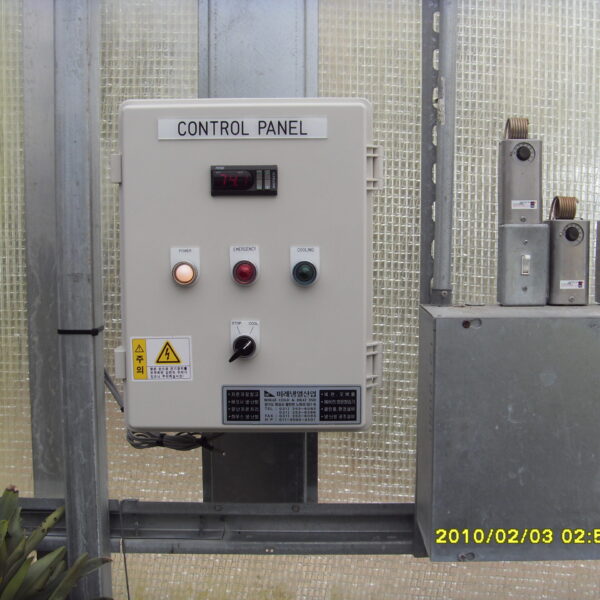
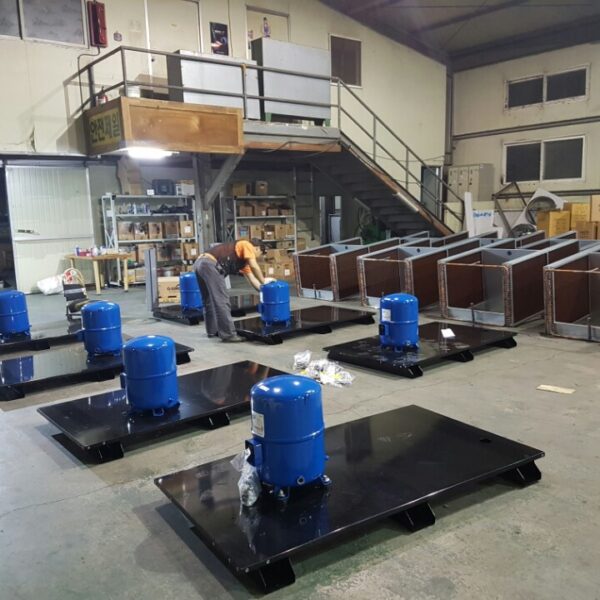
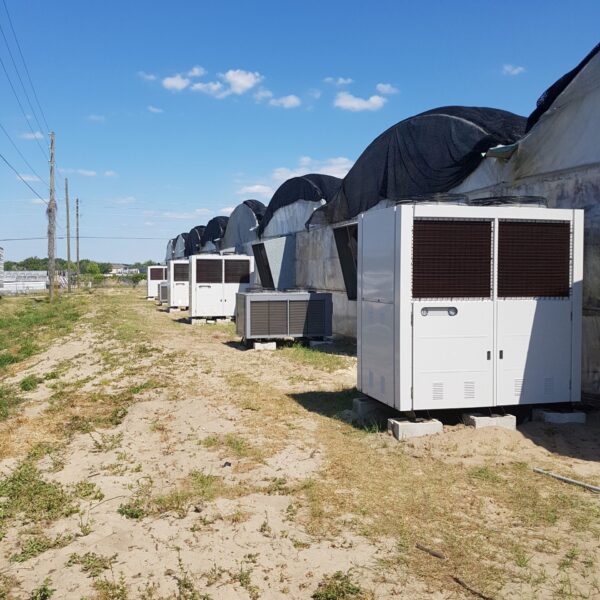
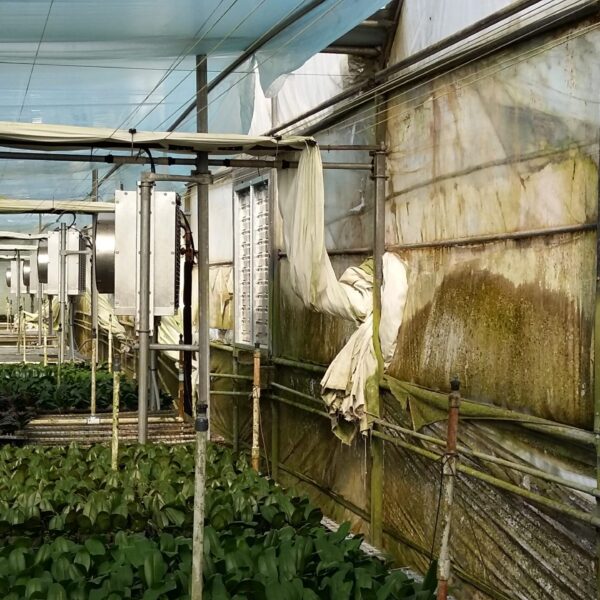
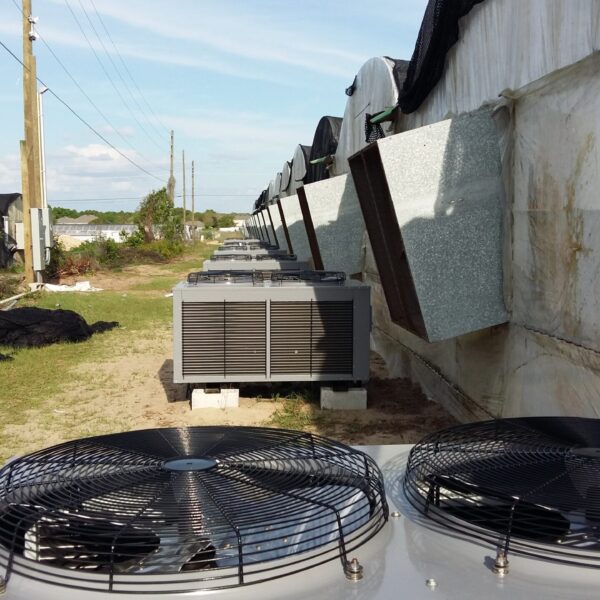
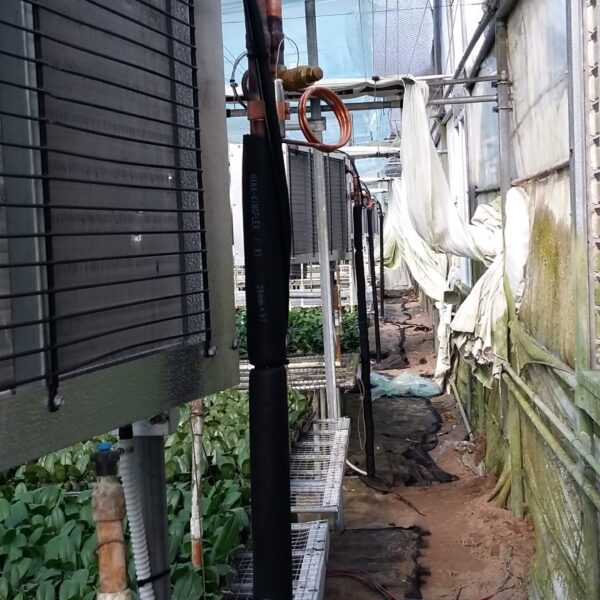
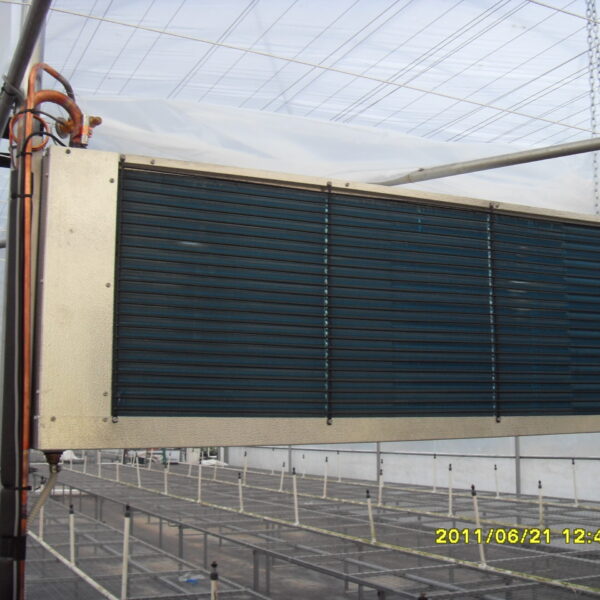
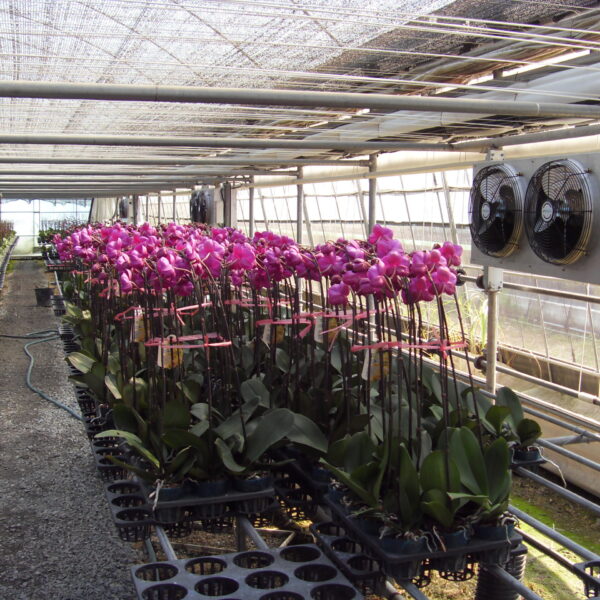
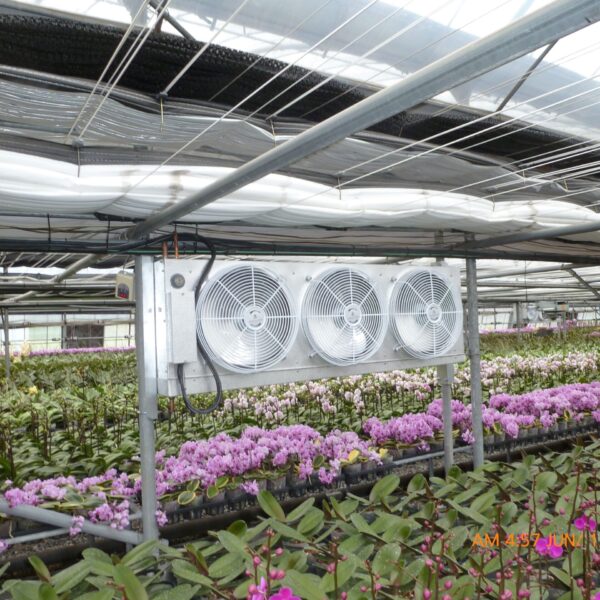
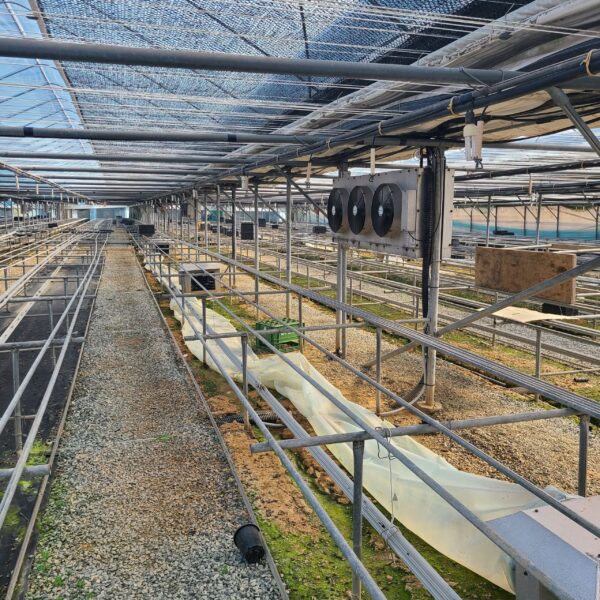
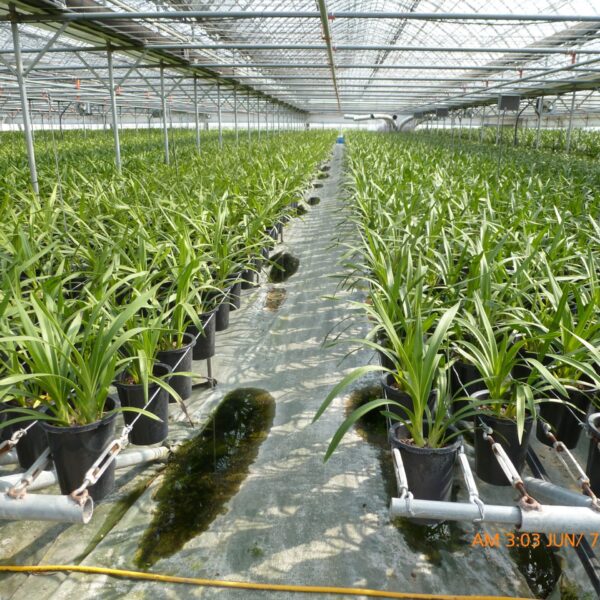
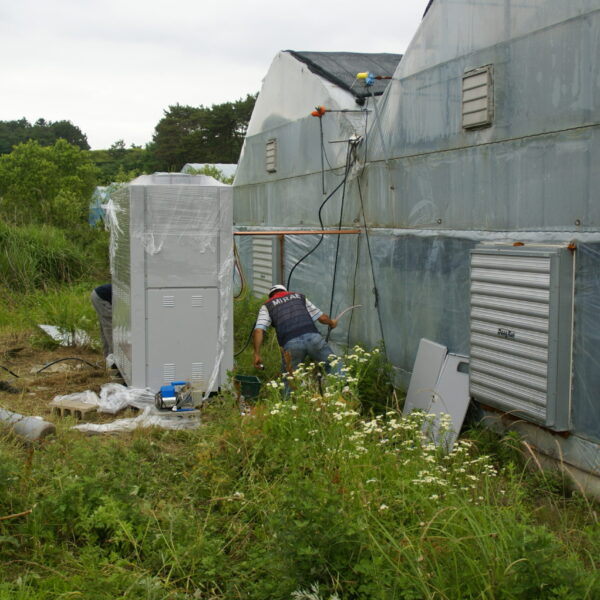
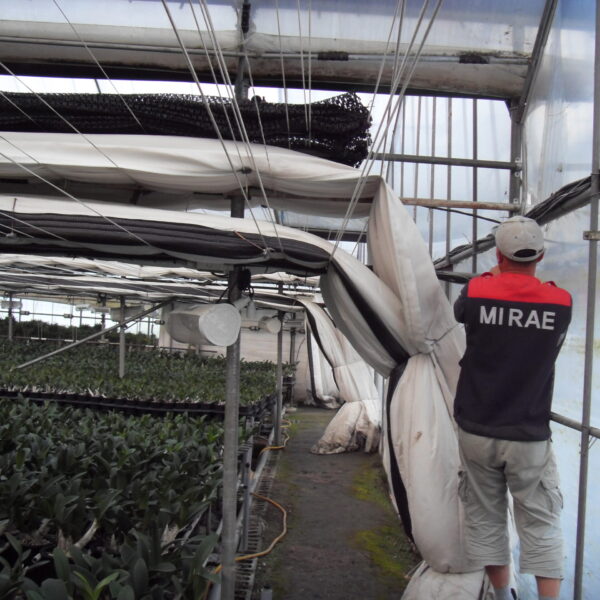
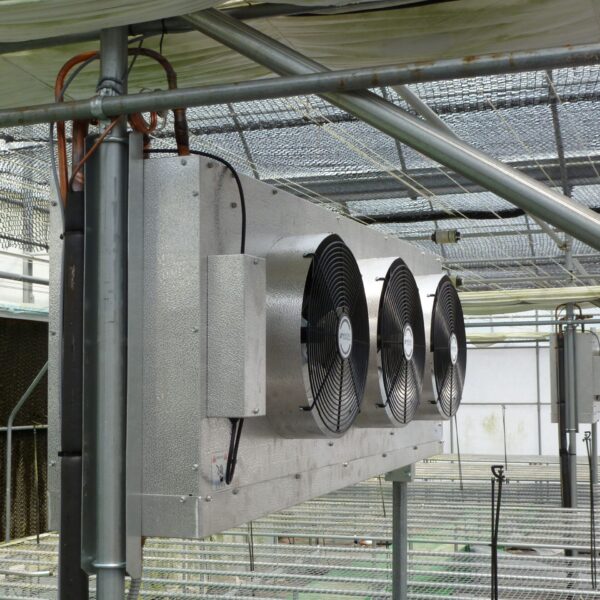
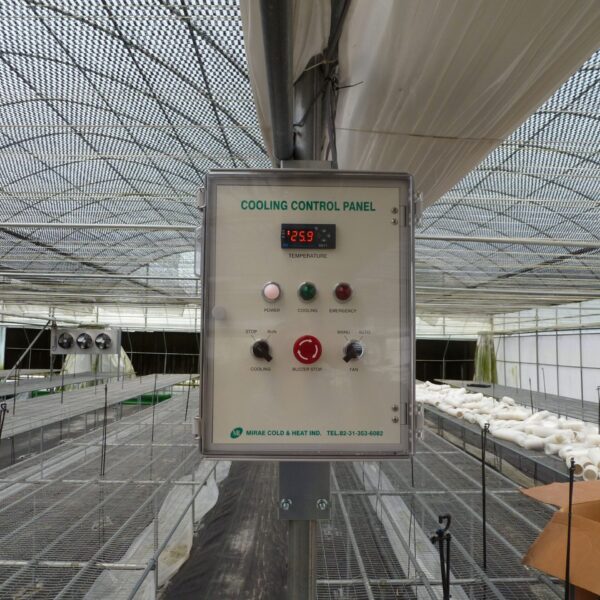
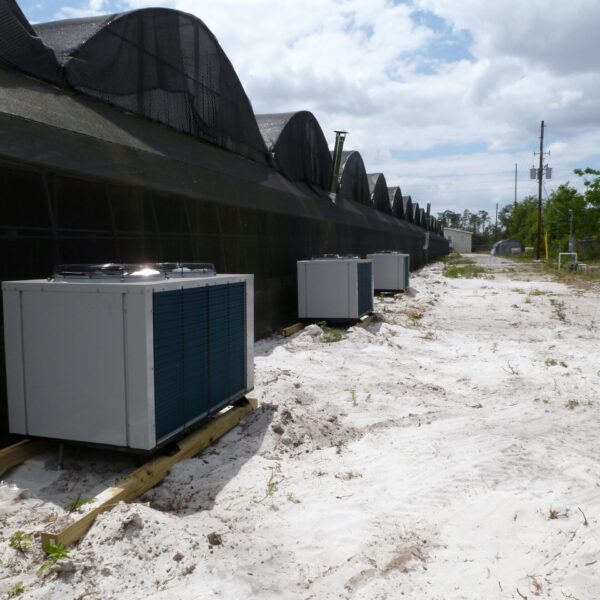
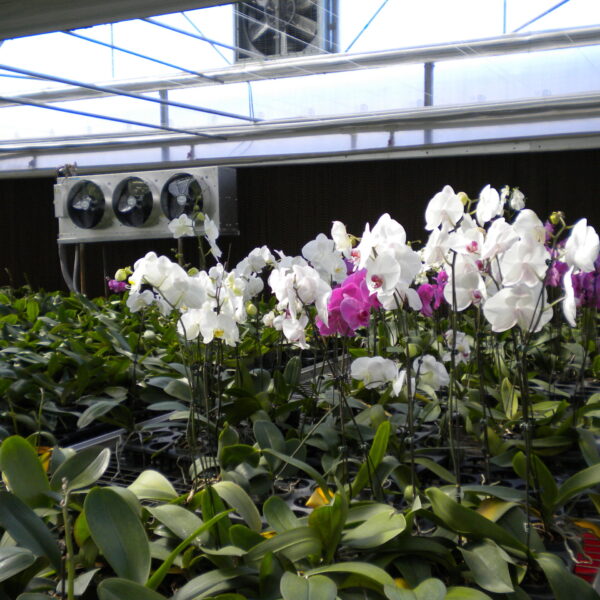
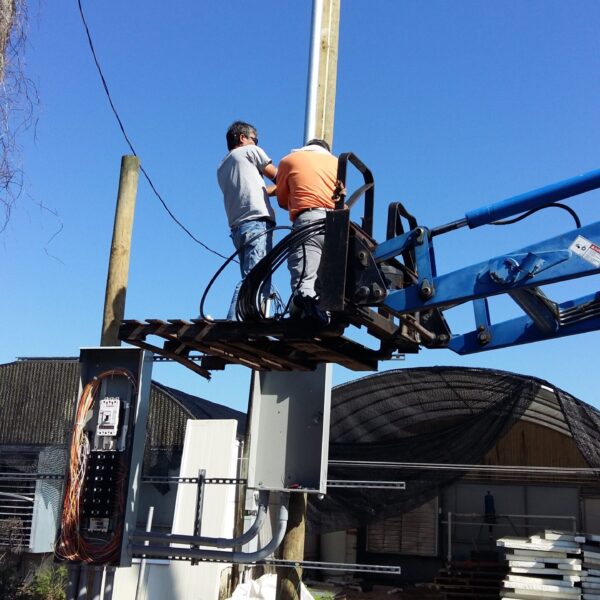
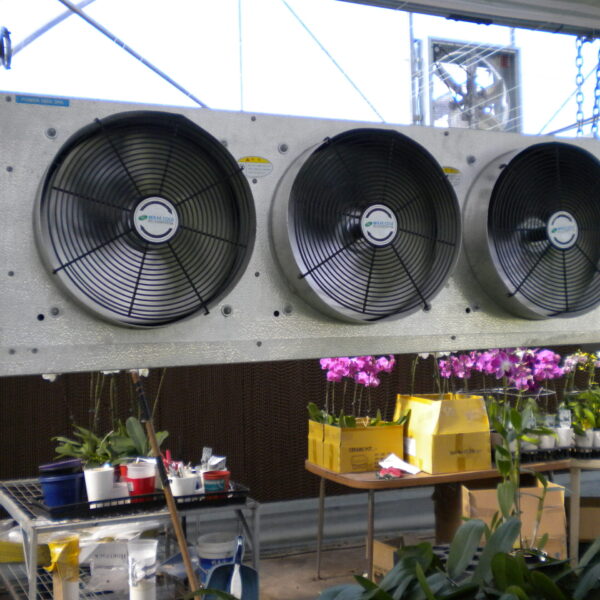
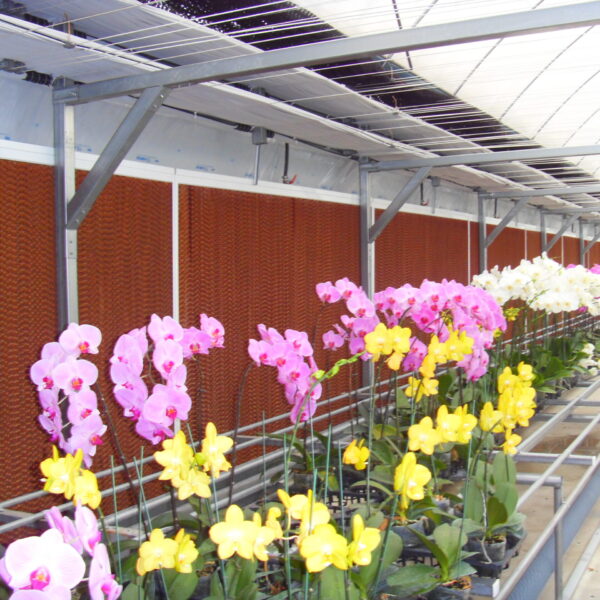
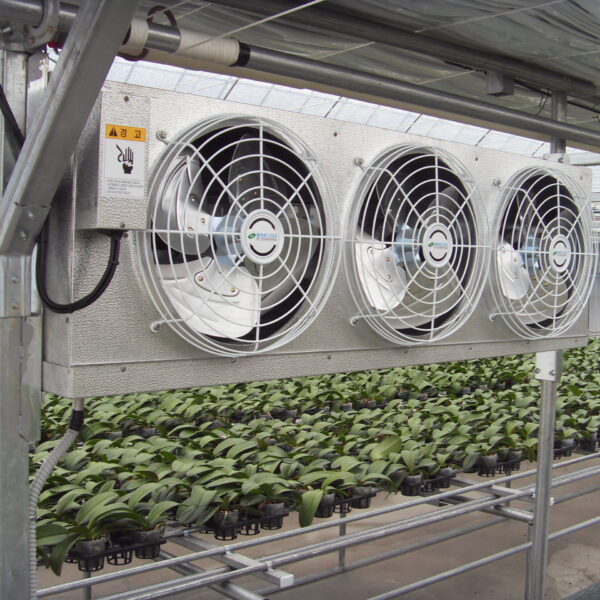
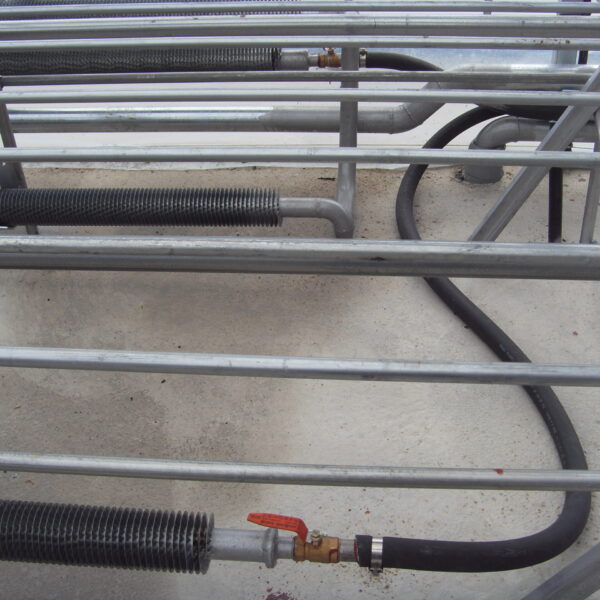
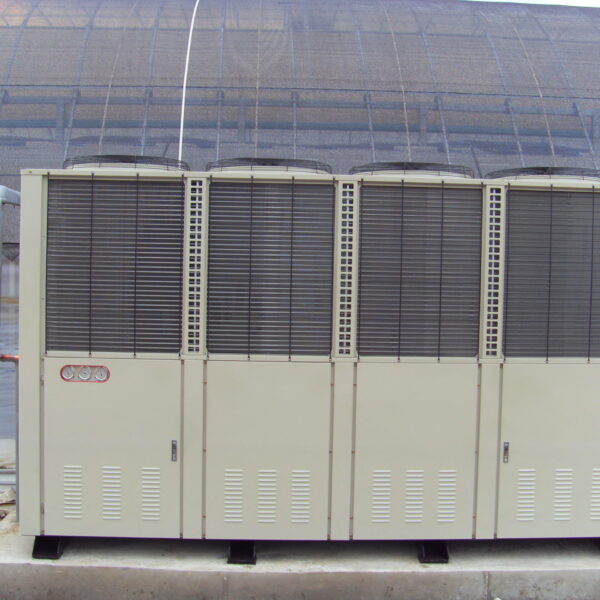
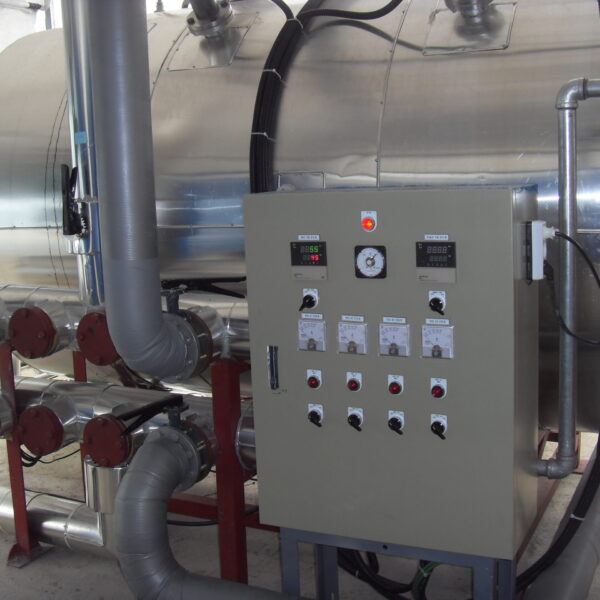
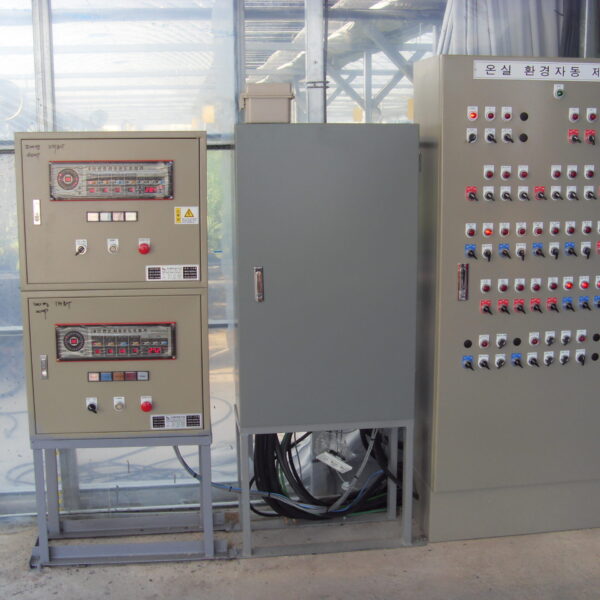
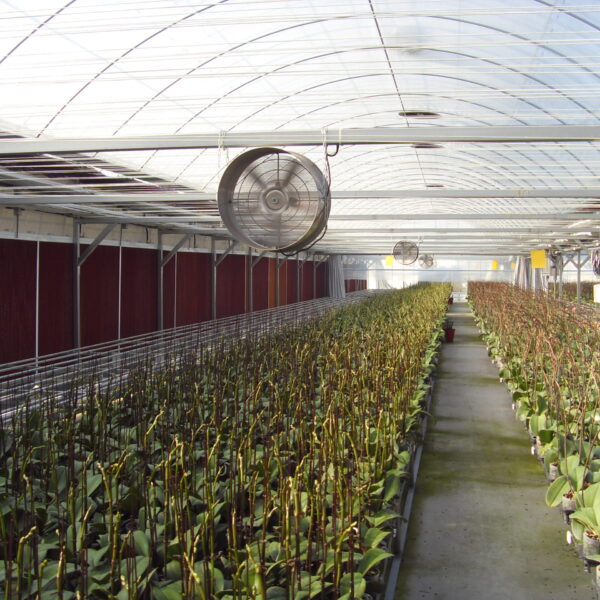
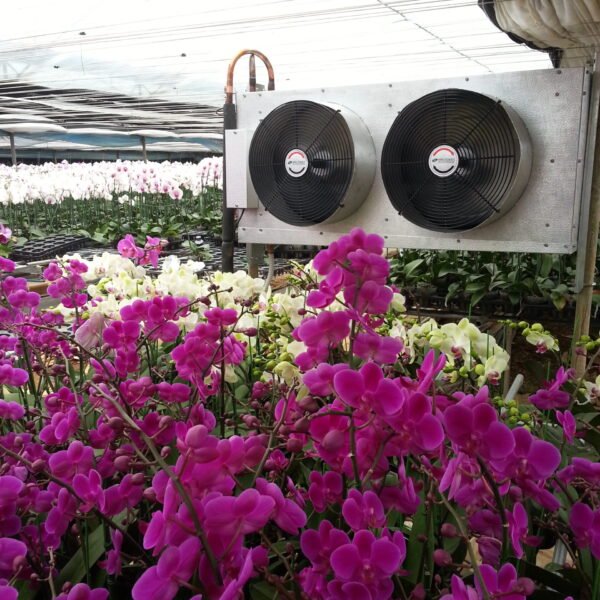
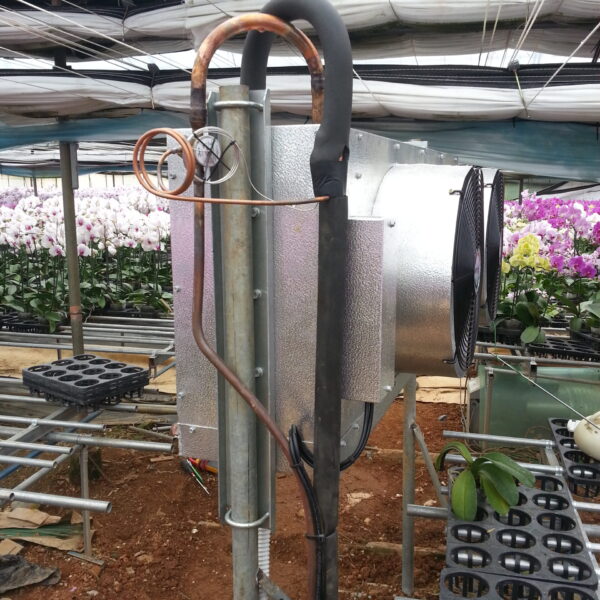
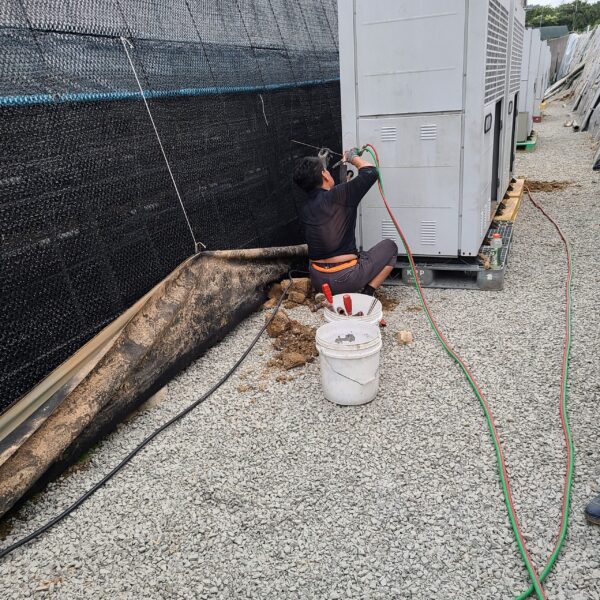
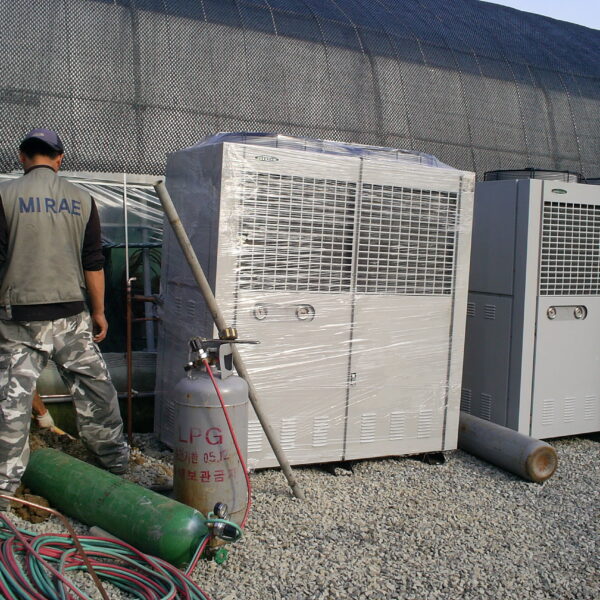
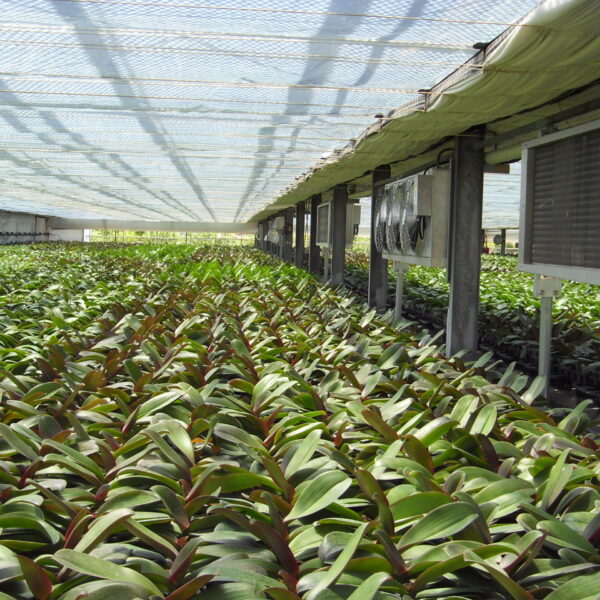
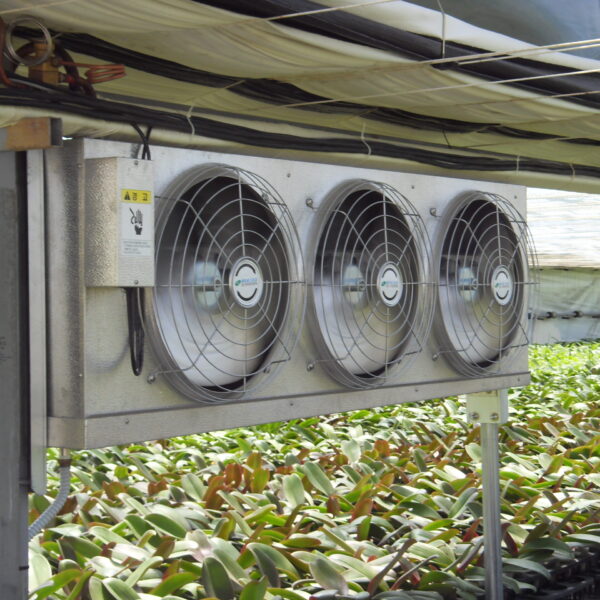
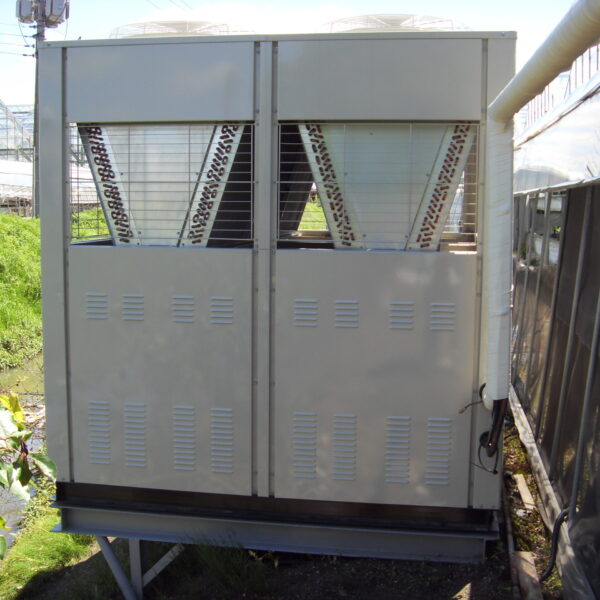
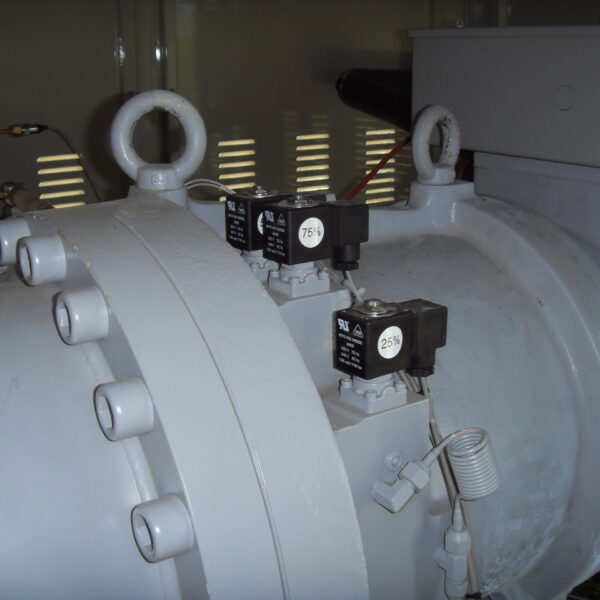
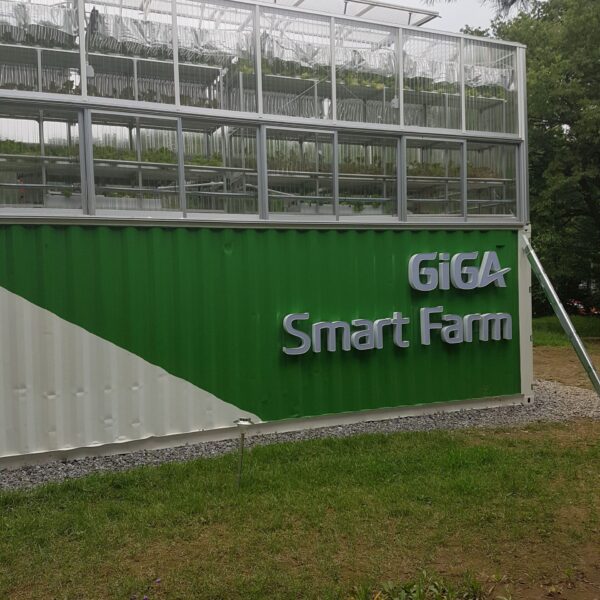
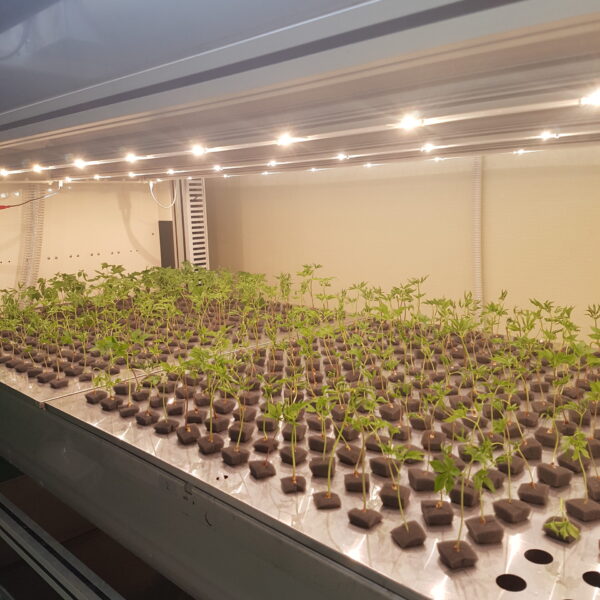
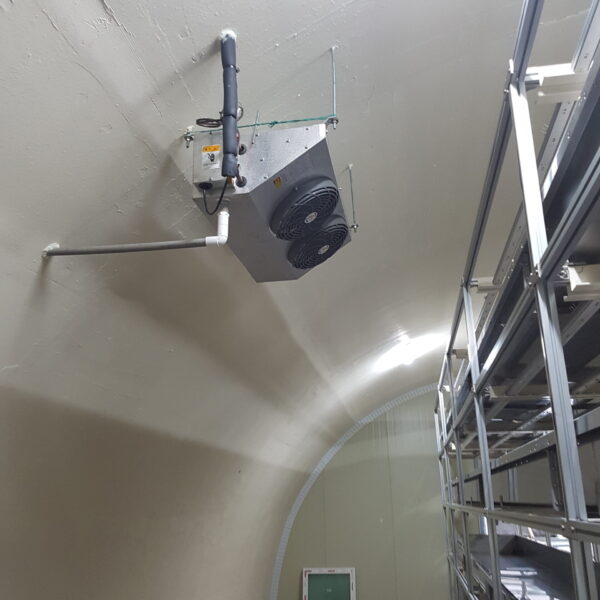
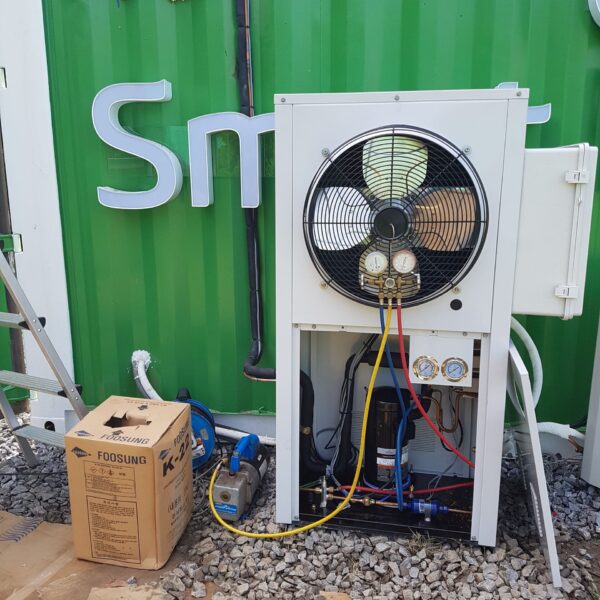
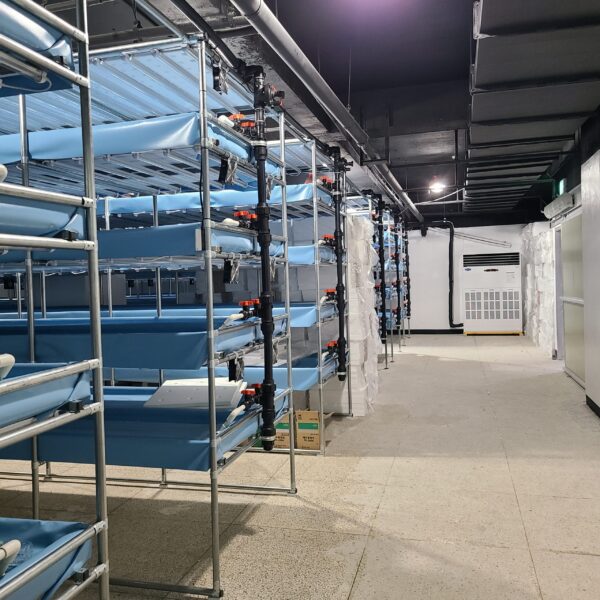
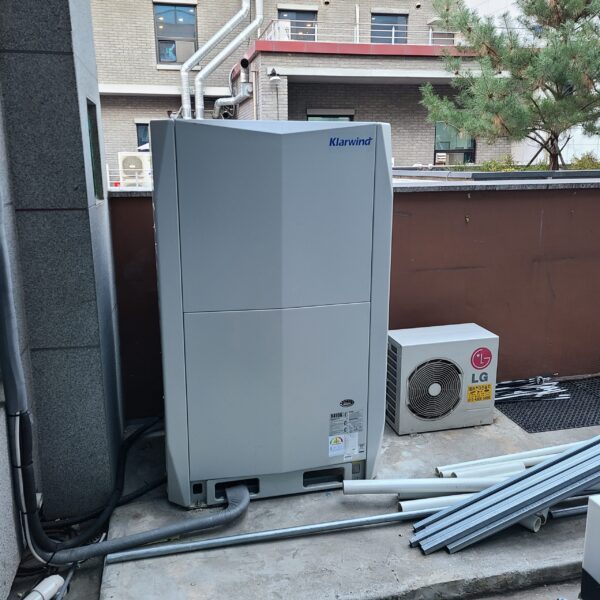
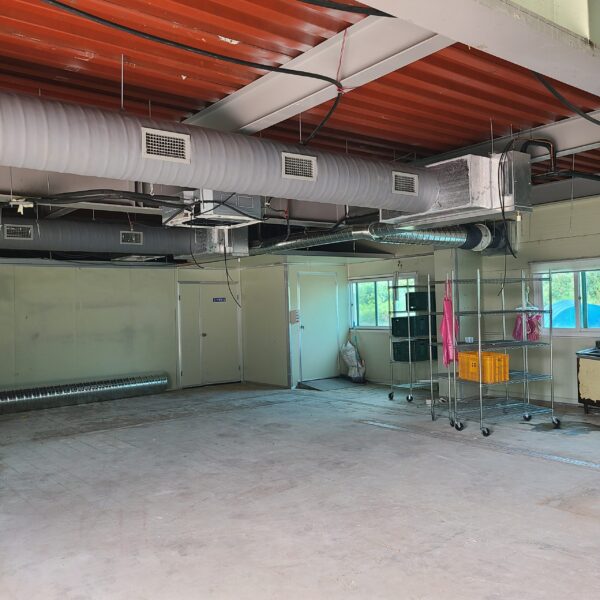
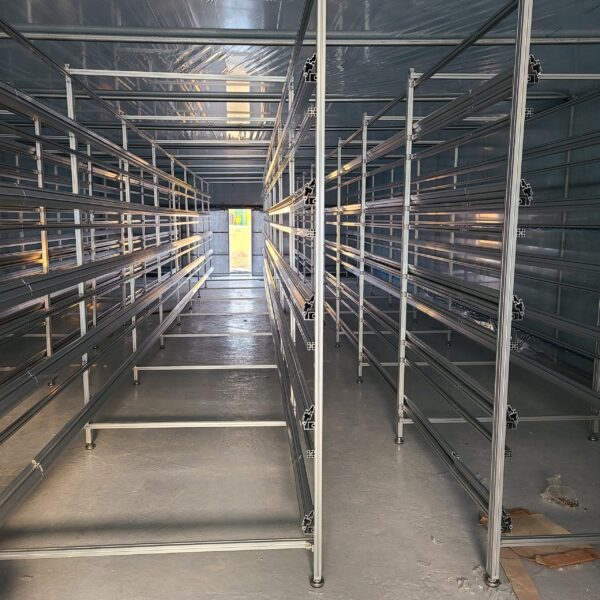
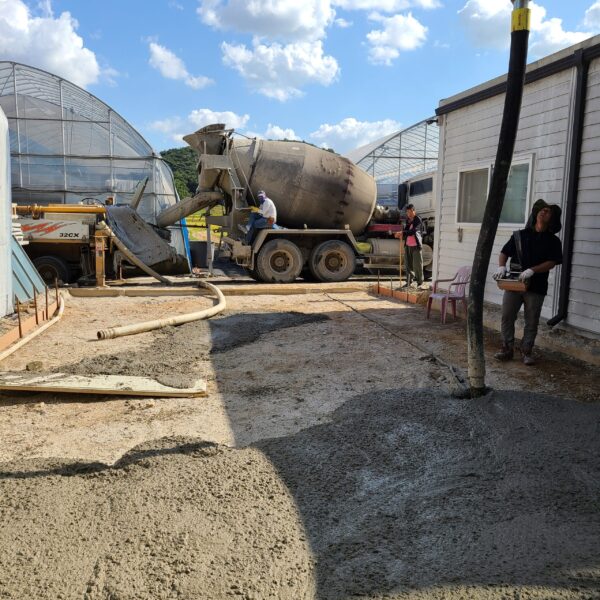
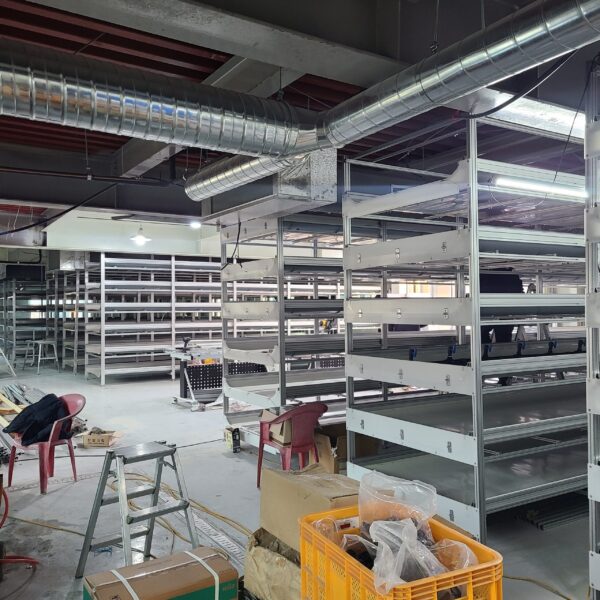
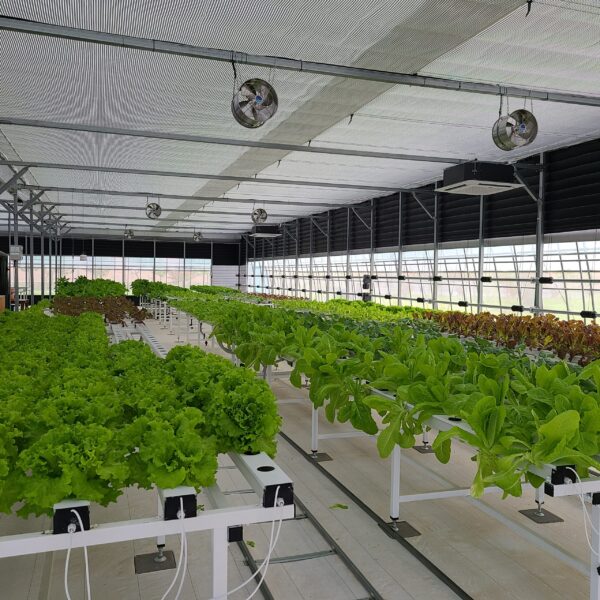
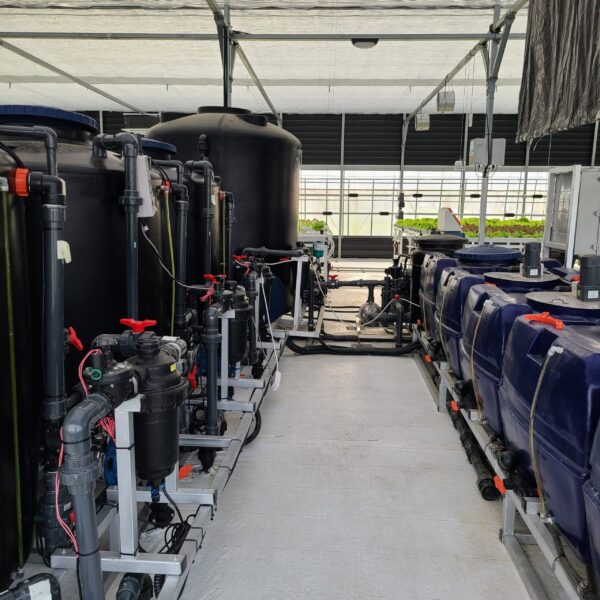
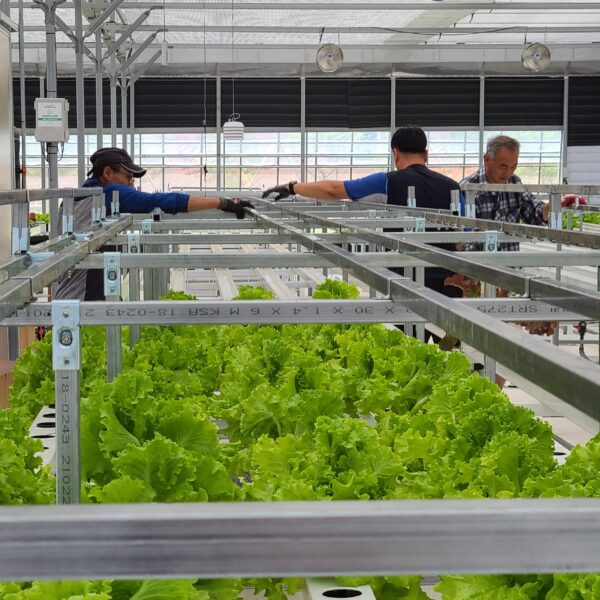
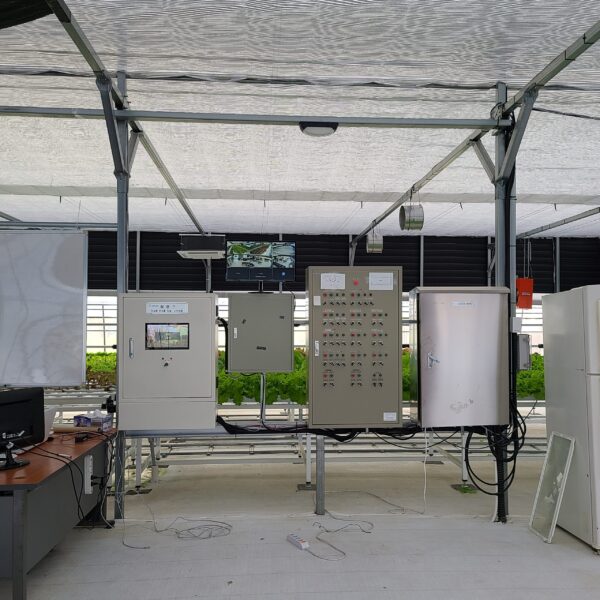
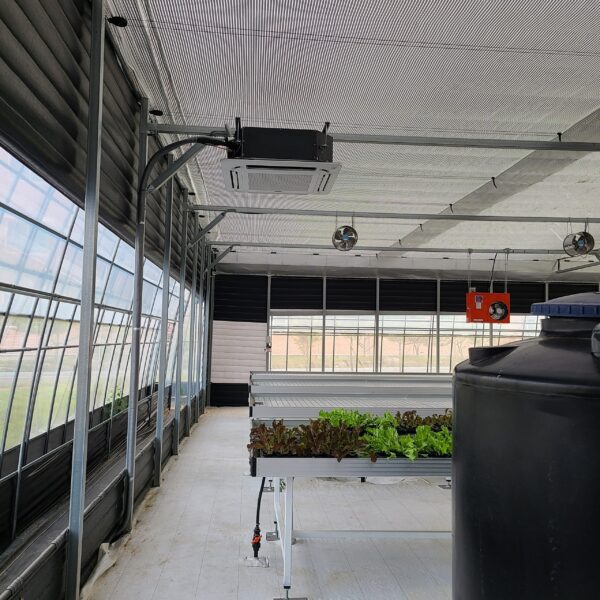
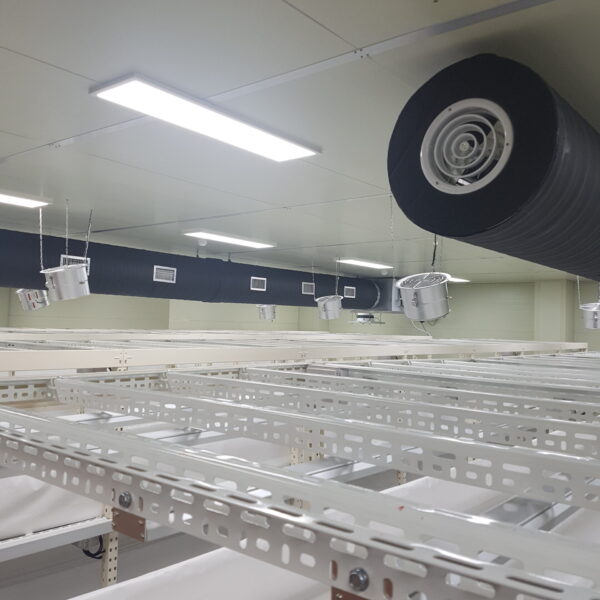
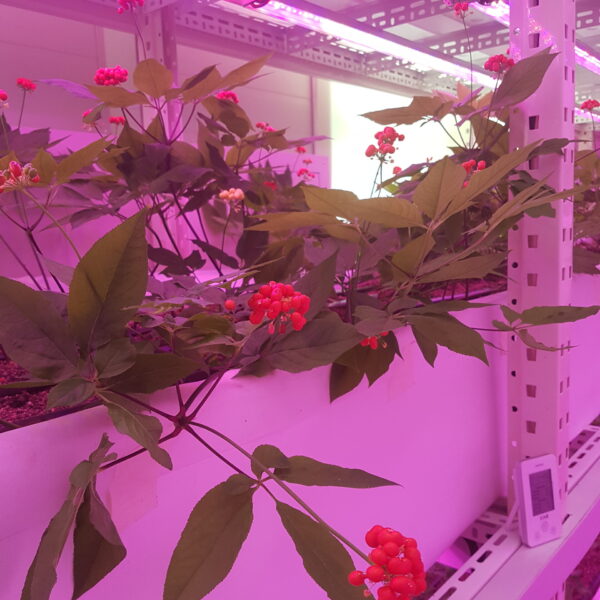
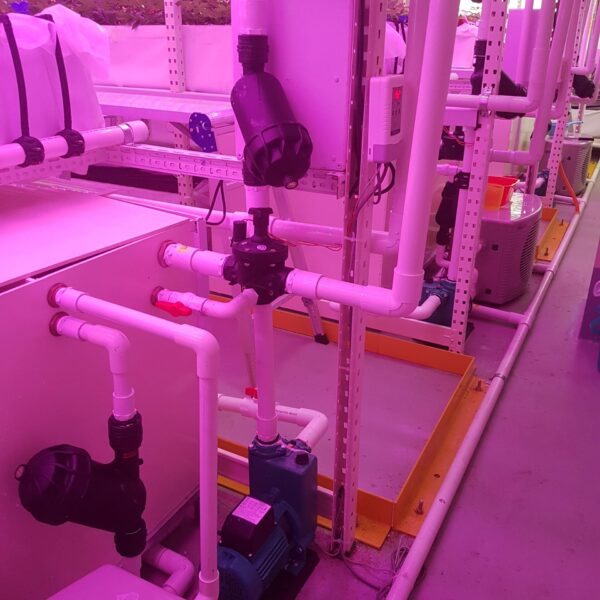
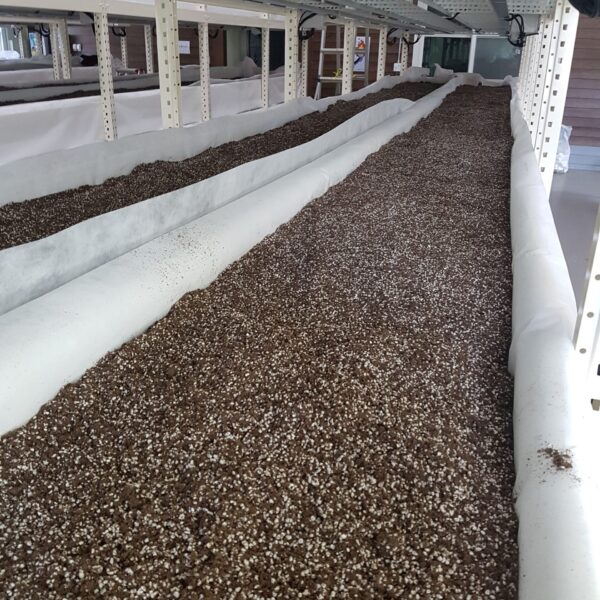
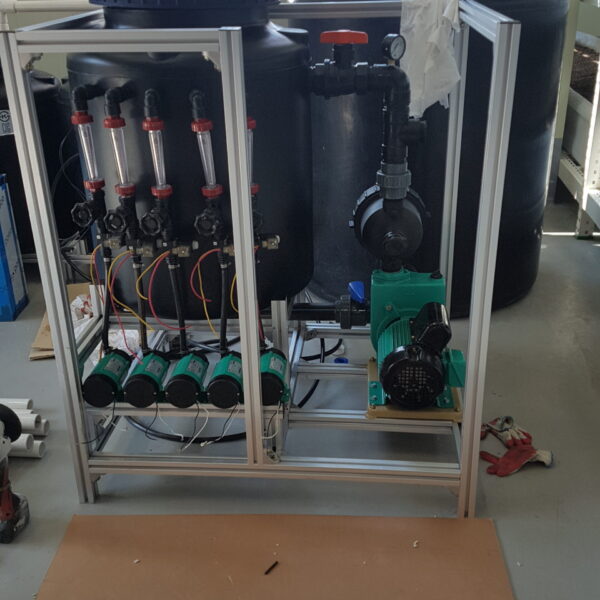
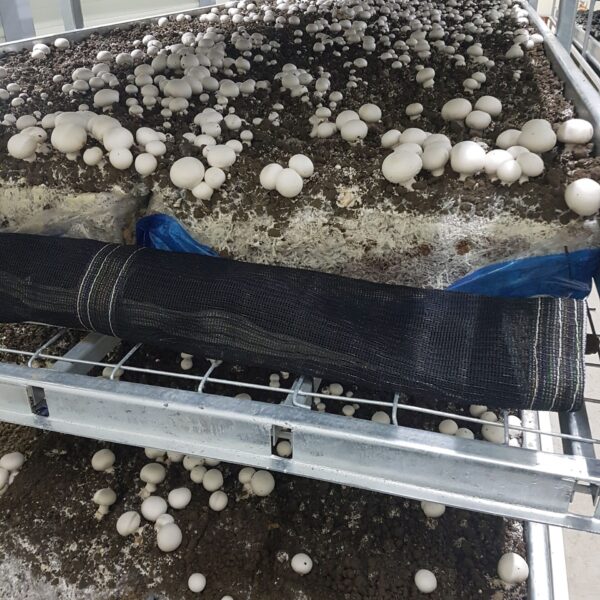
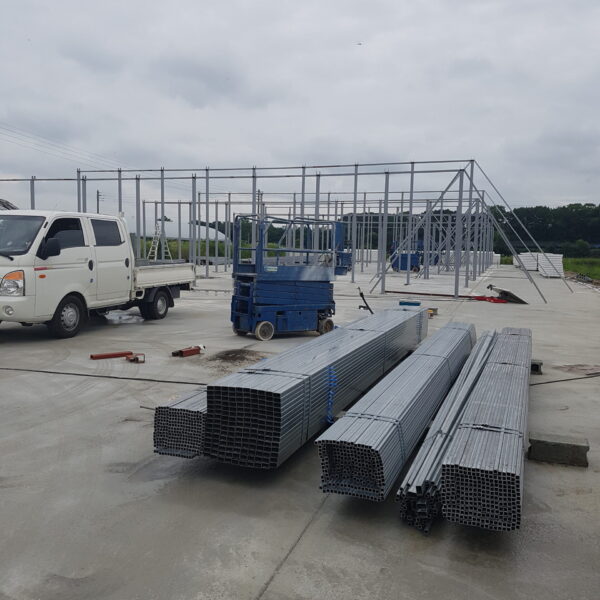
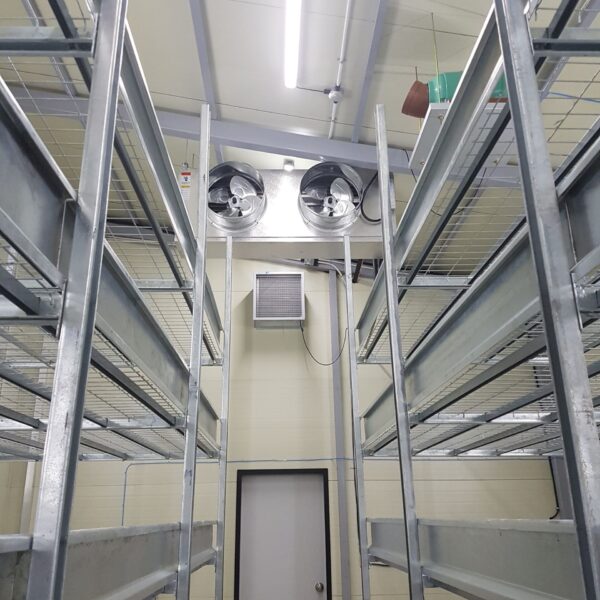
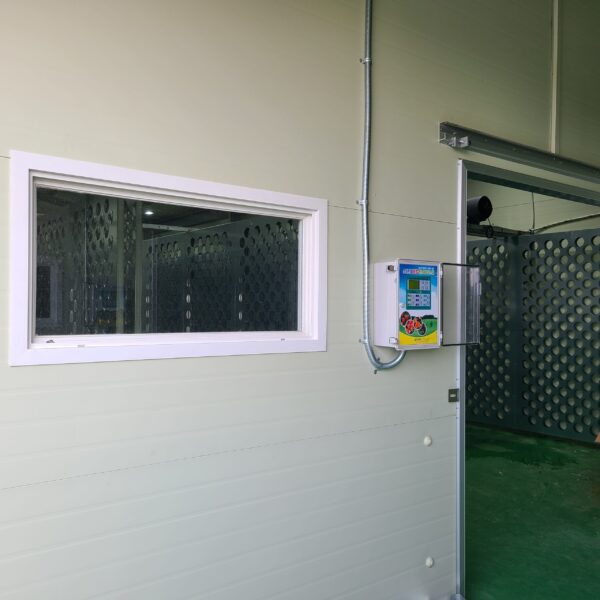
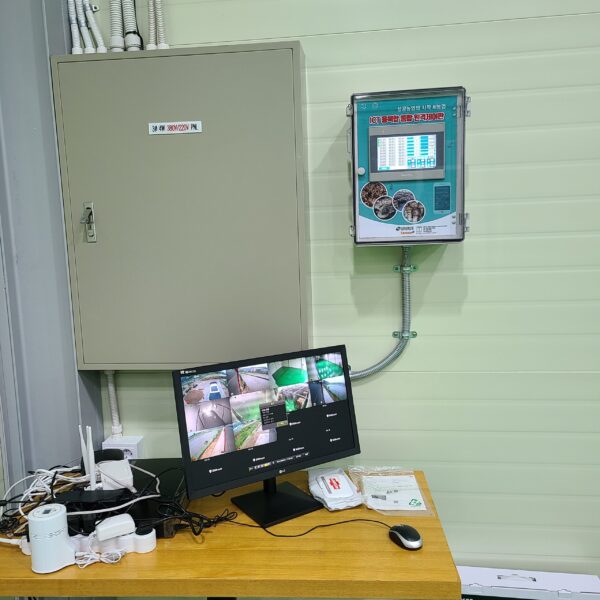
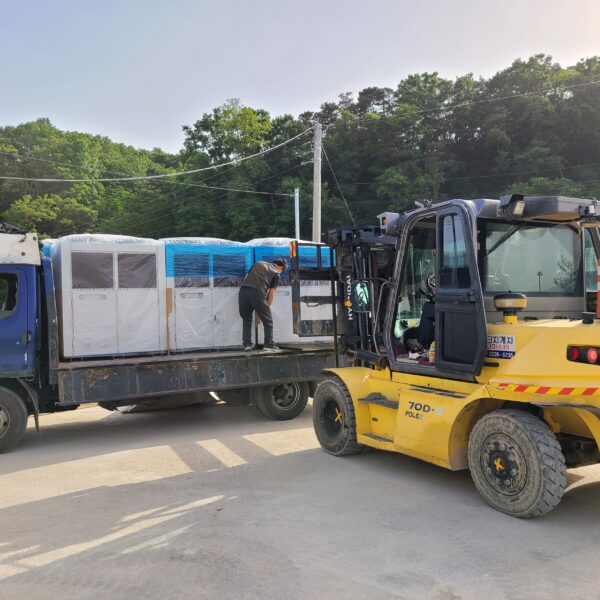
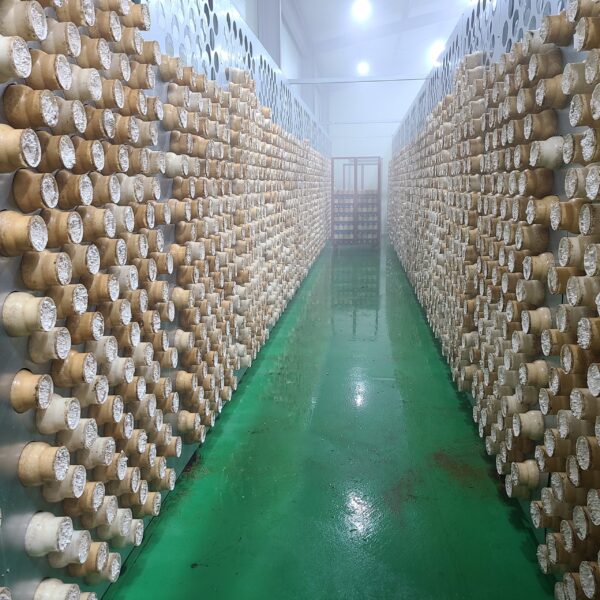
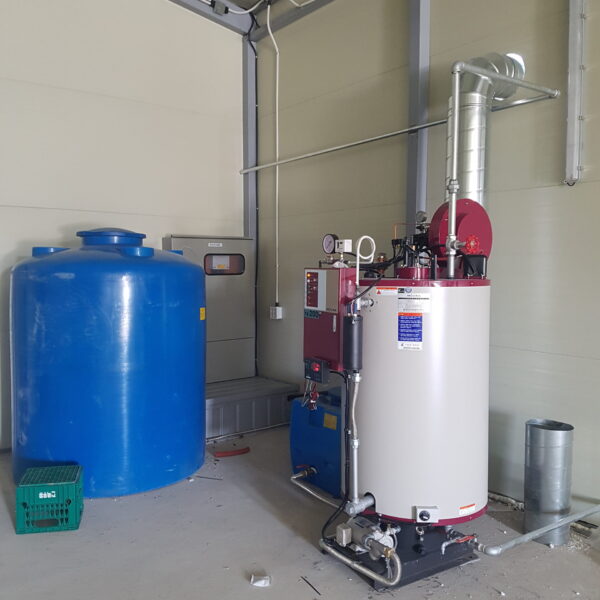
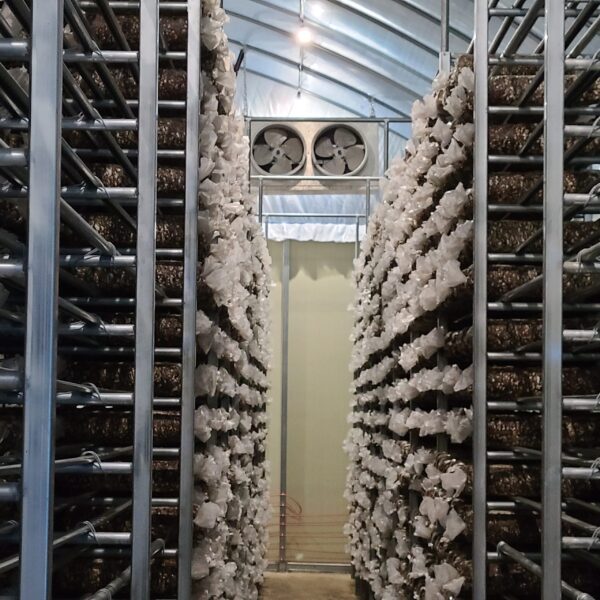
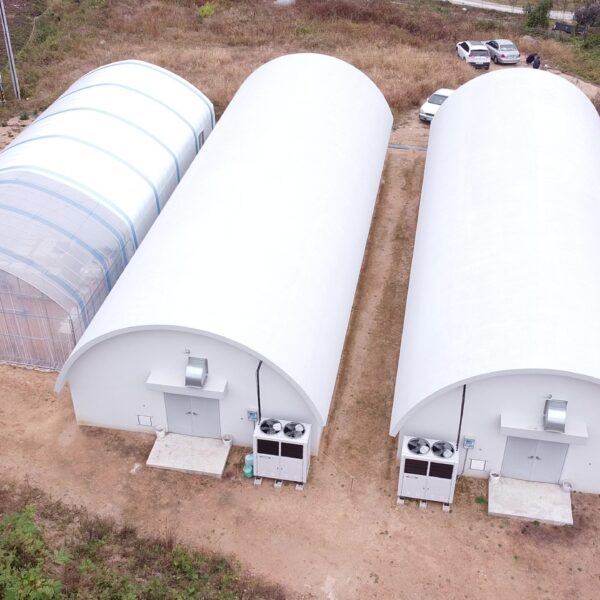
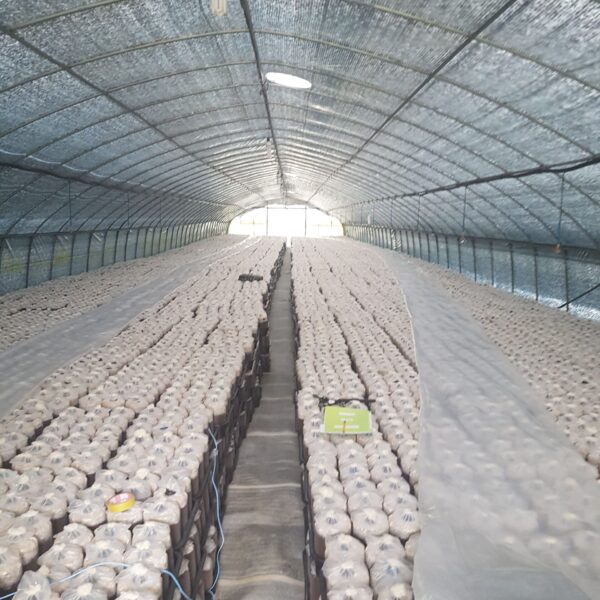
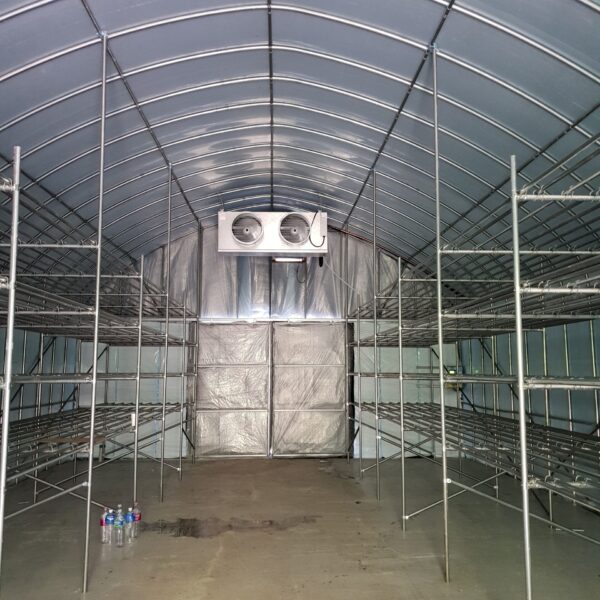
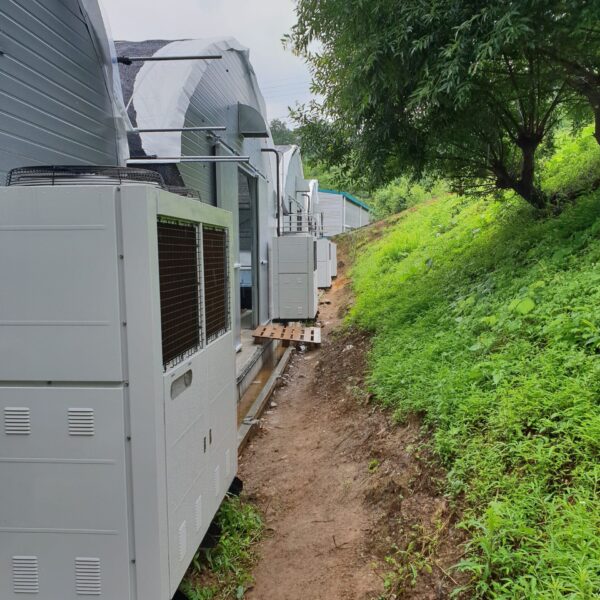
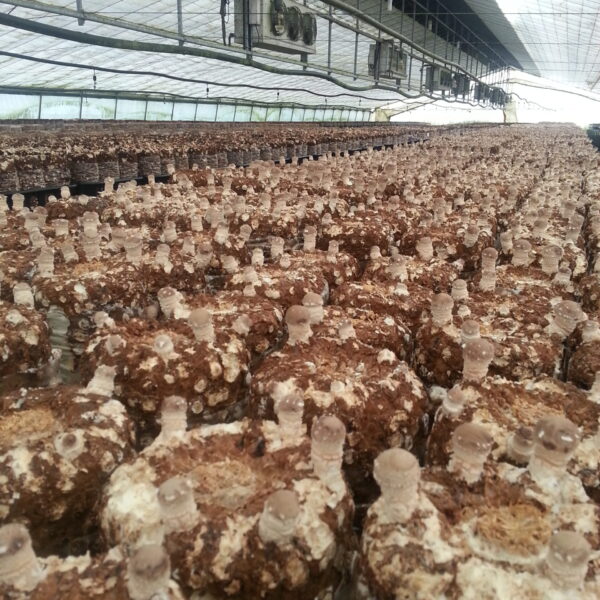
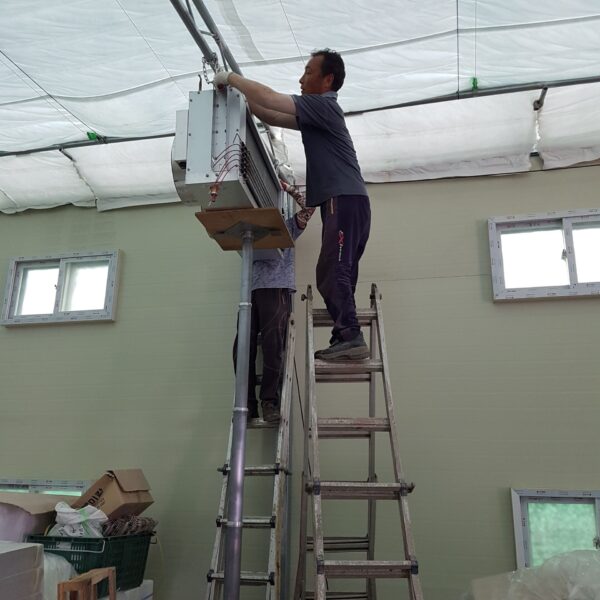
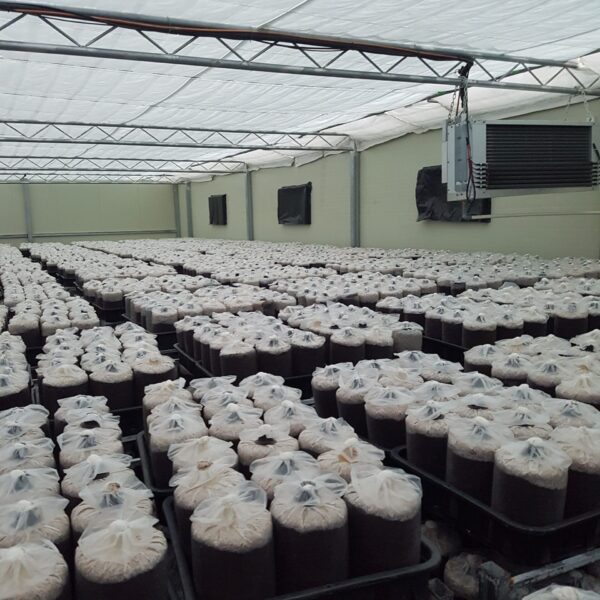
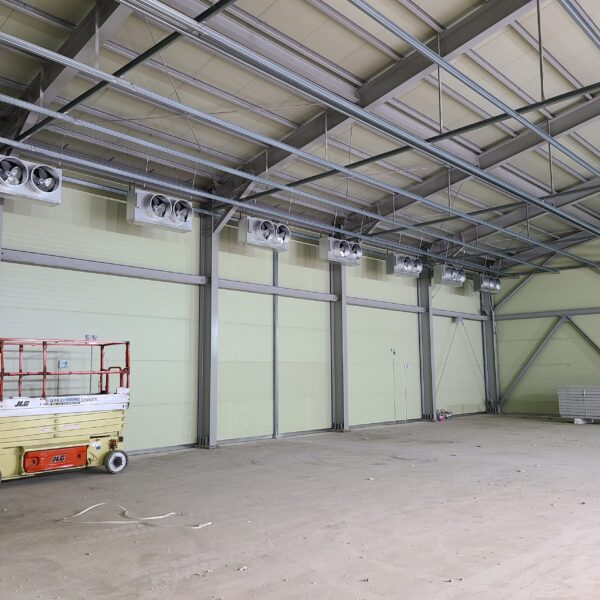
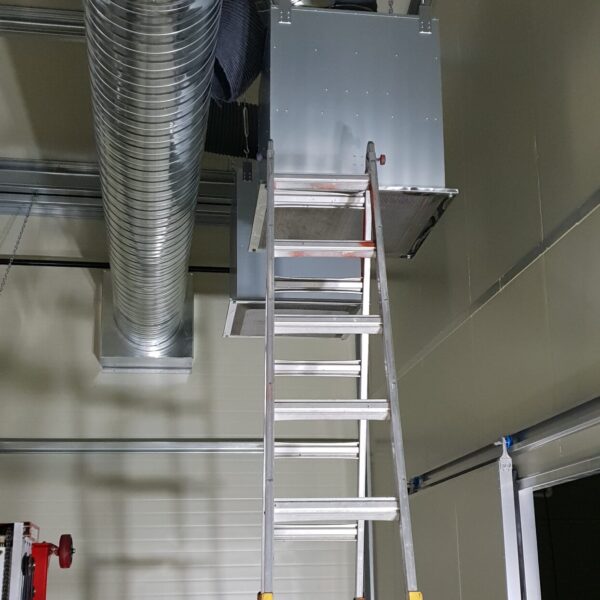
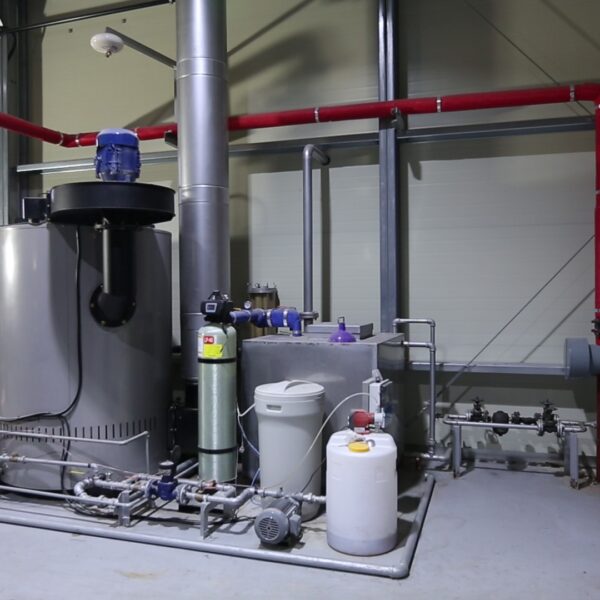
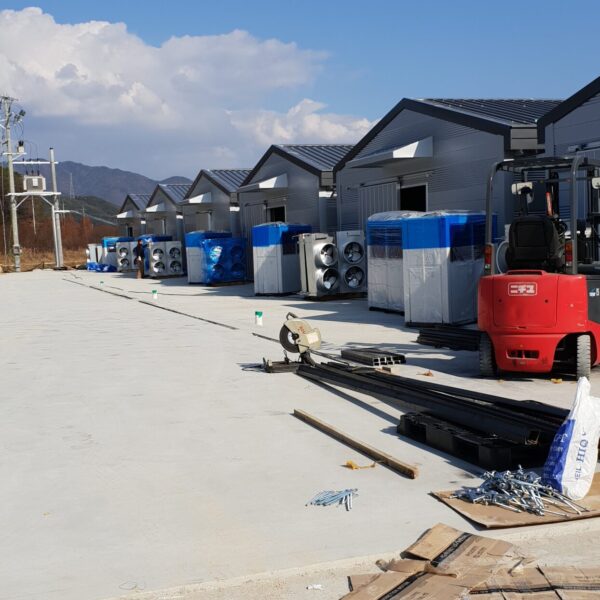
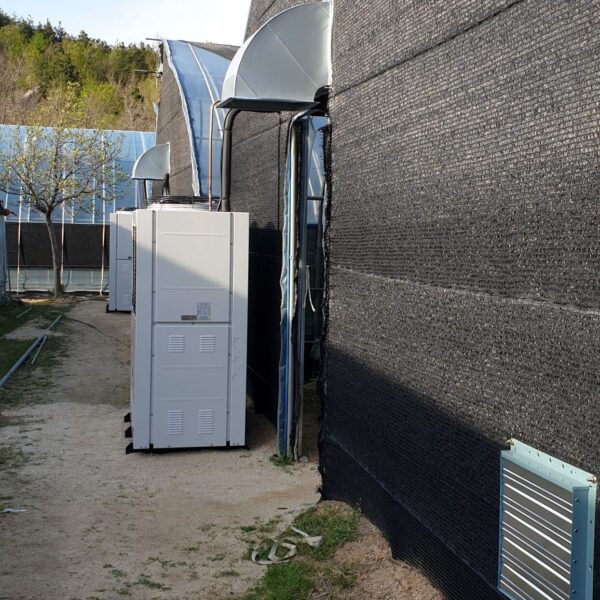
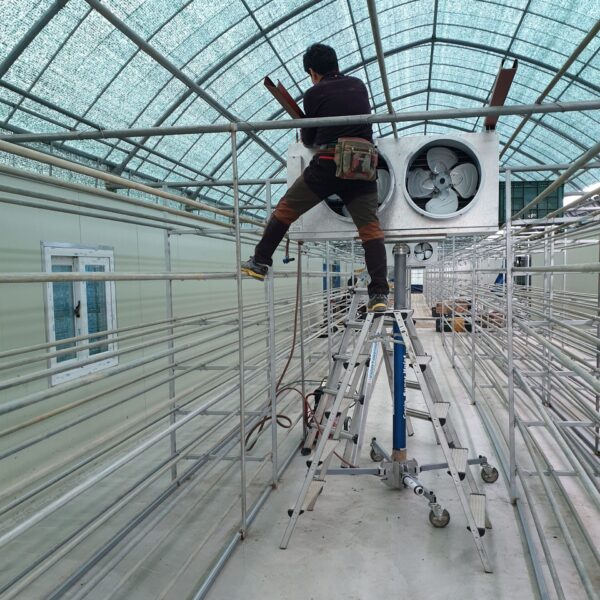
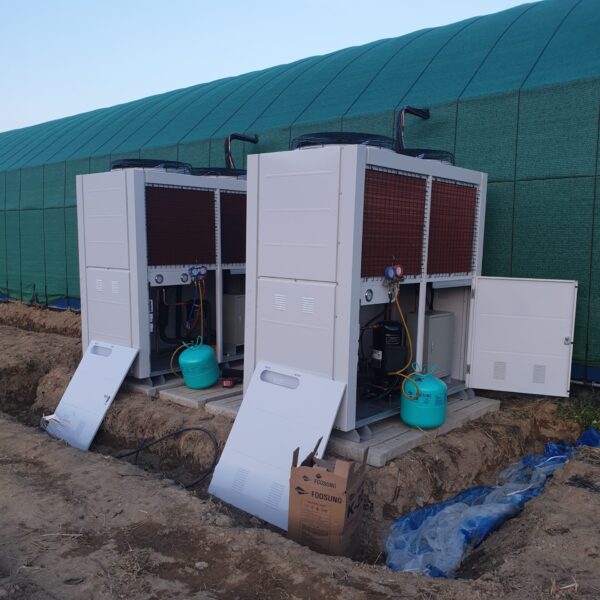
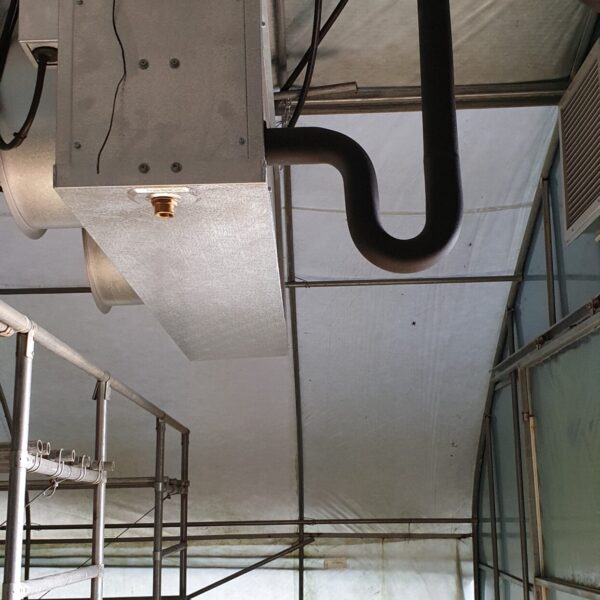
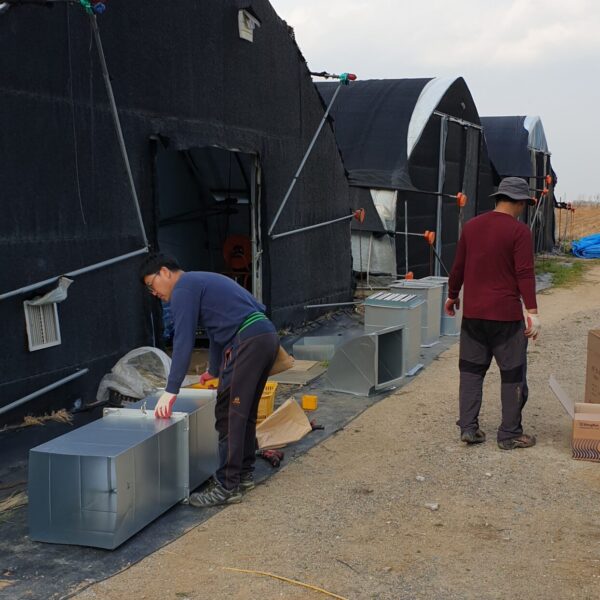
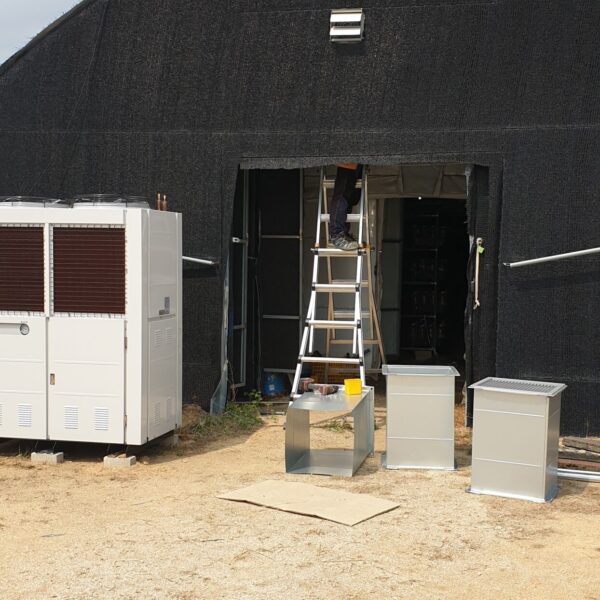
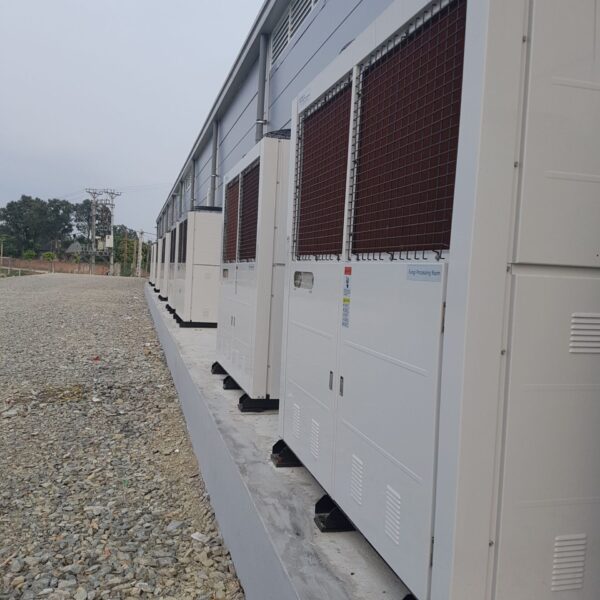
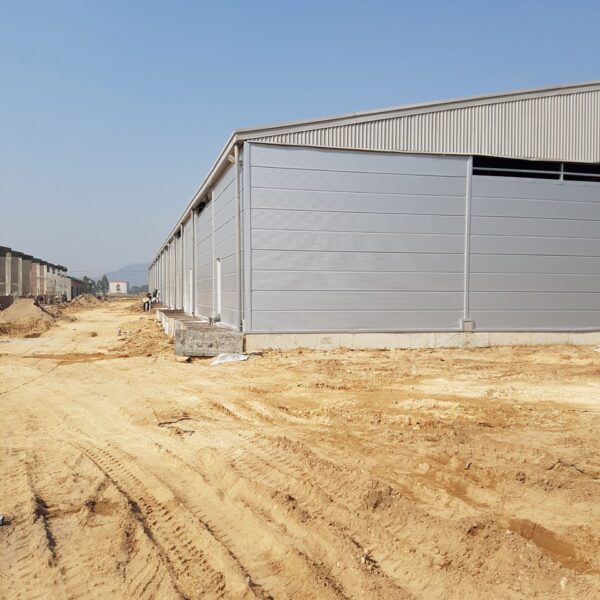
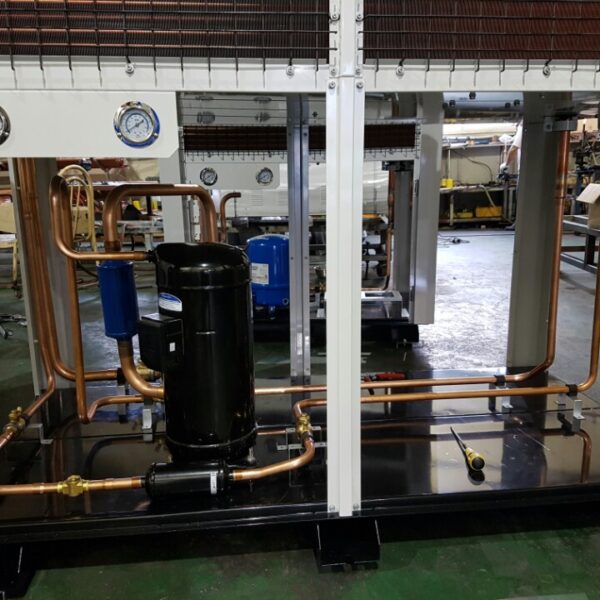
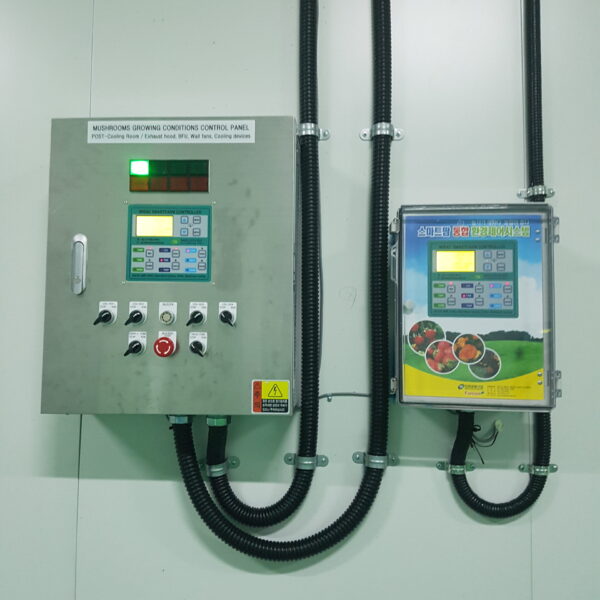
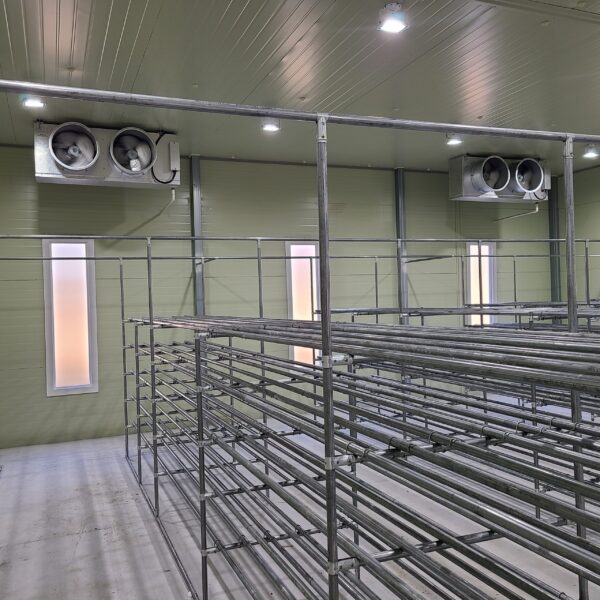
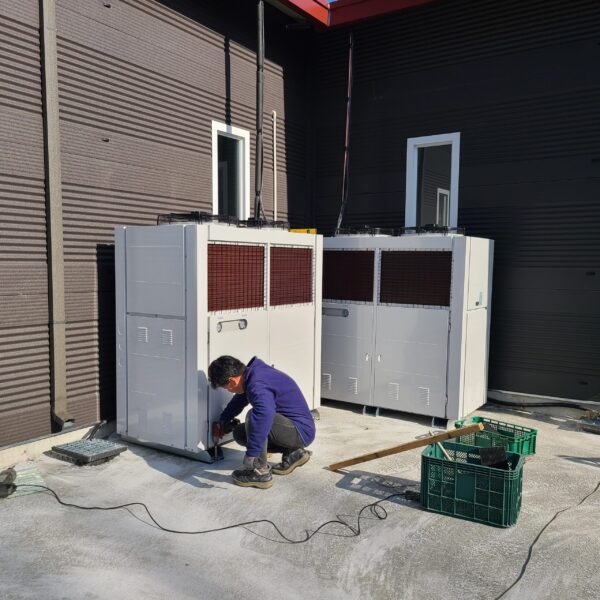
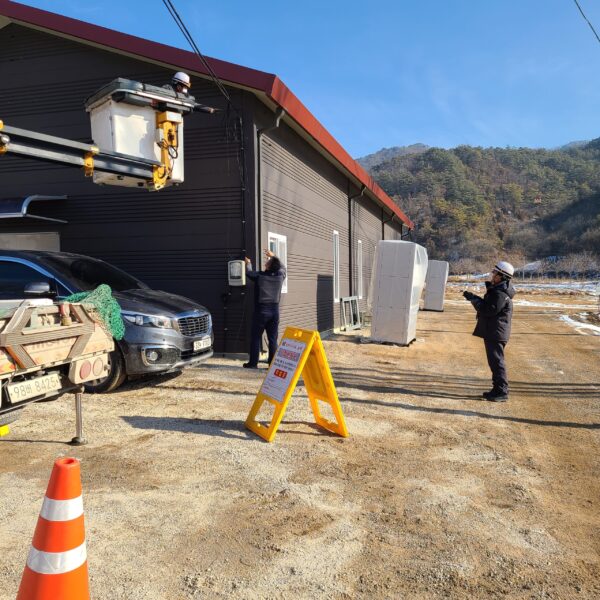
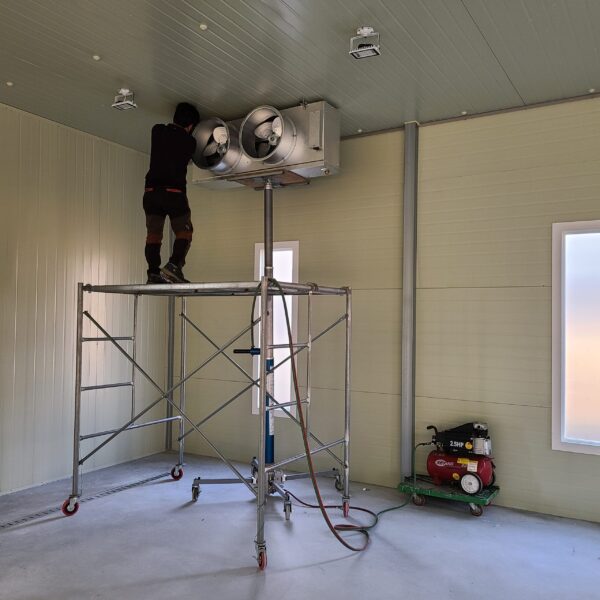
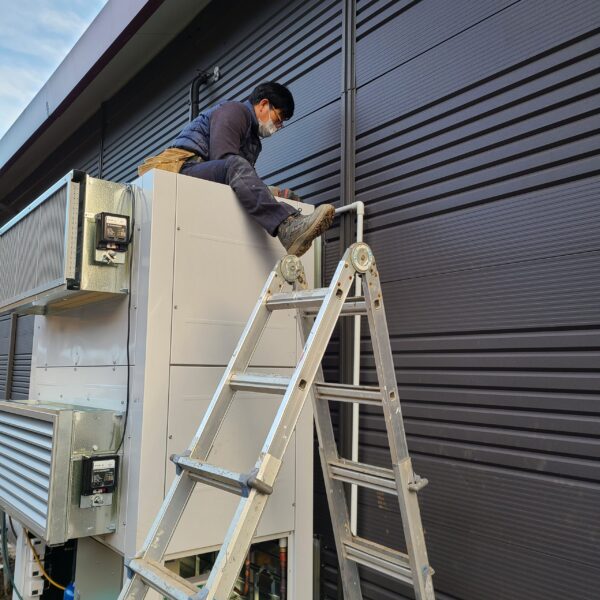
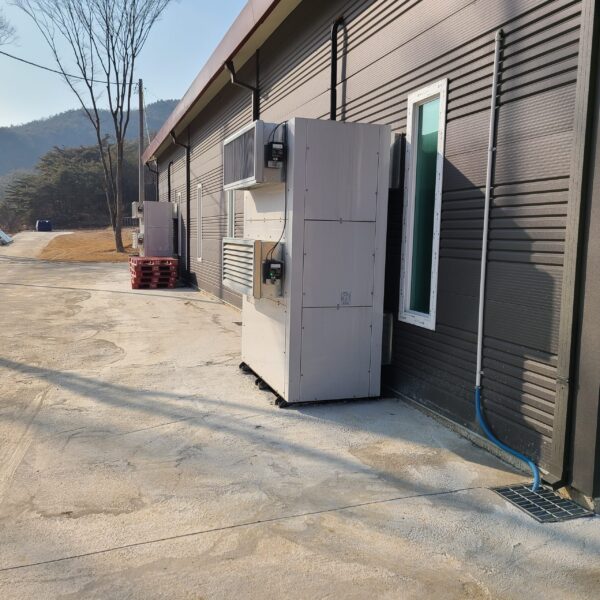
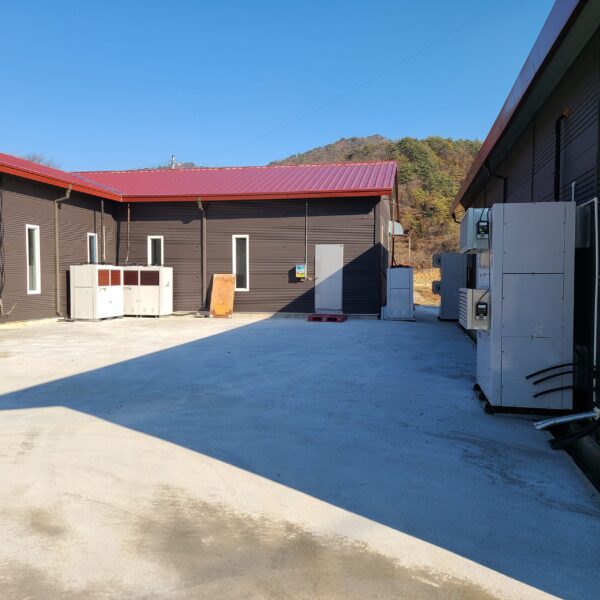
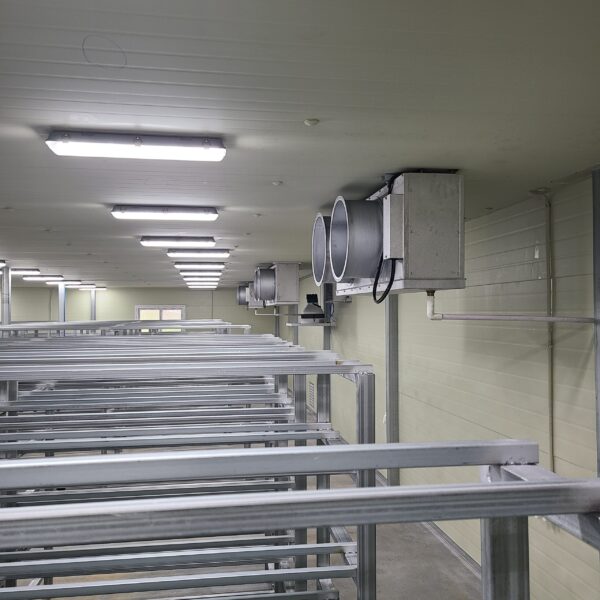
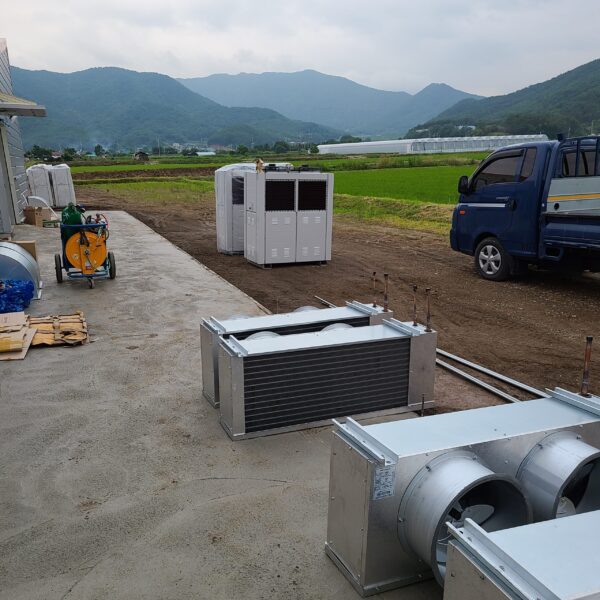
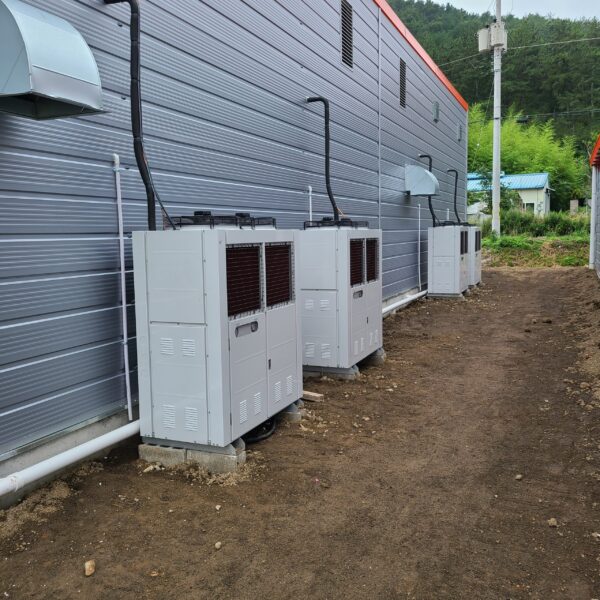
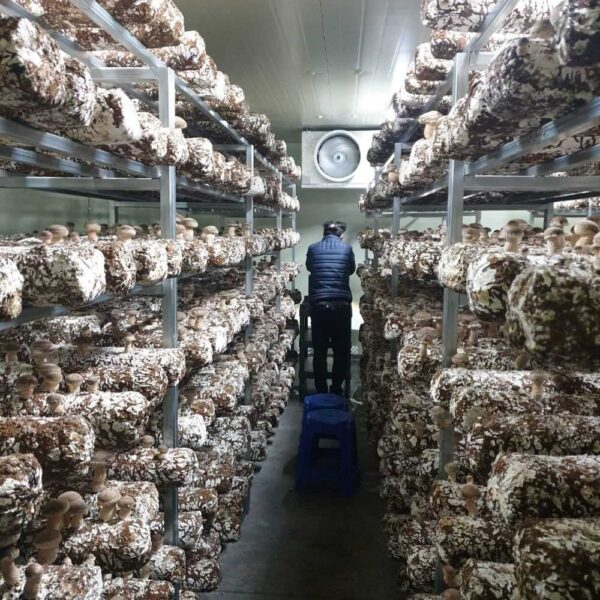
The conventional agriculture was 100% dependent on the natural environment, and when it was dependent on wind, wind, solar heat, and sunlight, it had no choice but to do what nature gave it to. With the development of indoor farming using facilities from such open-air farming, it has become possible to cultivate all year round. For year-round cultivation in a greenhouse, it is necessary to manage the temperature inside the facility according to the seasonal temperature change. Here, heating is to grow crops by physically raising the temperature inside the greenhouse to the optimum temperature for crop growth during the low-temperature period when the outside temperature is low.
Heating provides the optimum temperature for crop growth and internal humidity maintenance, and may be required throughout the year as well as winter. It is necessary for high quality and low cost because it can save money.