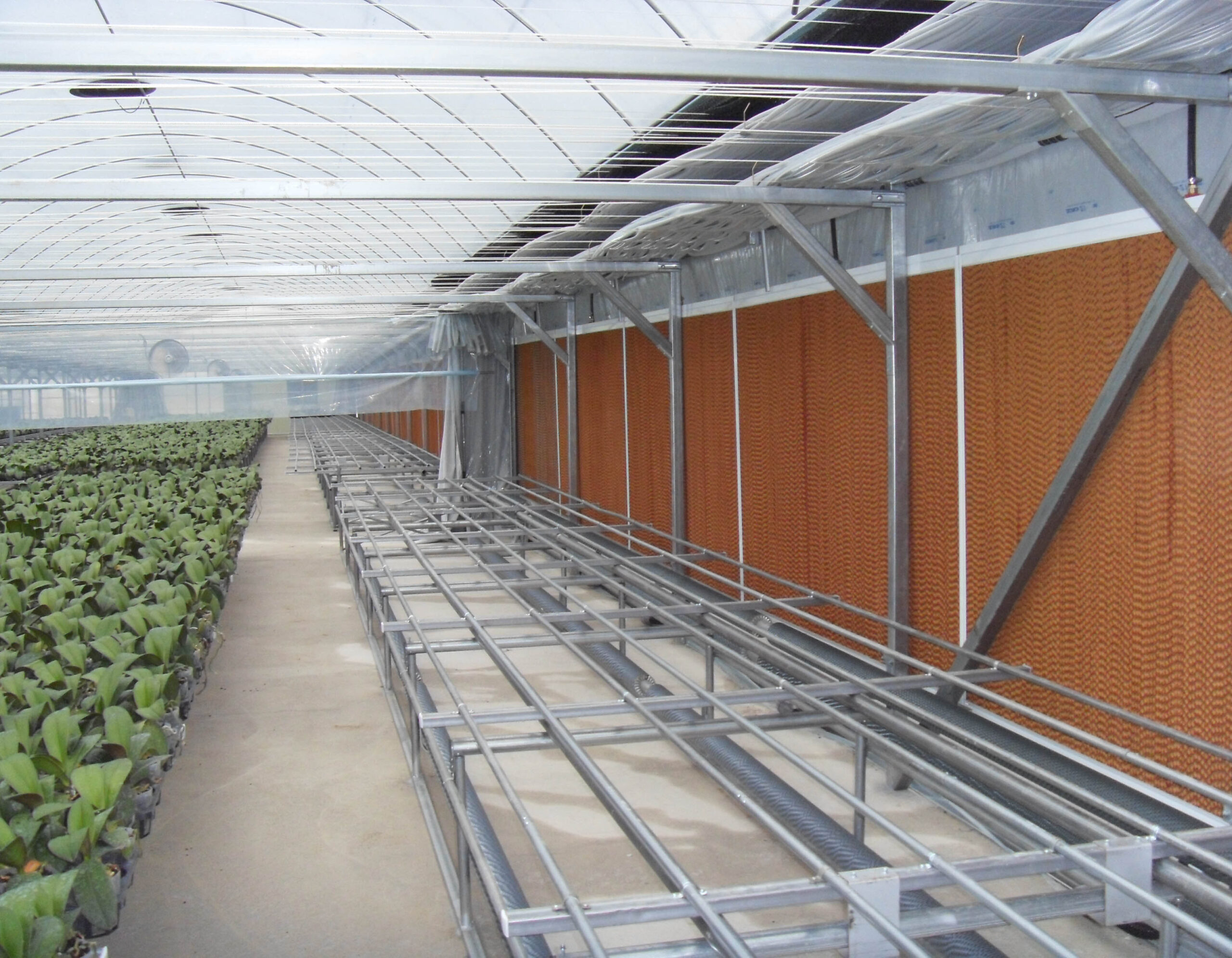
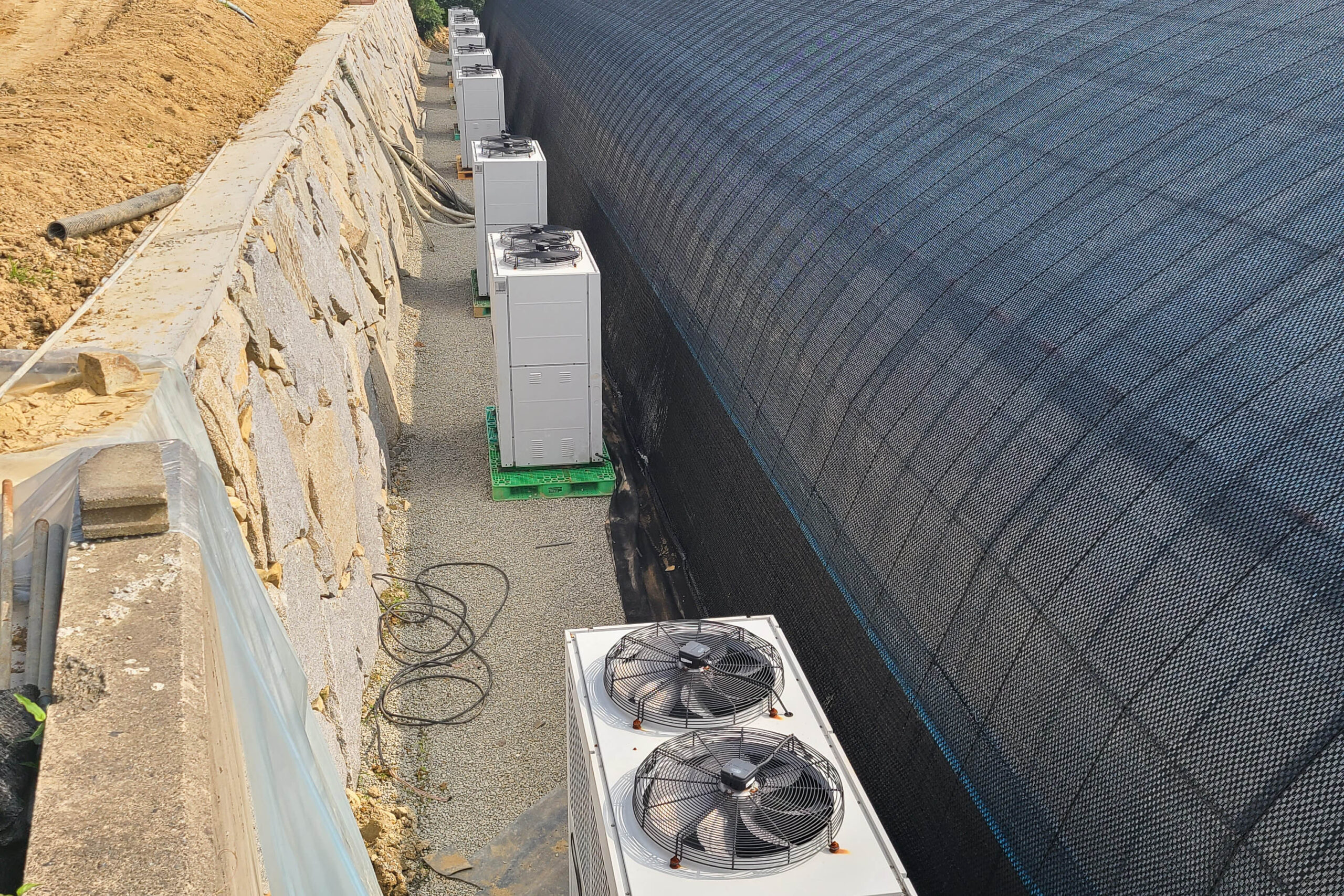
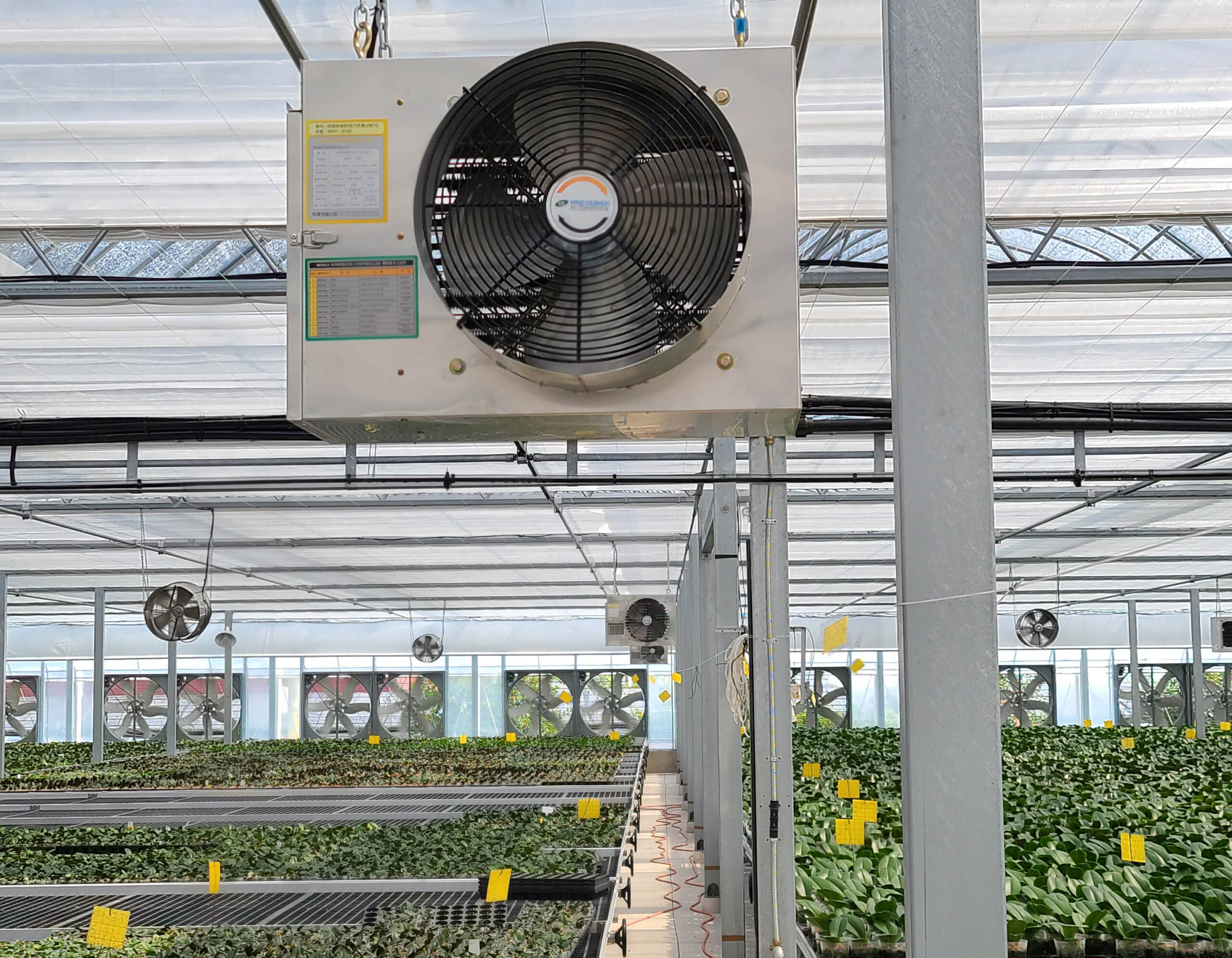
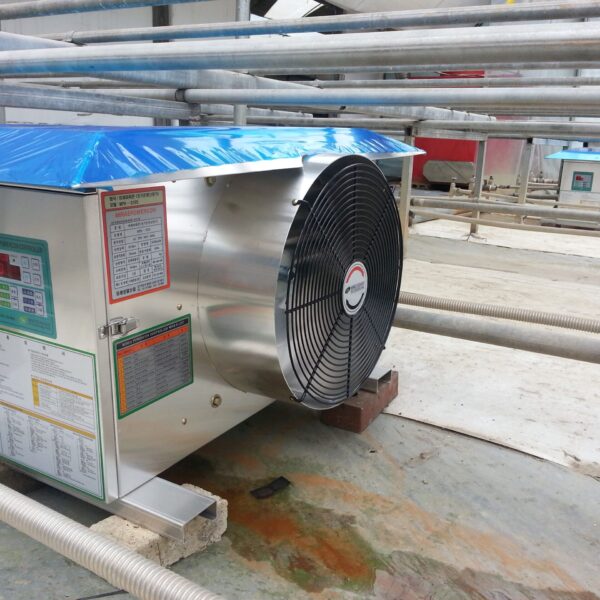
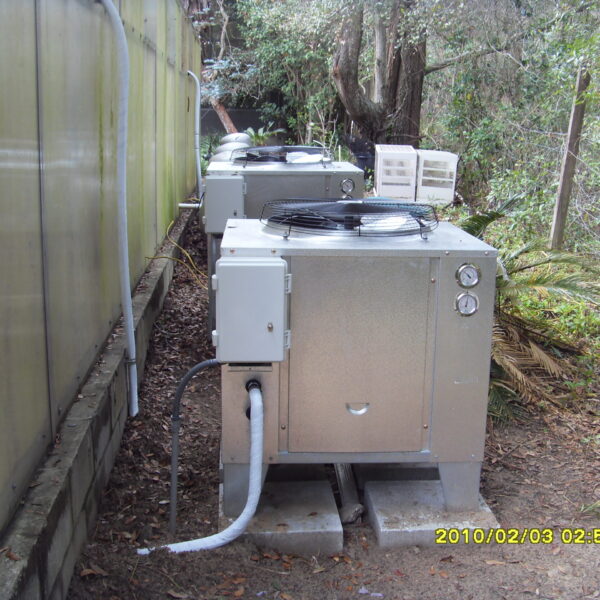
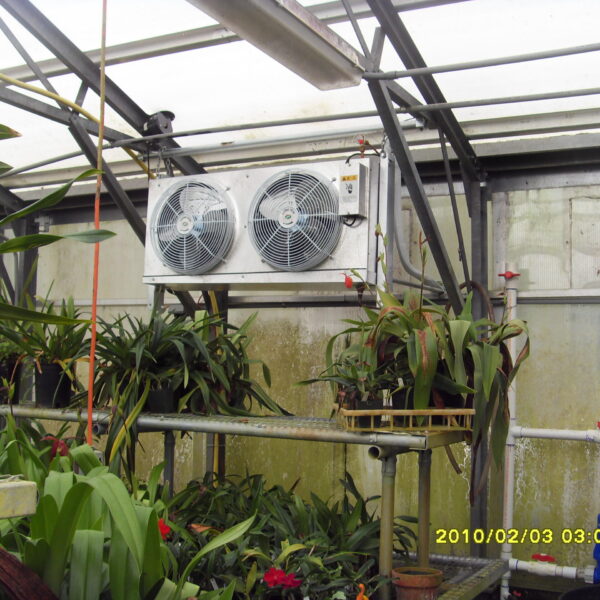
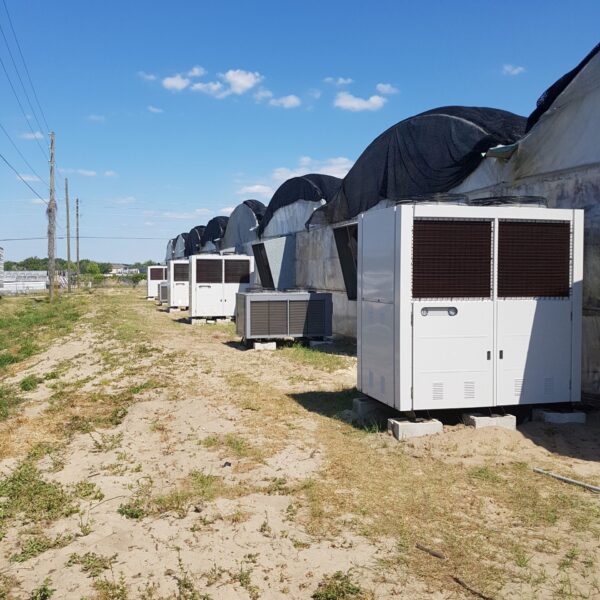
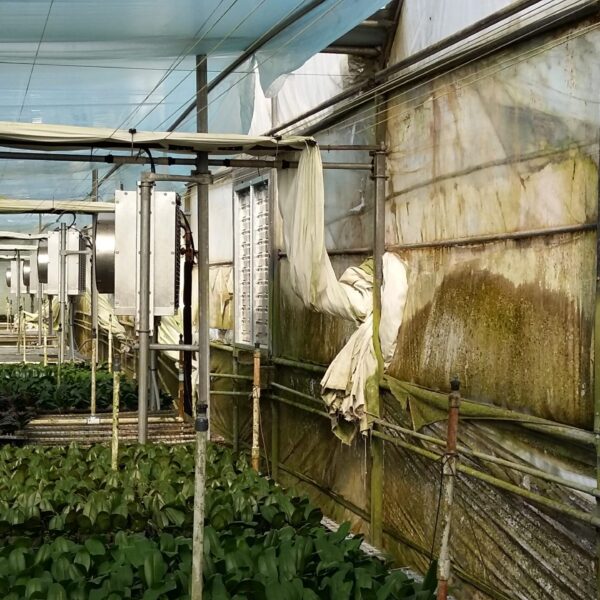
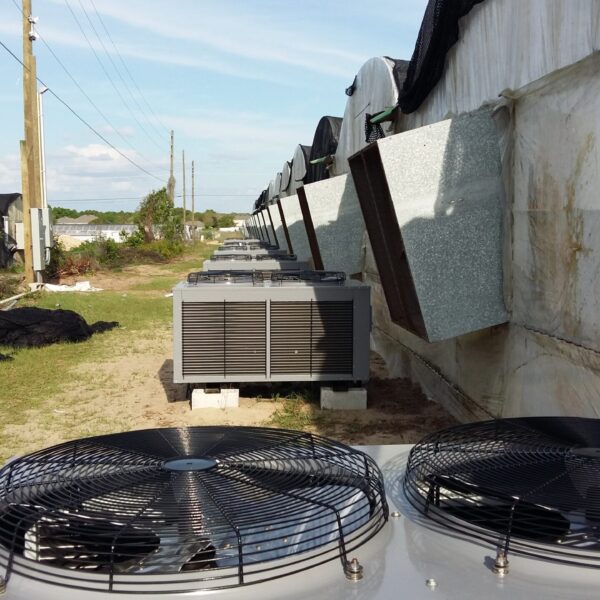
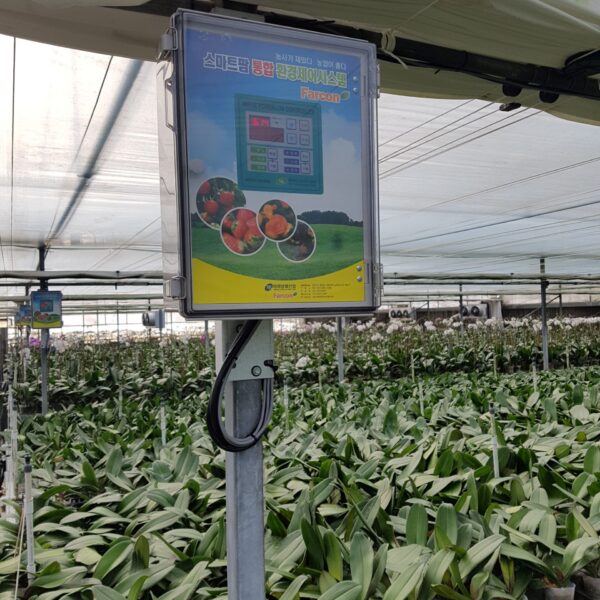
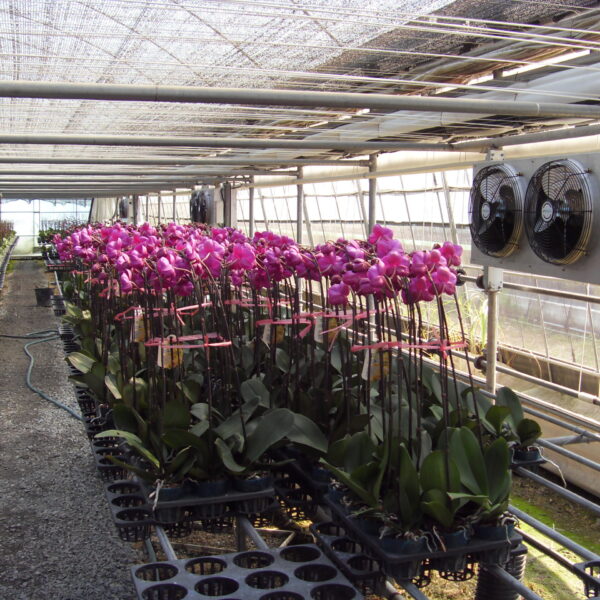
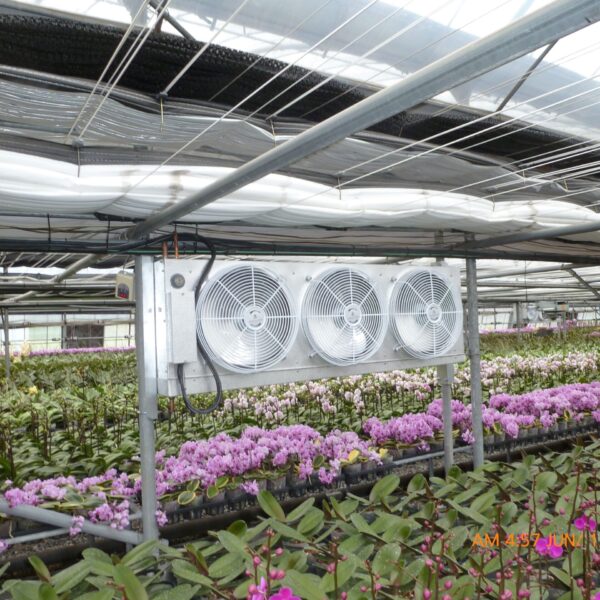
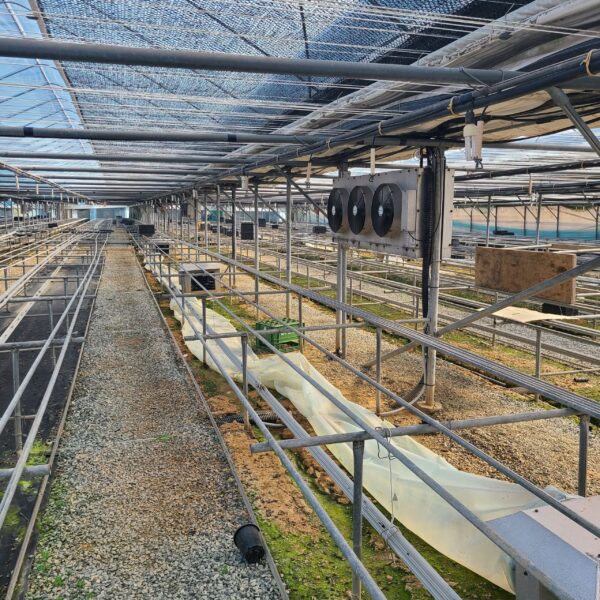
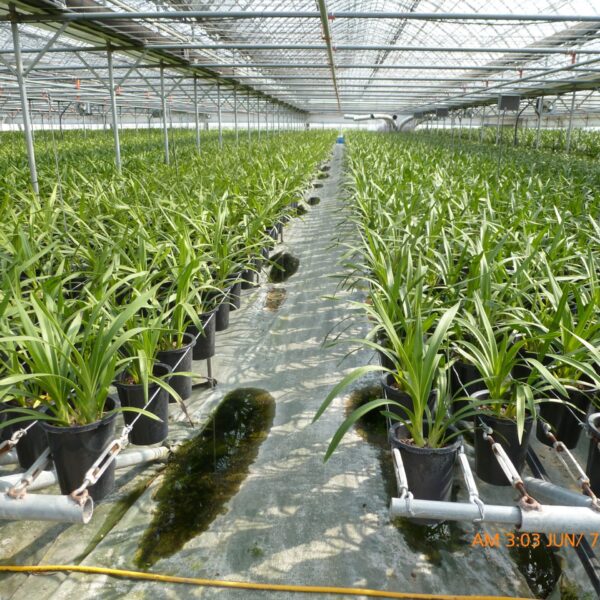
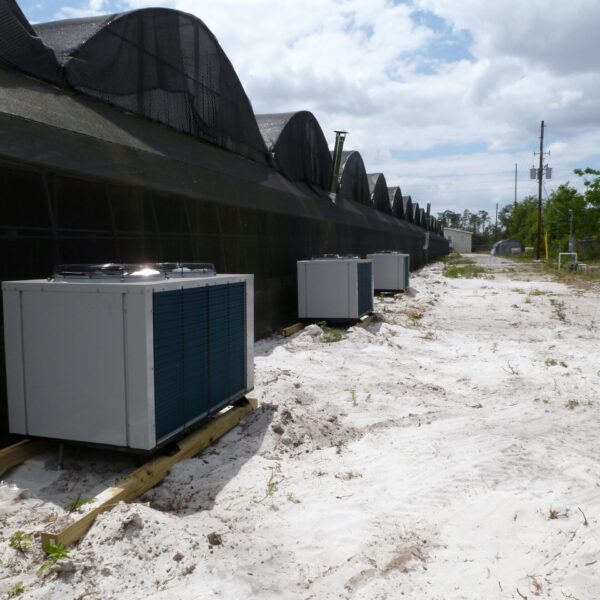
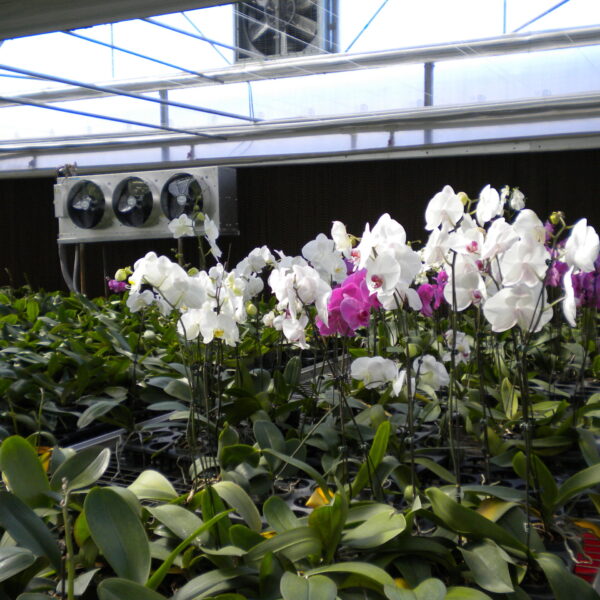
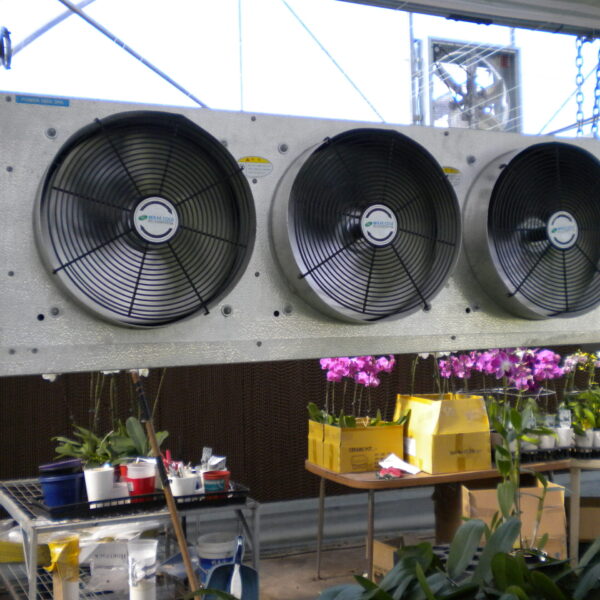
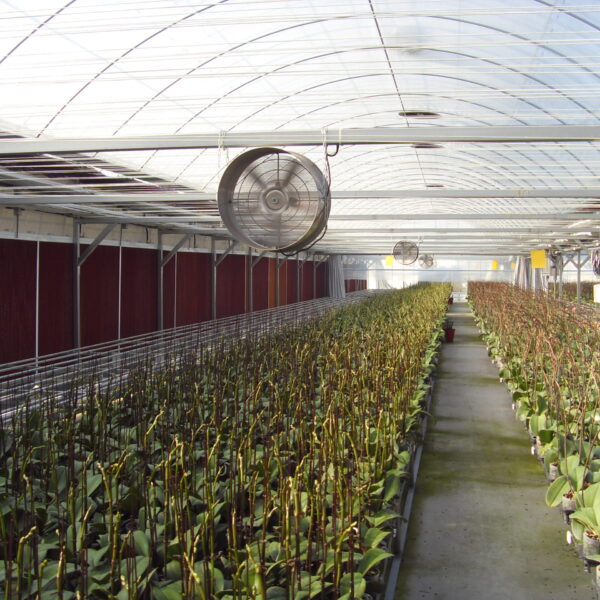
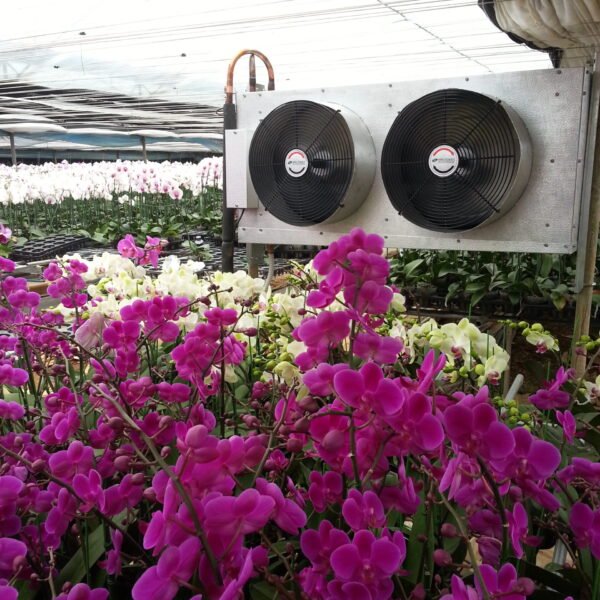
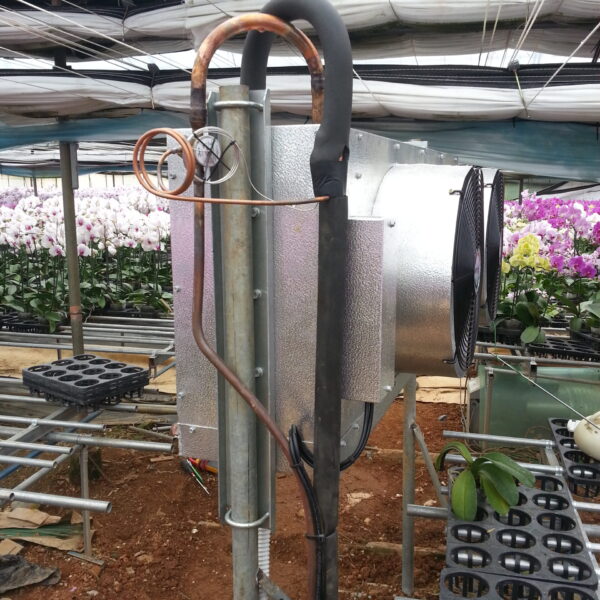
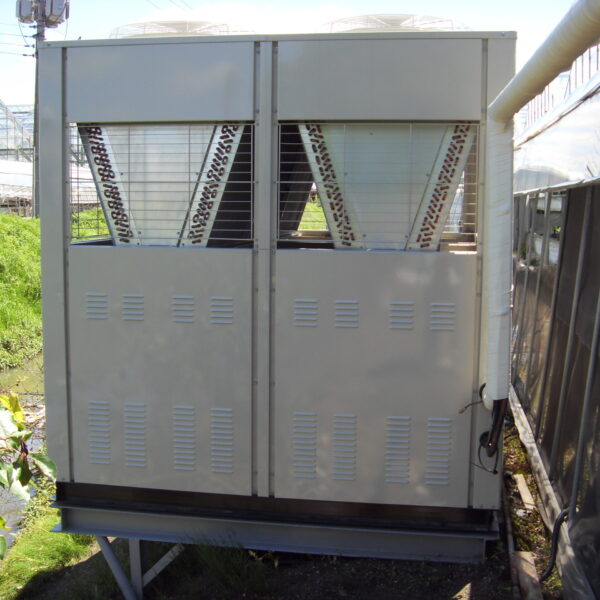
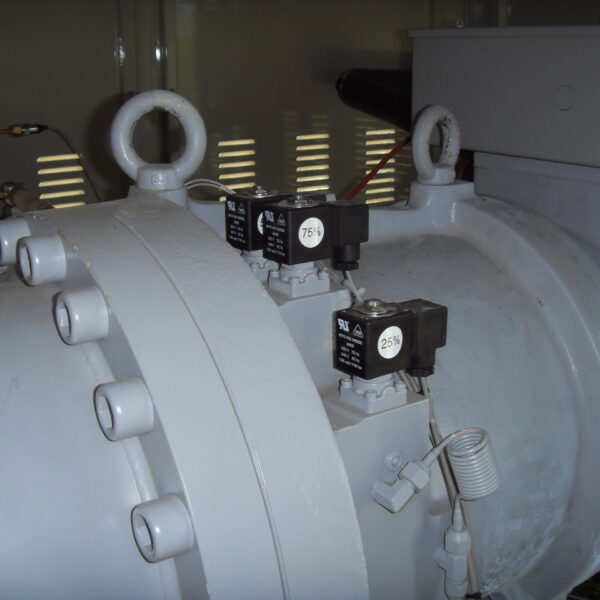
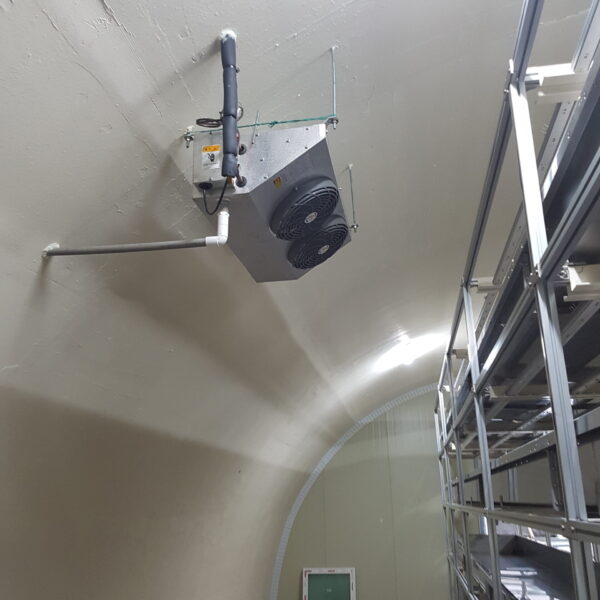
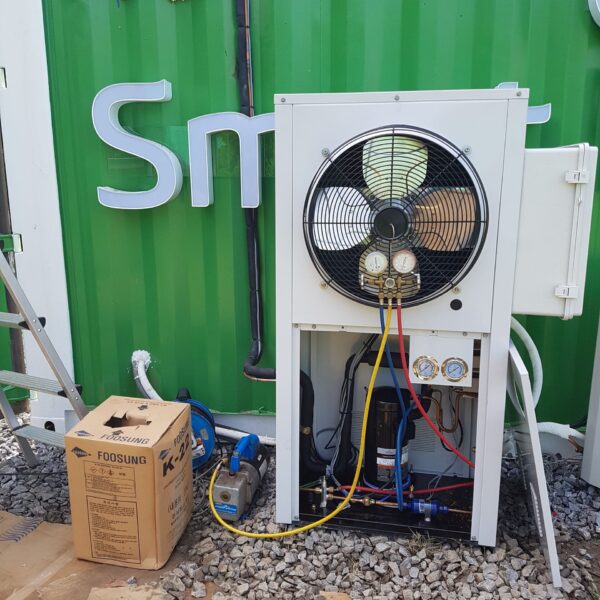
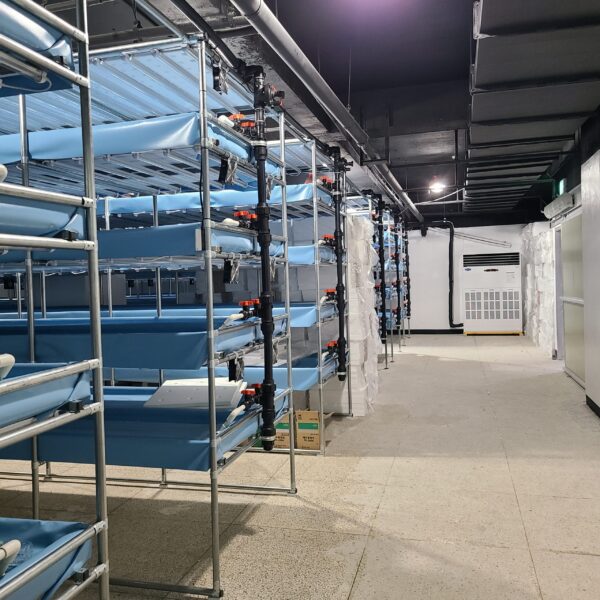
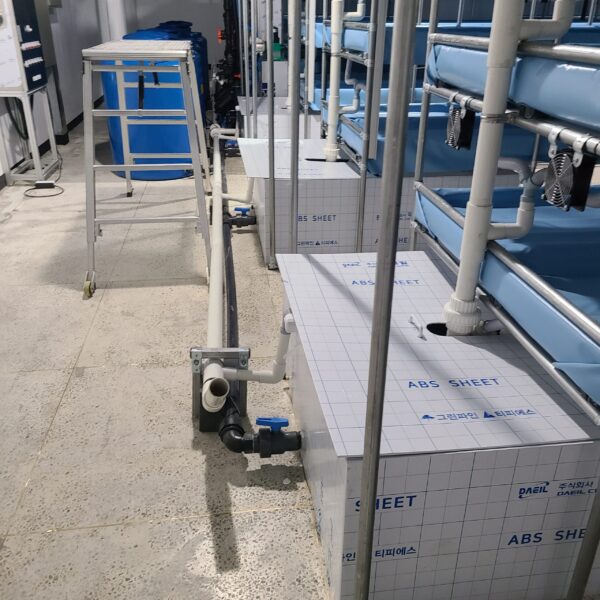
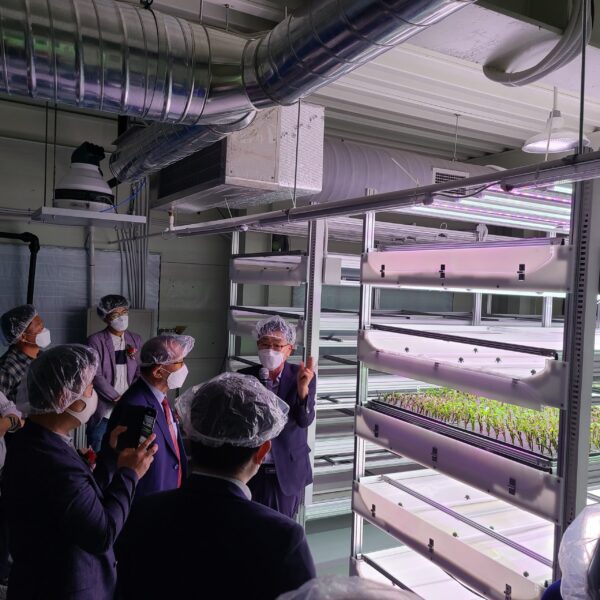
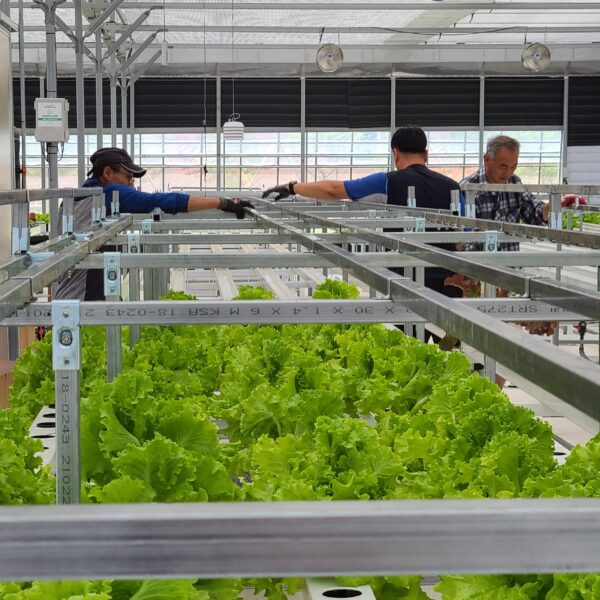
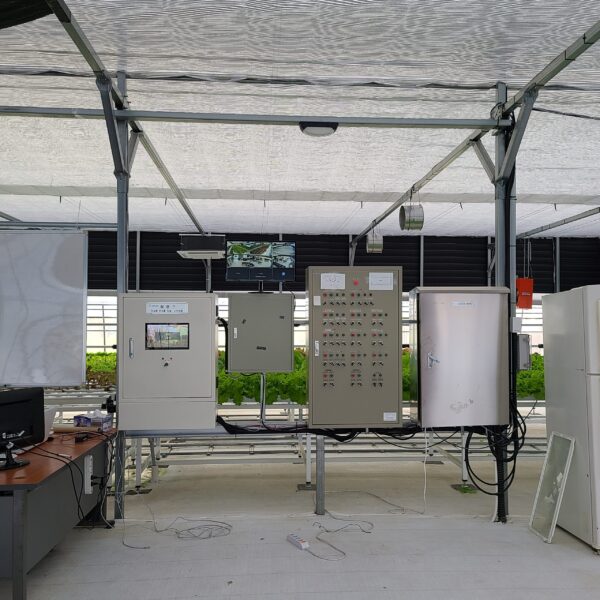
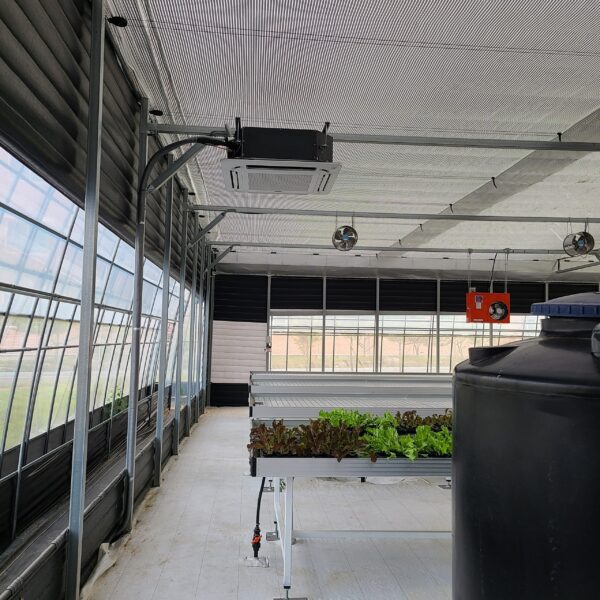
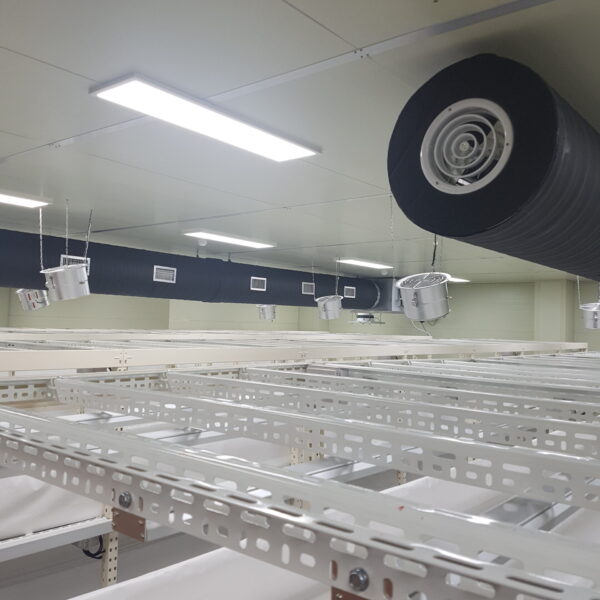
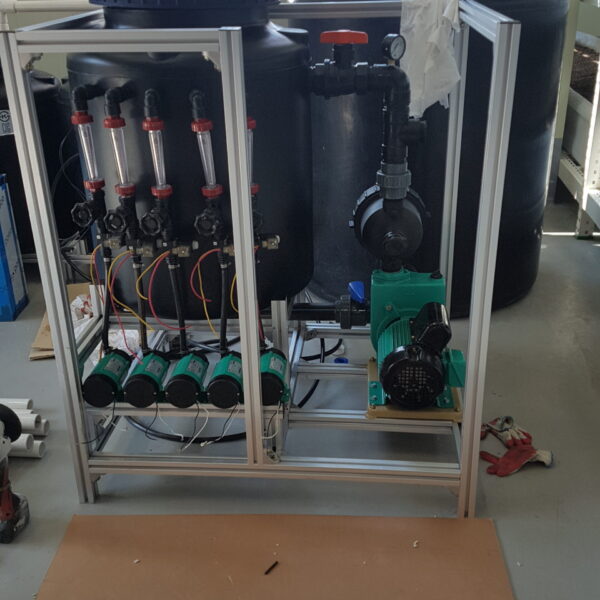
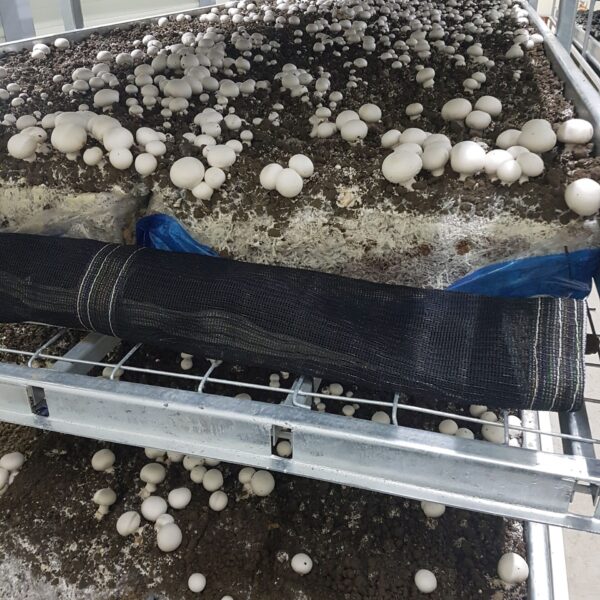
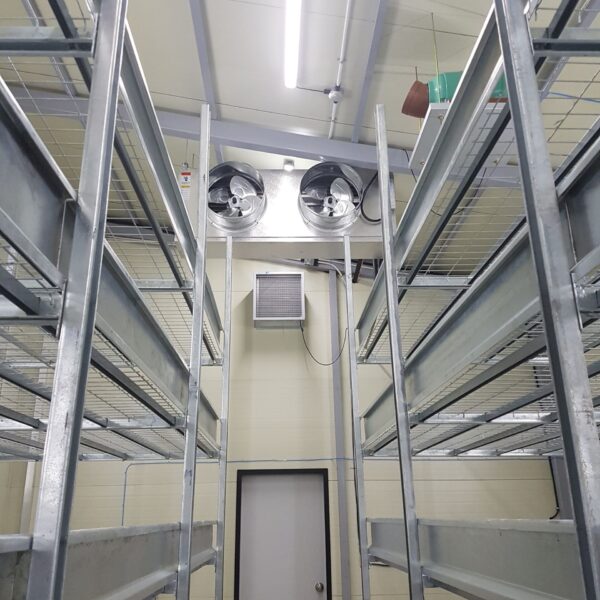
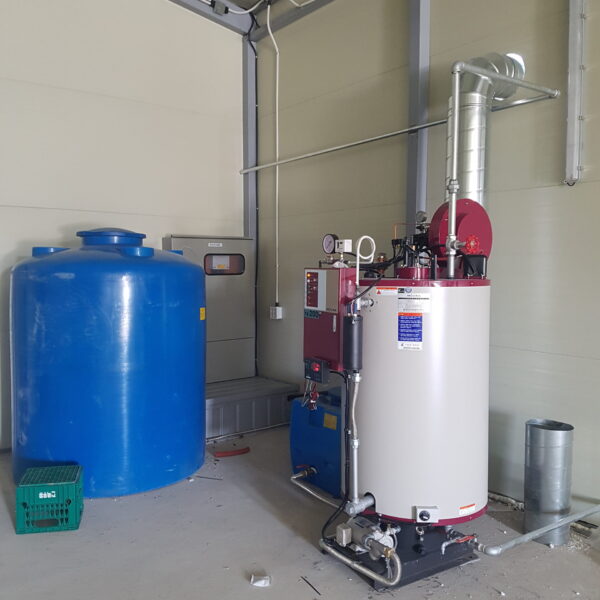
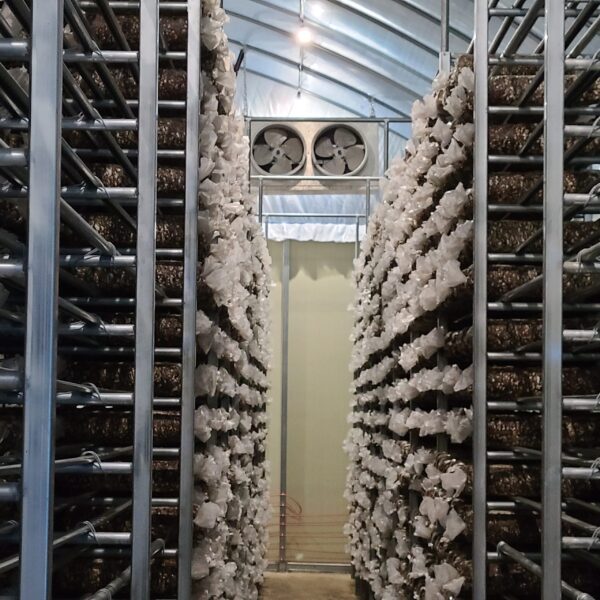
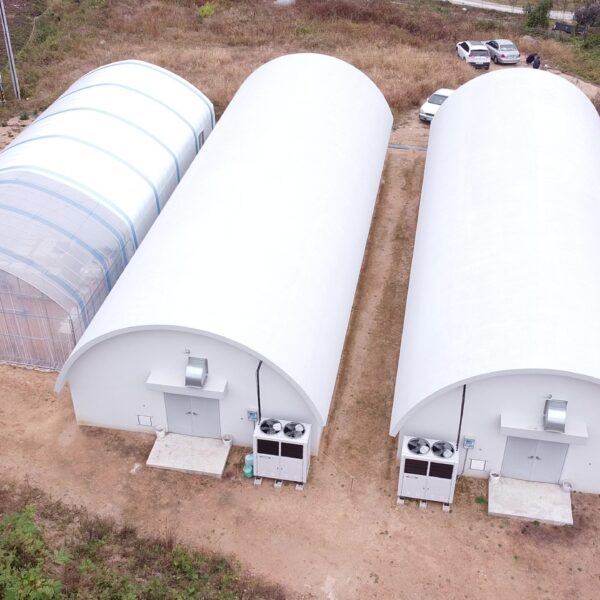
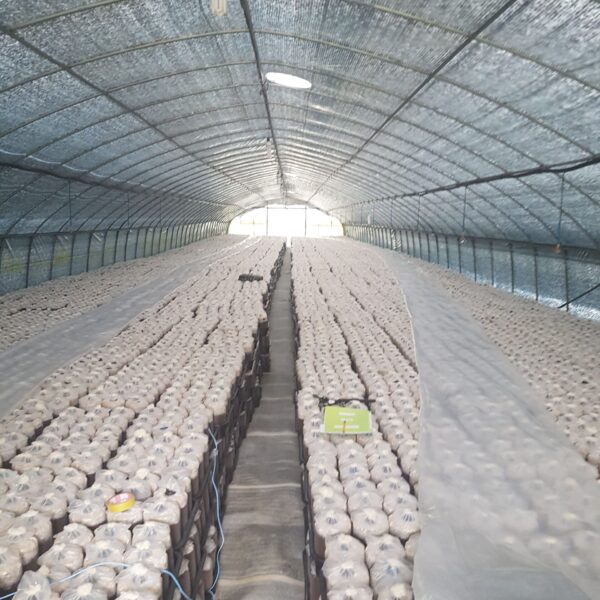
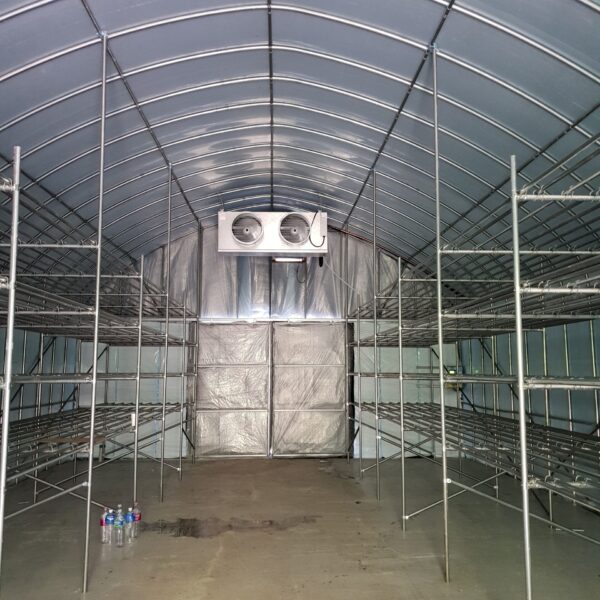
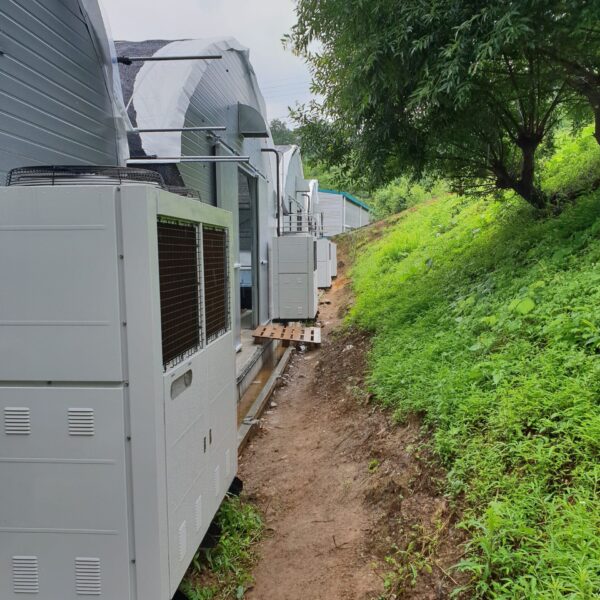
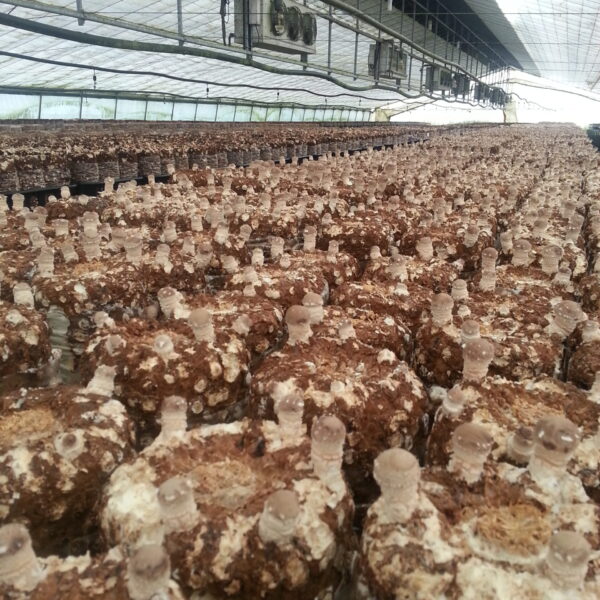
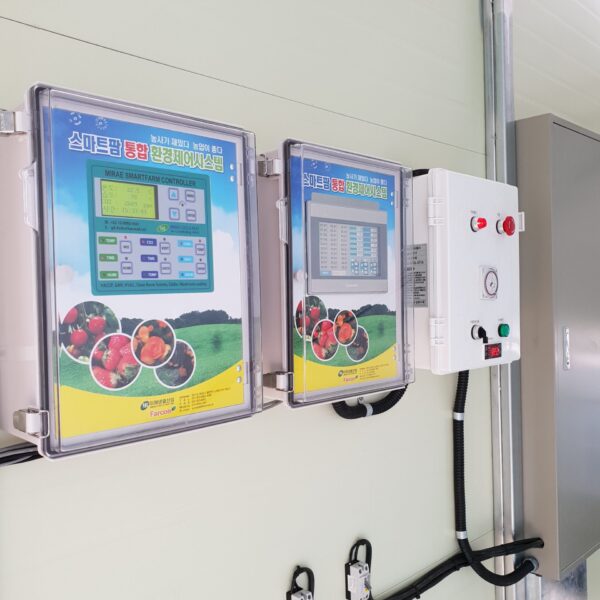
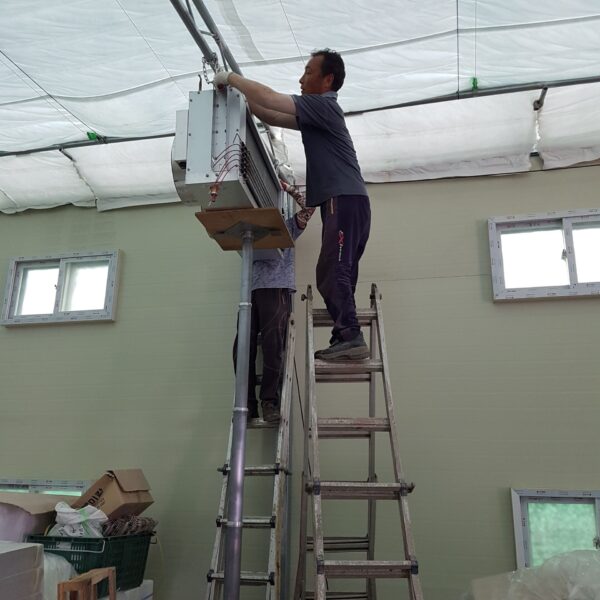
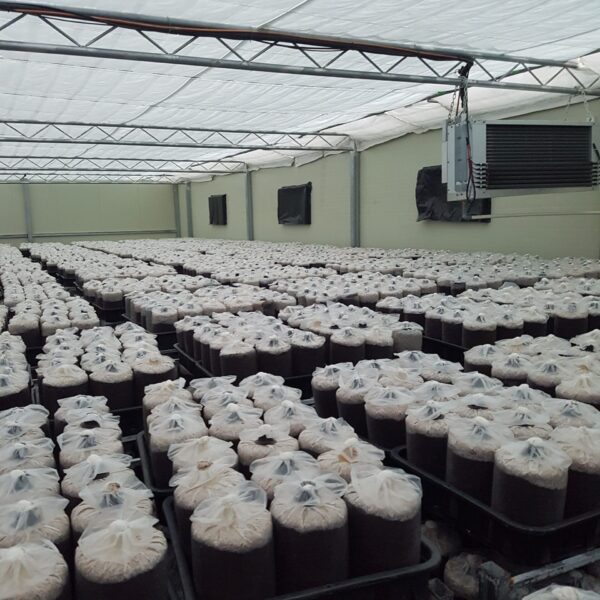
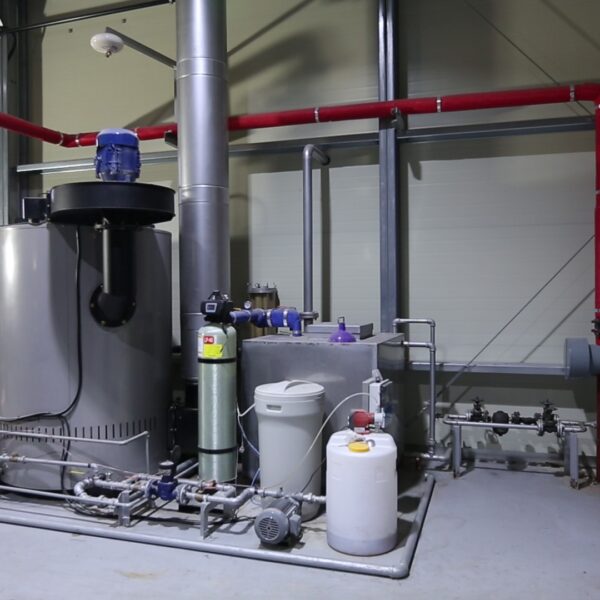
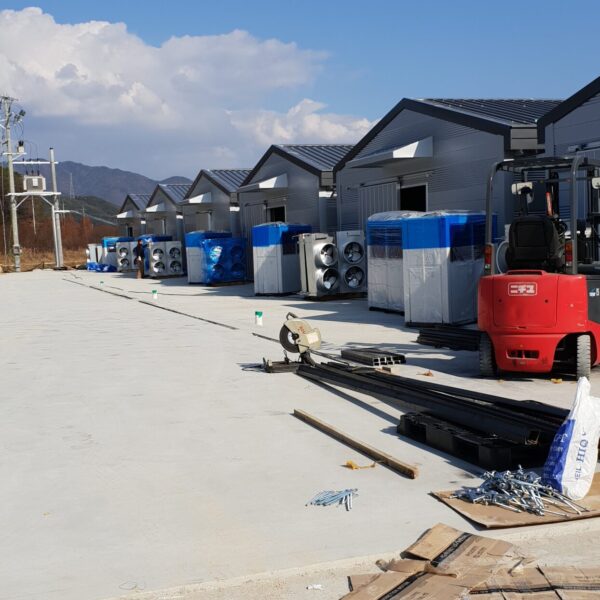
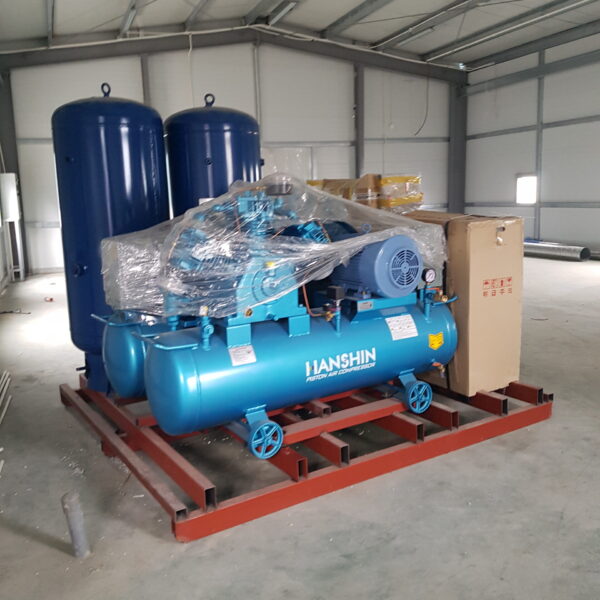
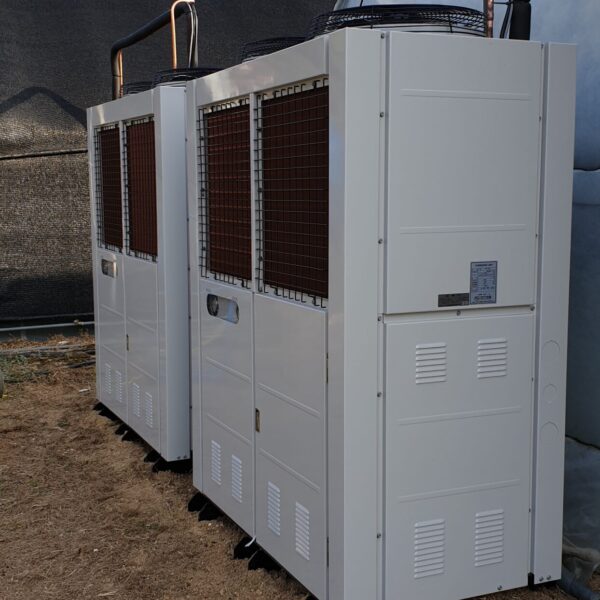
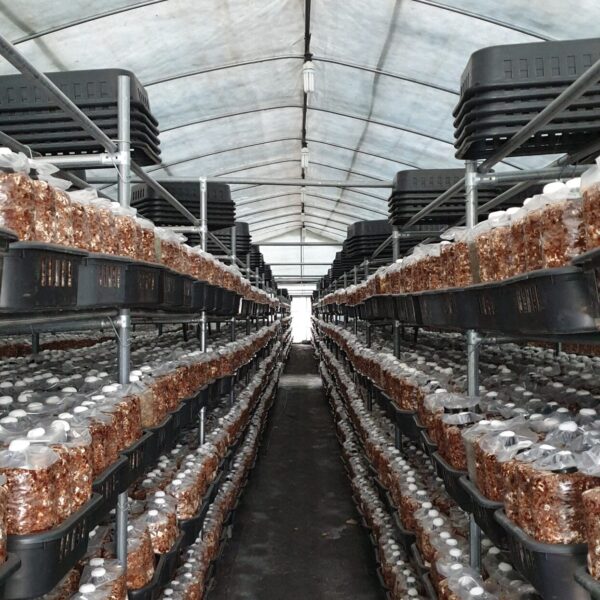
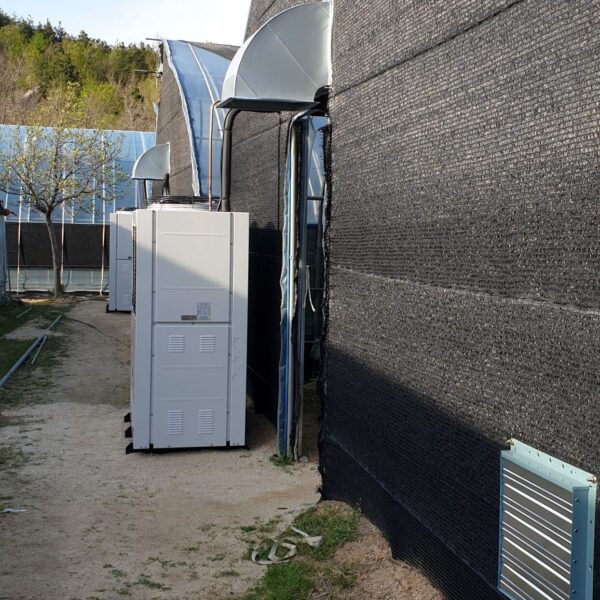
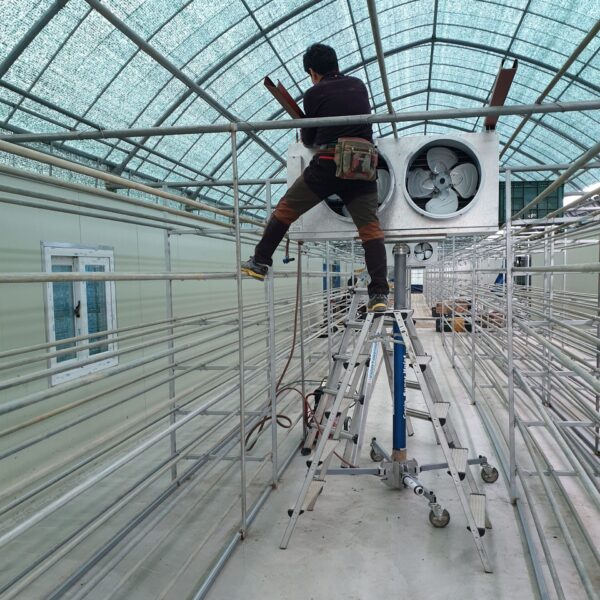
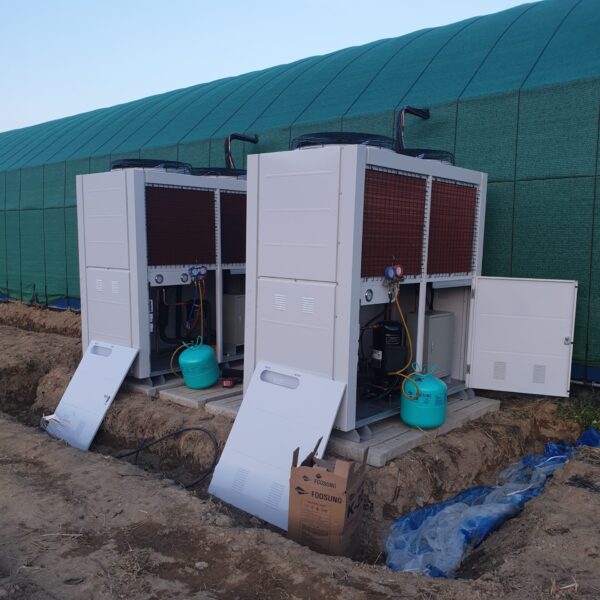
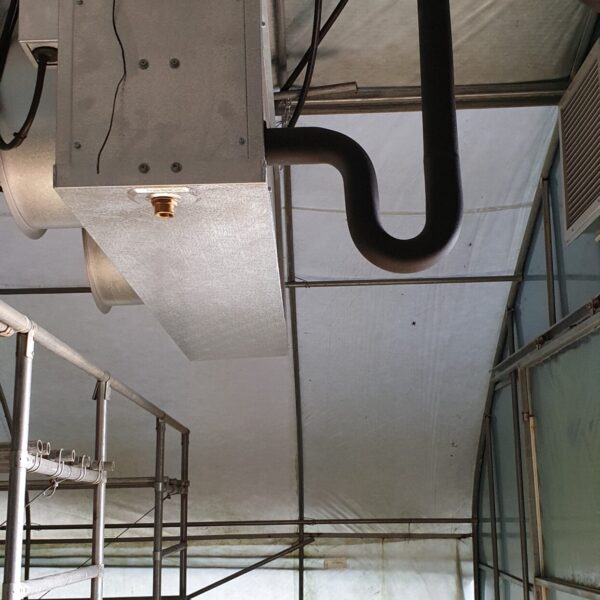
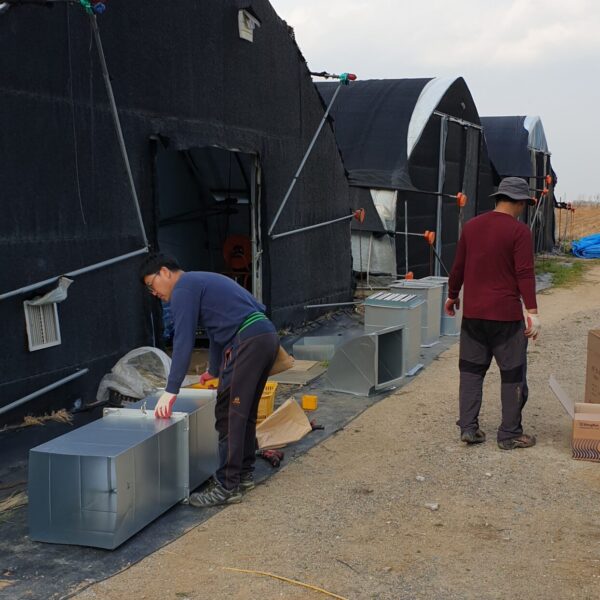
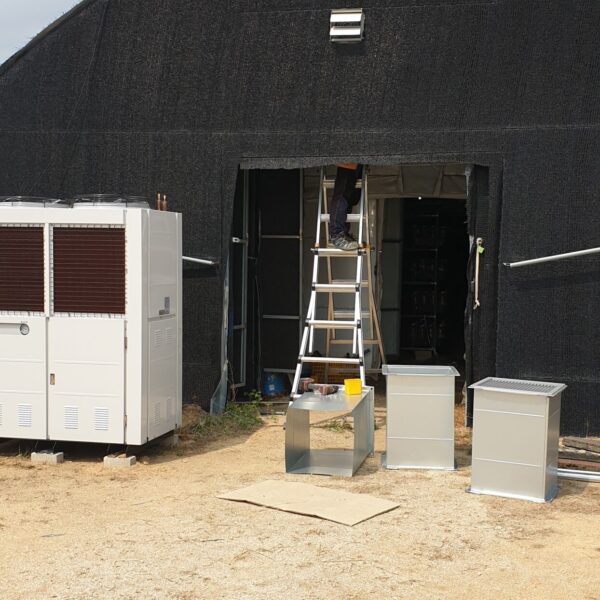
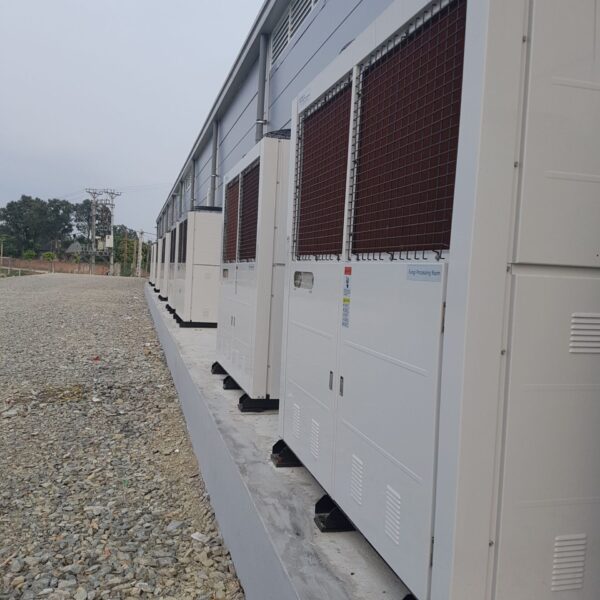
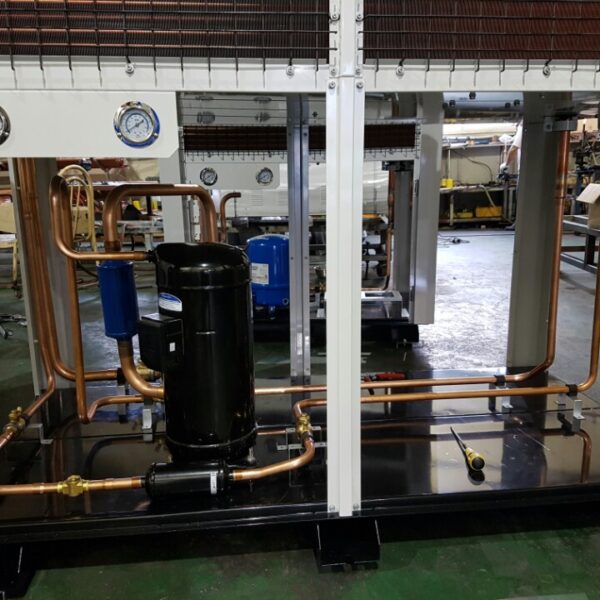
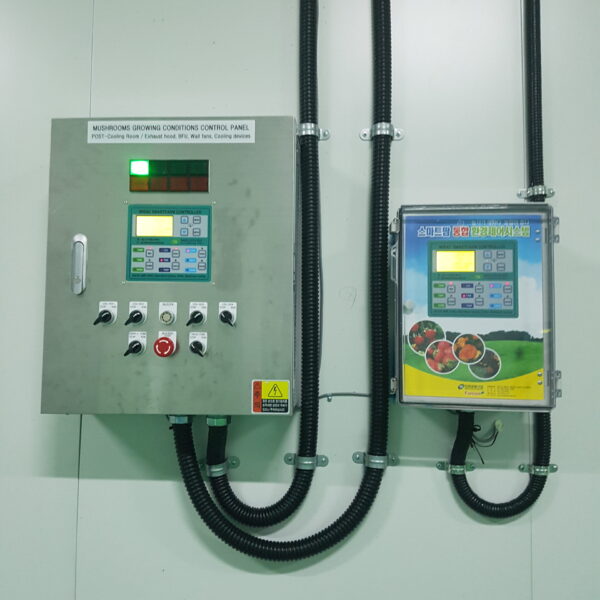
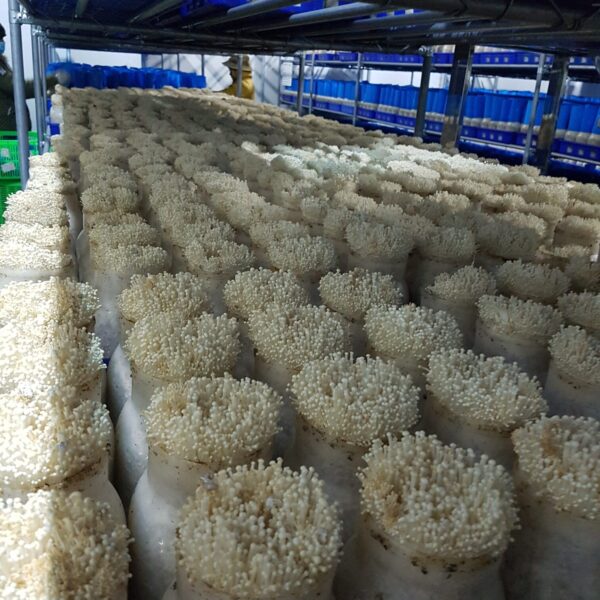
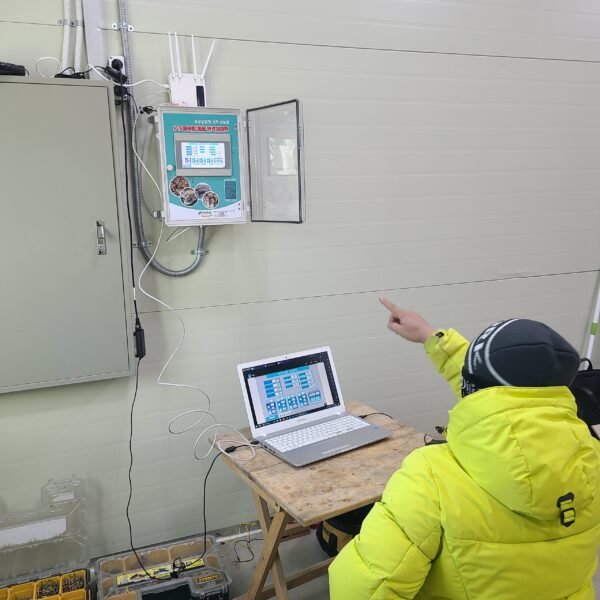
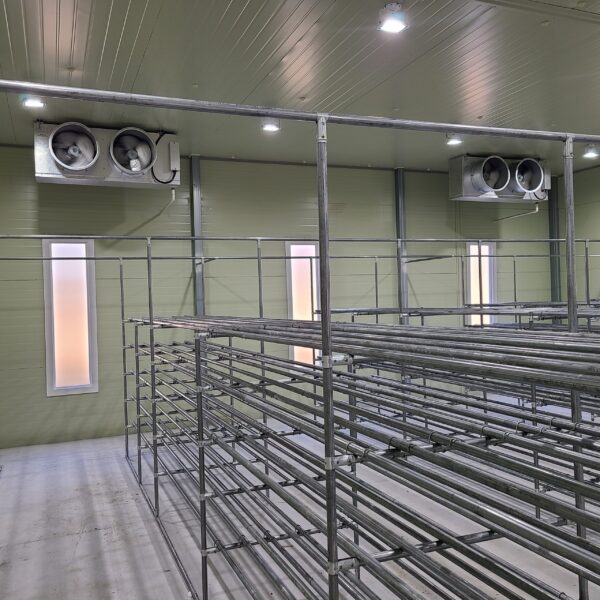
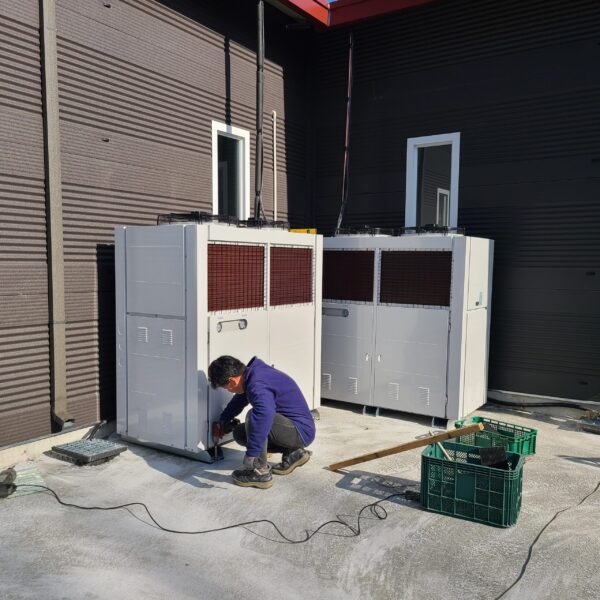
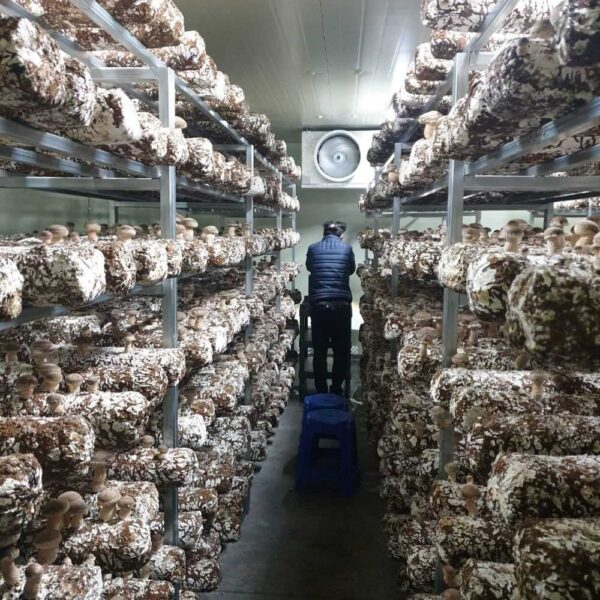
Energy saving technology in facility horticulture is a method of reducing input energy by using a heat pump type high-efficiency heater using geothermal hydrothermal solar heat, day and night alternate temperature management technology, heat storage using daytime sunlight in soil storage tanks, reduction of heating and cooling space, and use of low-cost fuel As a method of reducing the loss of input energy using heat retention performance improvement and exhaust heat recovery, energy saving technology may vary depending on the greenhouse type heating method.
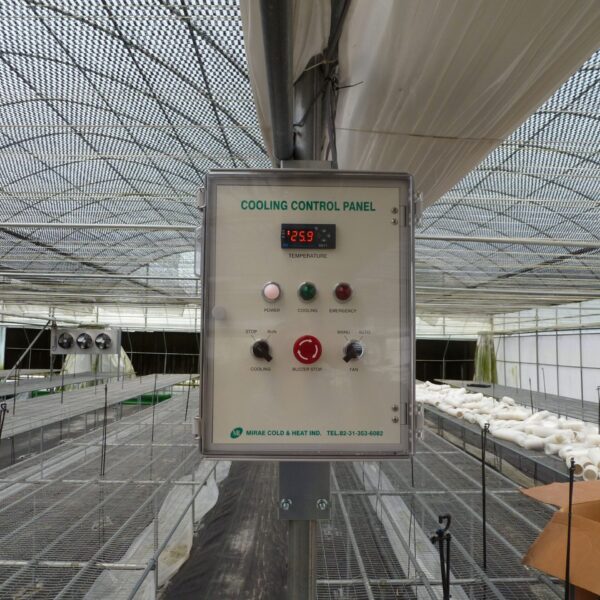
Reasonable temperature control within the facility is alternate temperature control. Crops start photosynthesis when the sun rises, but since the temperature inside the facility is not high enough for photosynthesis, pre-heat for 1 to 2 hours at this time. give. For 4 to 6 hours after sunset, keep the temperature slightly elevated to promote the current of assimilation products. After the current is over, it is managed at a low temperature that does not interfere with crop growth to reduce consumption by respiration. It is desirable to apply the day and night alternate temperature management method according to crops and weather conditions, and with such reasonable alternate temperature management, the quantity and quality of crops can be improved and heating costs can be greatly reduced.