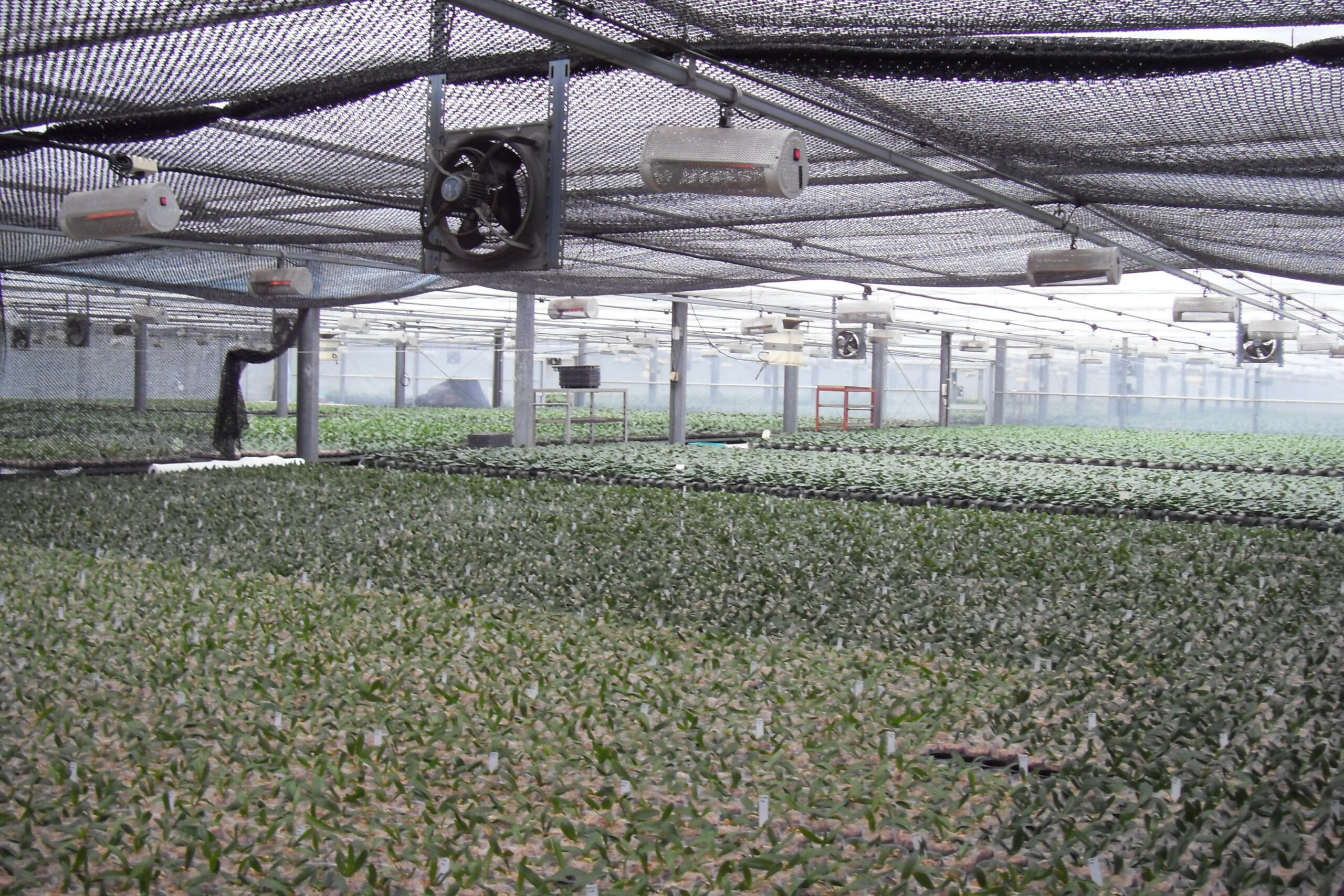
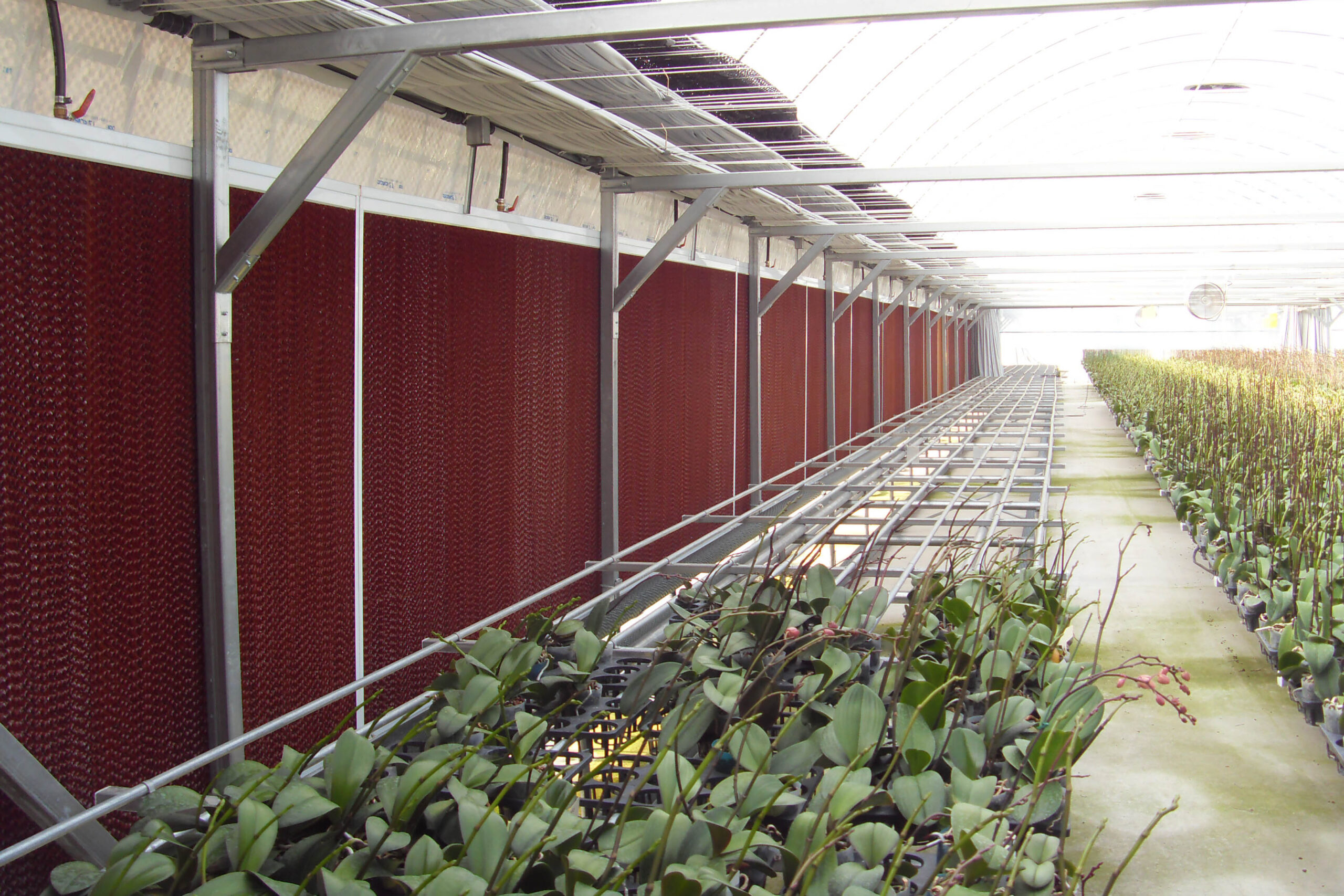
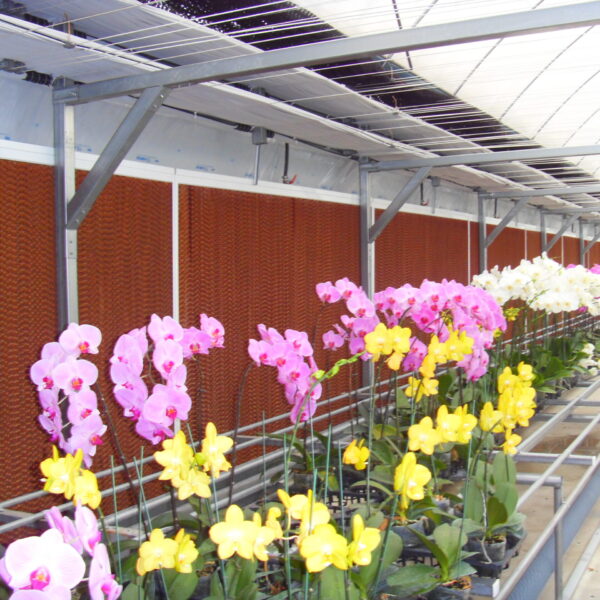
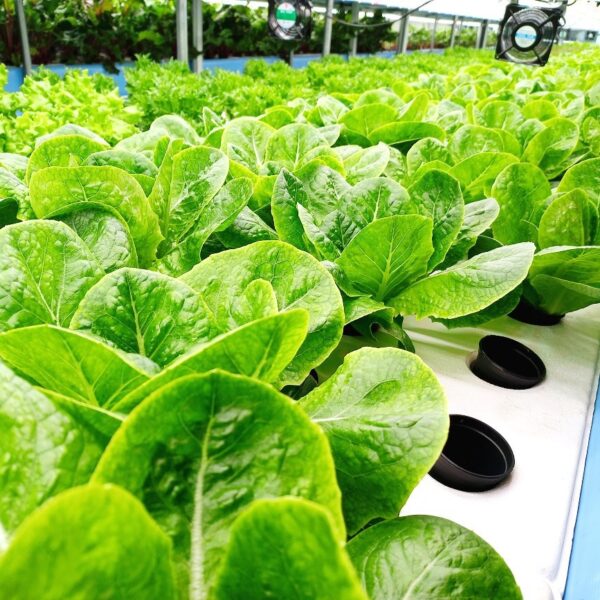
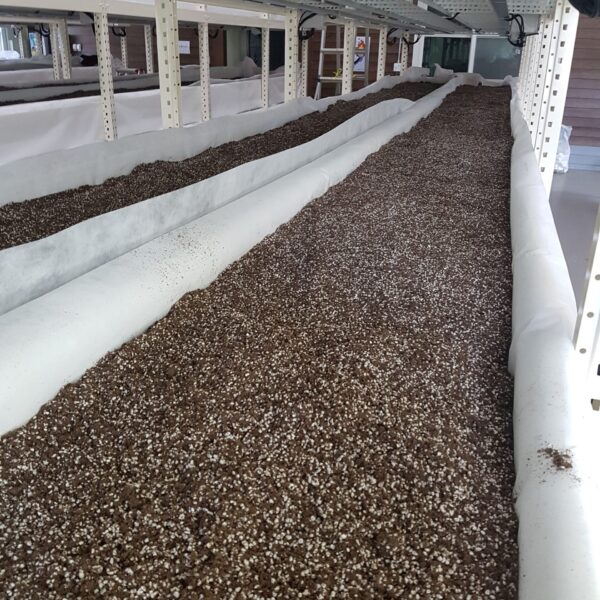
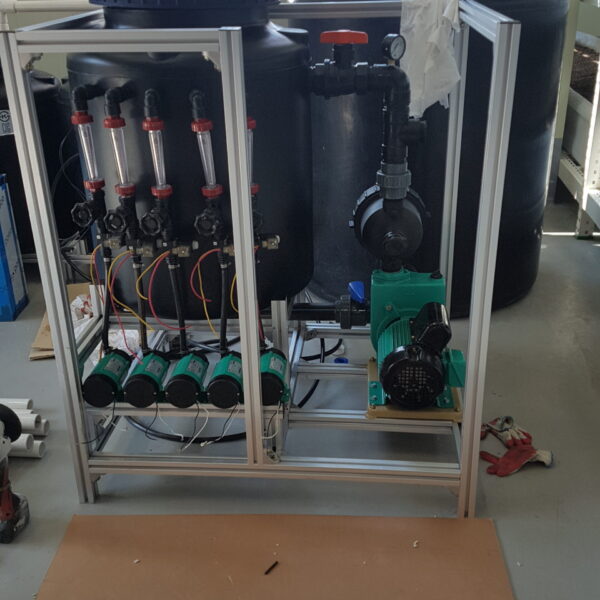
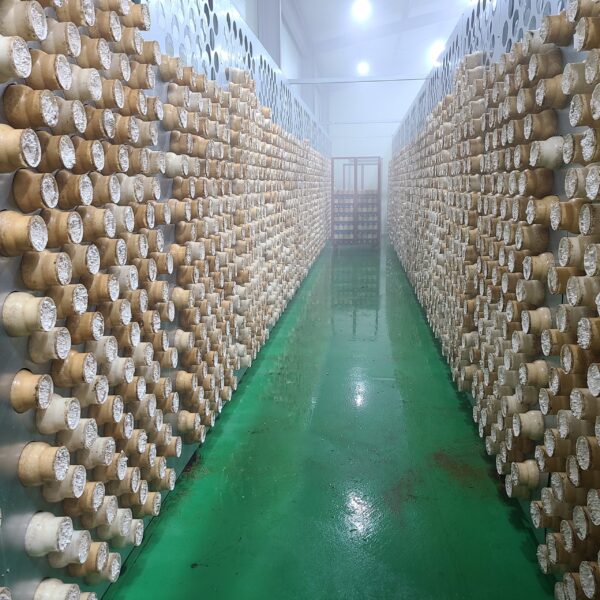
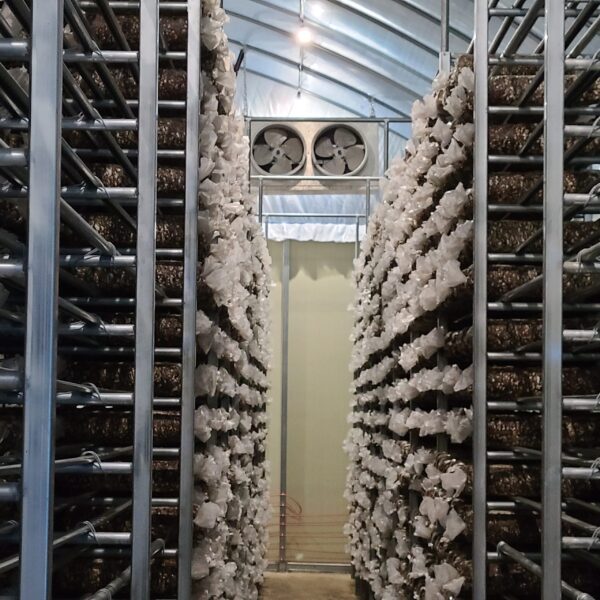
Next, as a cooling method using fog mist, this is also vaporization cooling using the latent heat of evaporation of water. When water comes into contact with air with relatively low humidity and air with a lower temperature than this, heat is given to water to evaporate and the temperature of the air goes down at the same time to be. It is a facility that installs a nozzle capable of uniformly spraying high-pressure spray water inside the greenhouse, splits the water finely, and sprays it into the air to induce evaporation. It is effective in a high-temperature and dry environment. The humidity in the greenhouse, which has increased during the evaporative cooling process, must be maintained at a low humidity continuously. There are a method using a ventilation fan and a method of replacing the indoor and outdoor air by opening the greenhouse. This method should be applied after fully understanding the characteristics of the crops, since the humidity in the greenhouse rises above the appropriate humidity, causing damage such as the occurrence of diseases and pests and deterioration of the growth of cultivated crops due to various humidity.
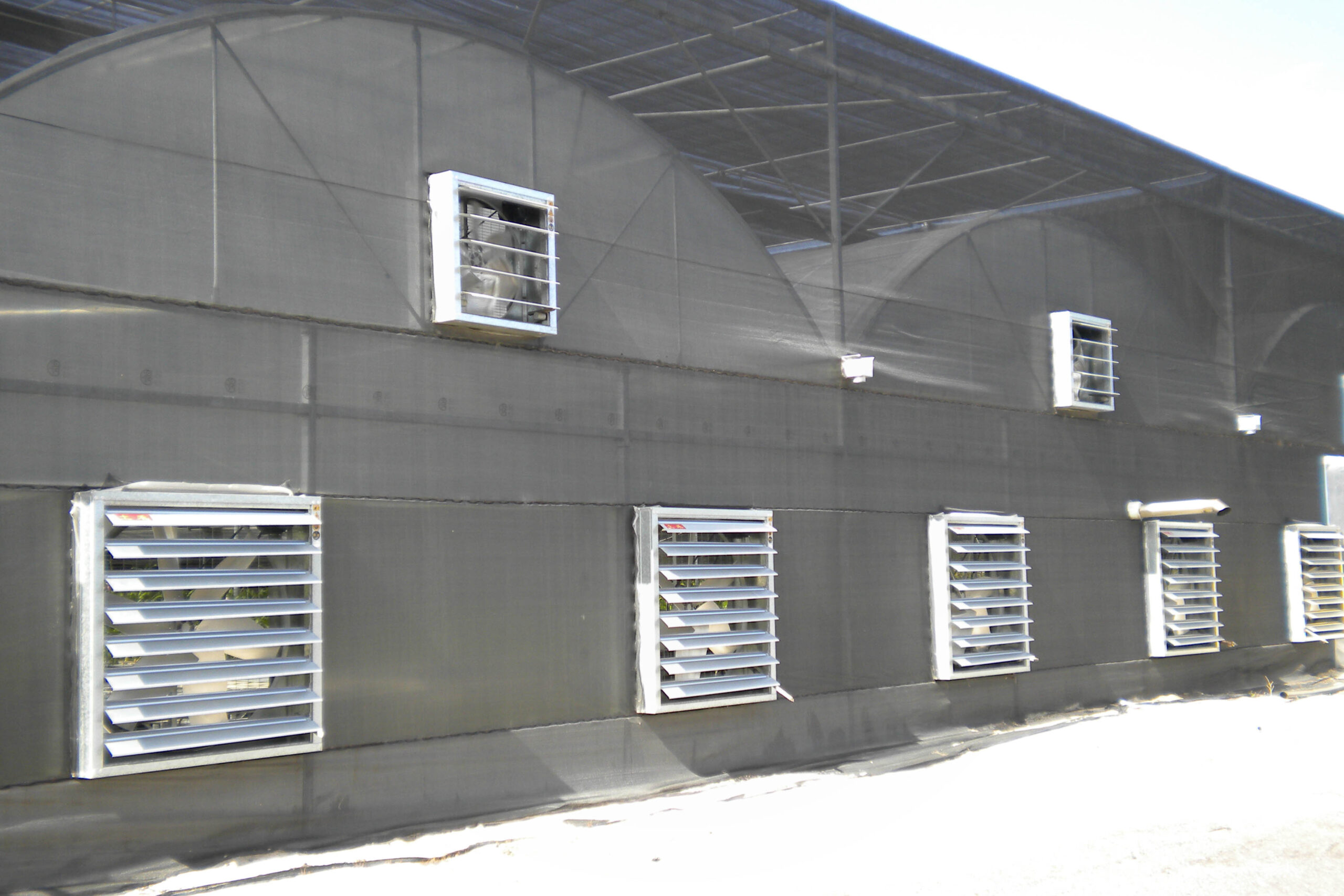
High-pressure mist Cooling using high-pressure mist can be used with both natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation. The optimal system should be designed by carefully examining the ventilation rate, characteristics of the cultivated crops, and the climate around the greenhouse. It uses less water than the pad system and the facility cost is lower. Fine water droplets of 10 to 20 microns easily absorb heat from the air and evaporate when sprayed in the air.
This evaporative cooling method can control the greenhouse environment by contacting water and air, and the greater the difference between the dry-bulb temperature and the wet-bulb temperature, that is, the lower the humidity in the air, the greater the effect. The cooling effect is limited.
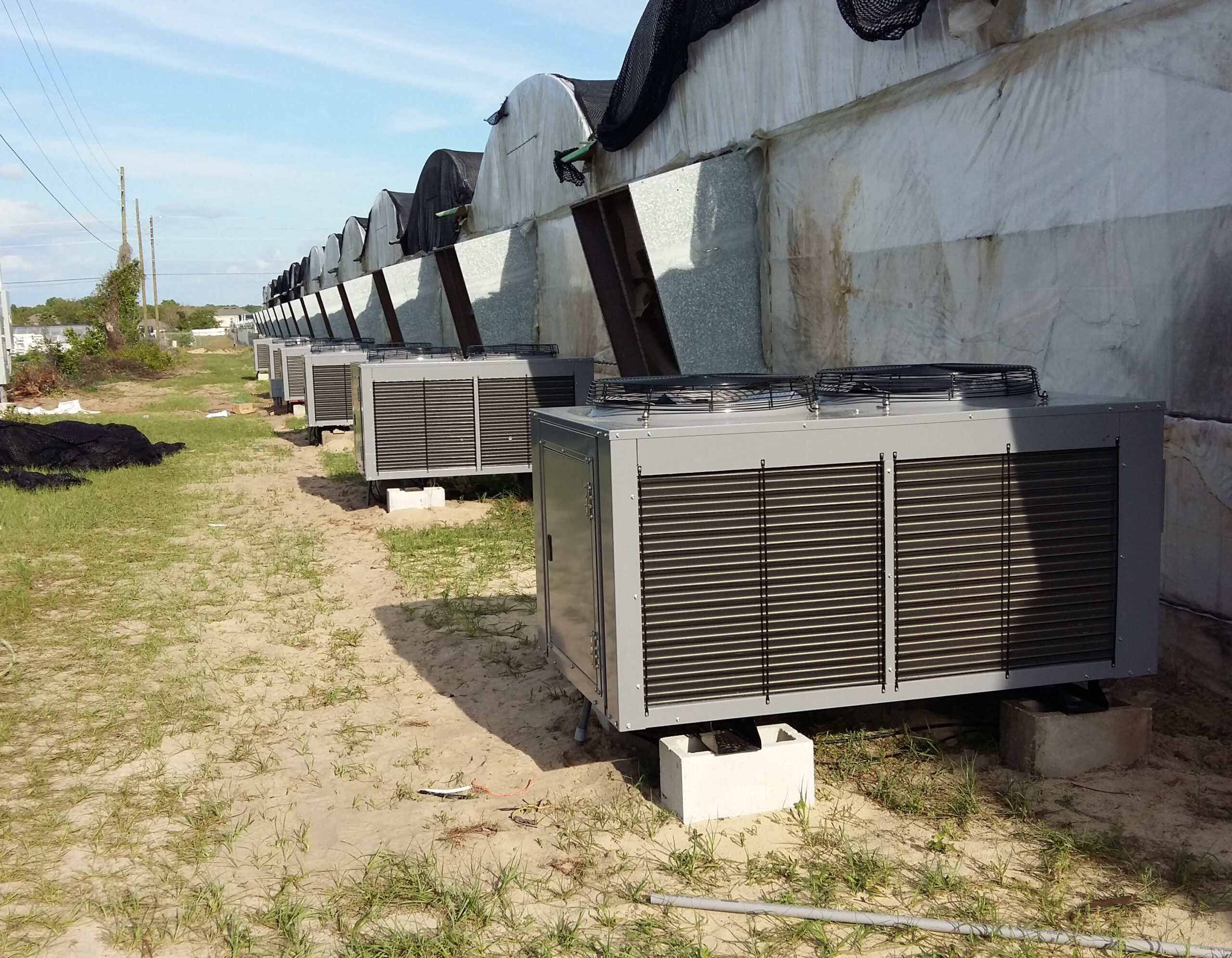
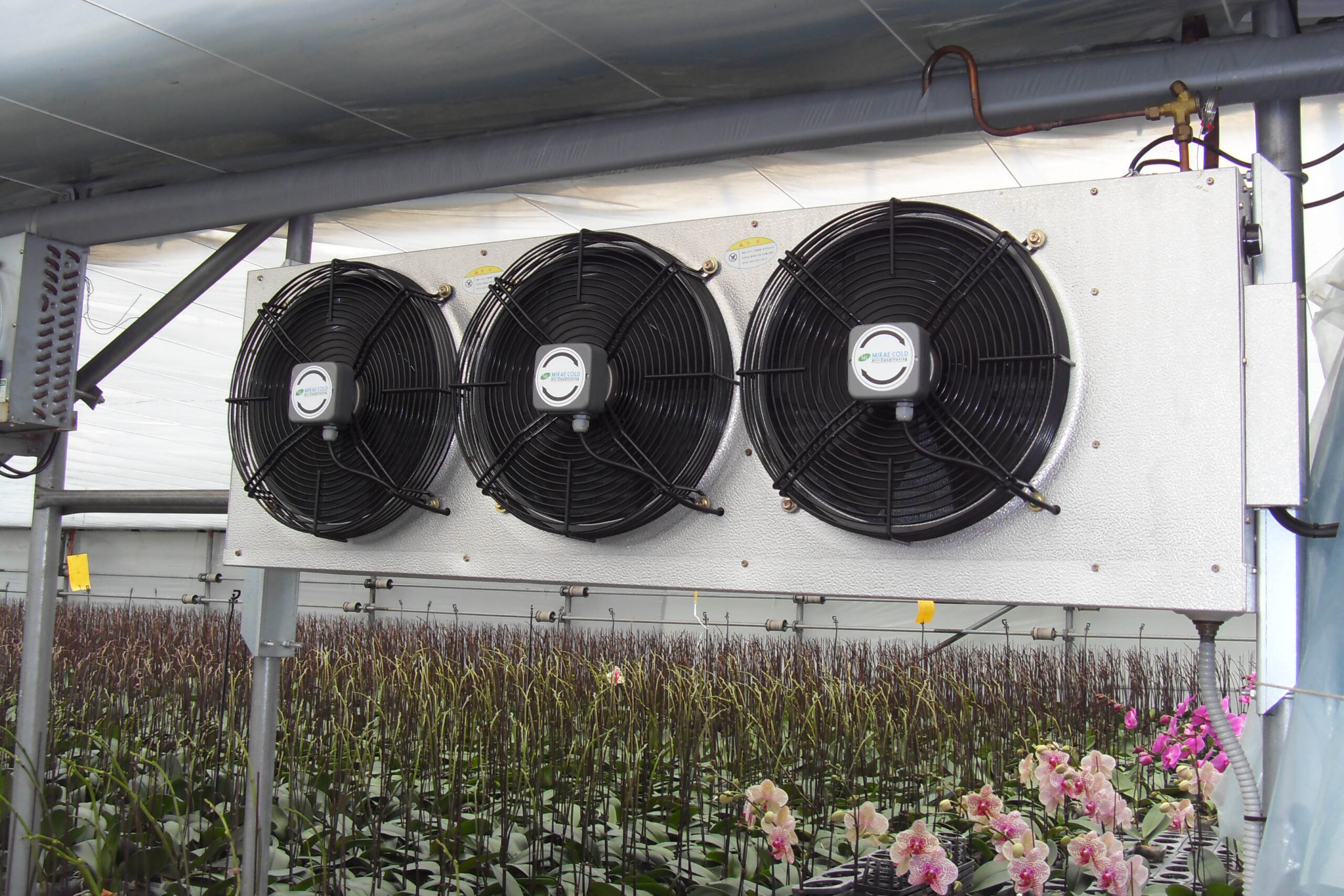
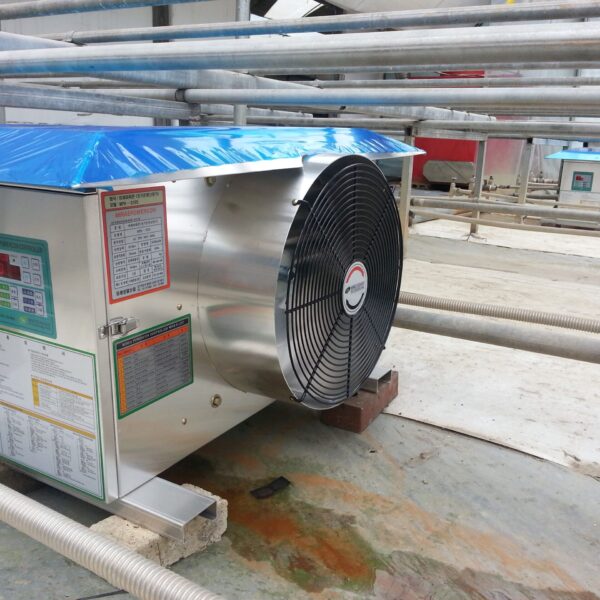
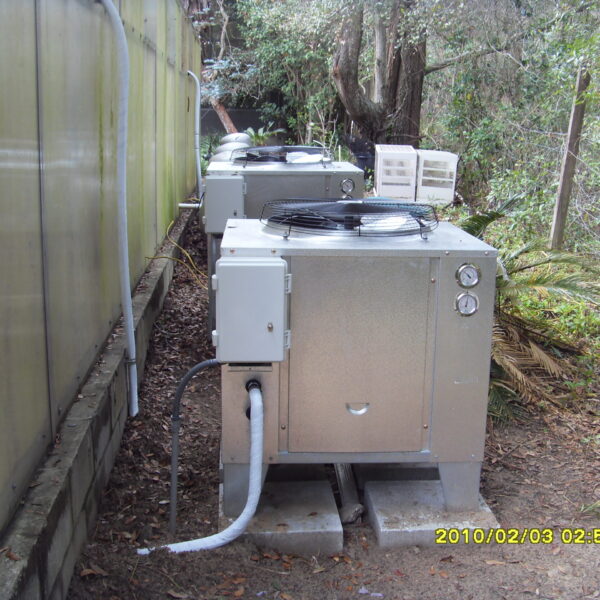
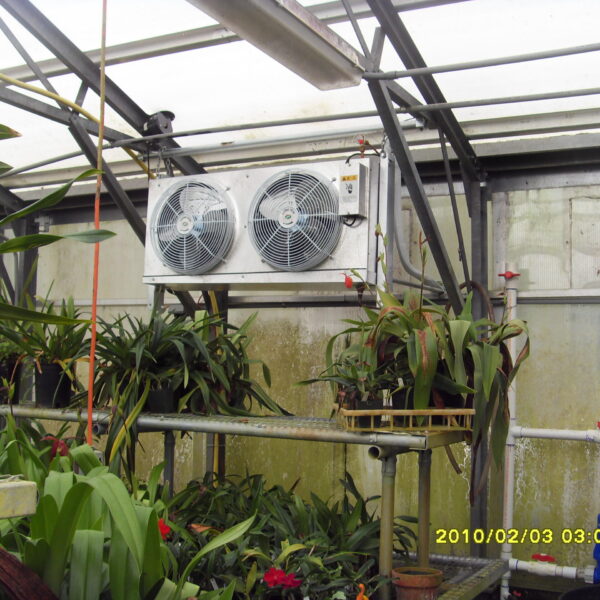
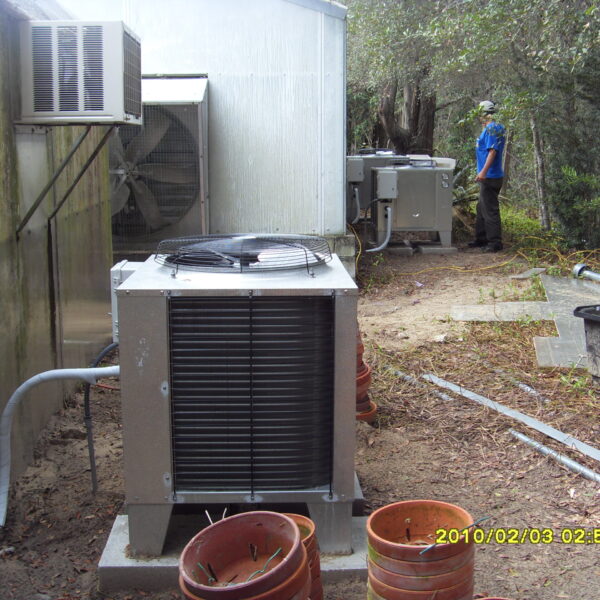
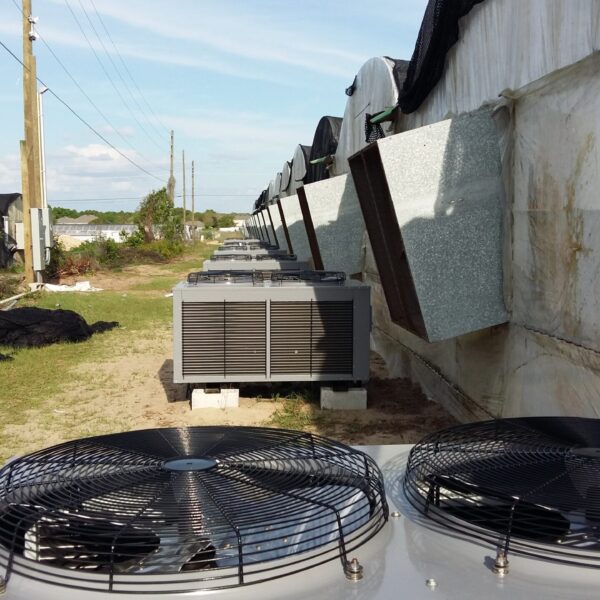
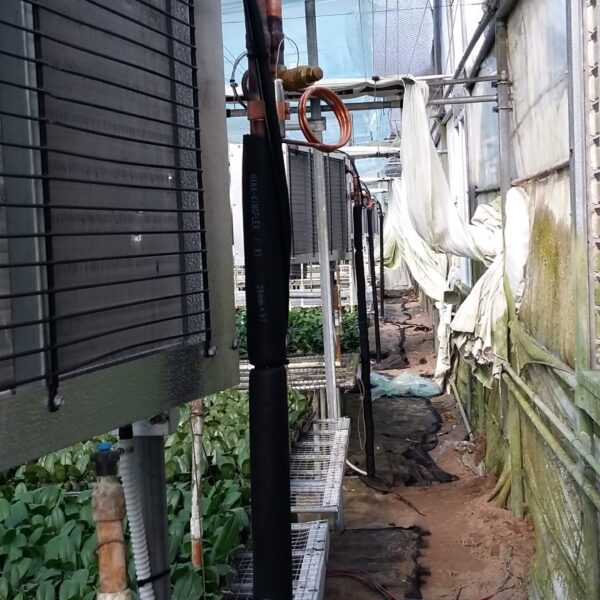
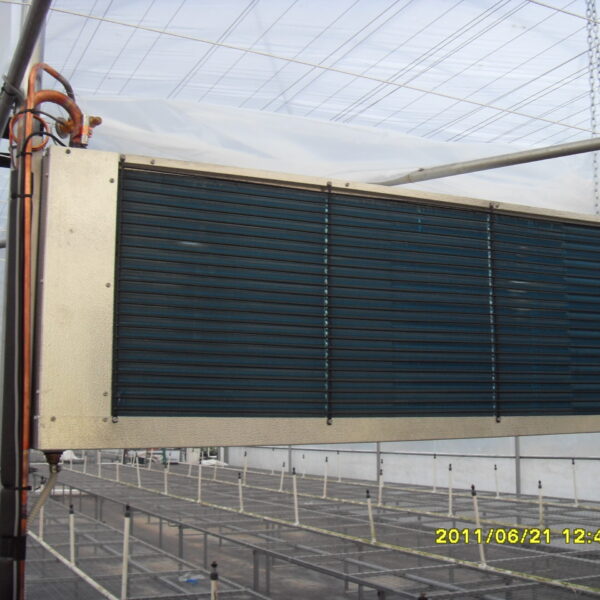
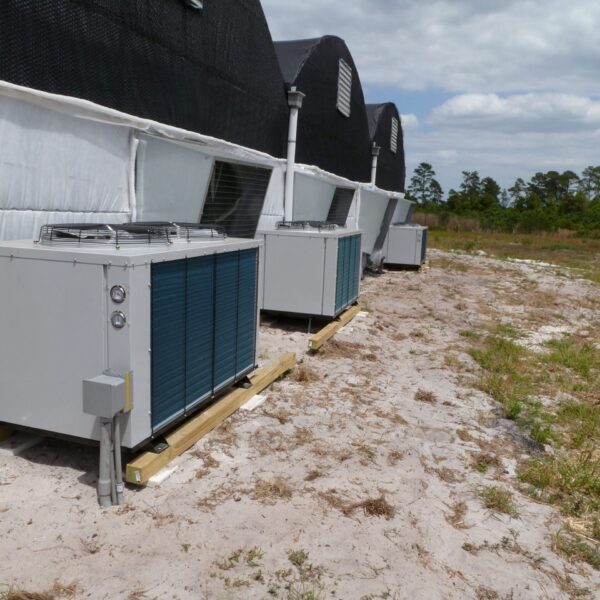
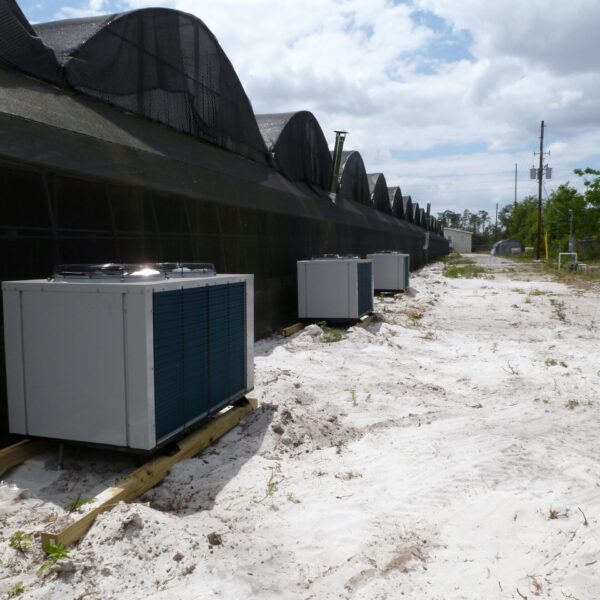
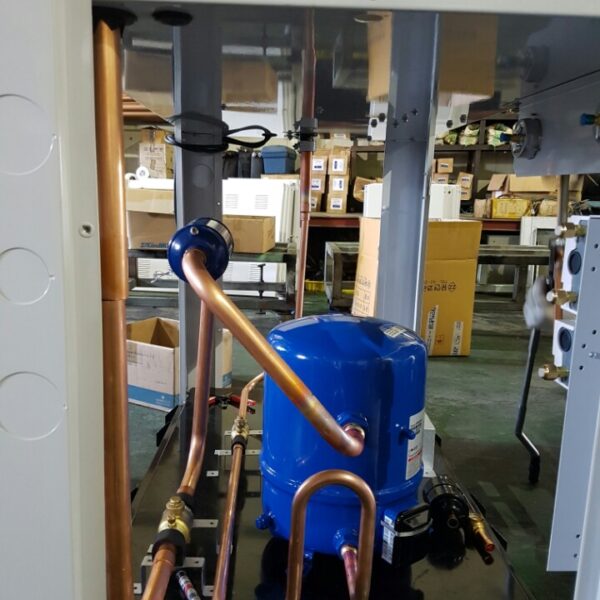
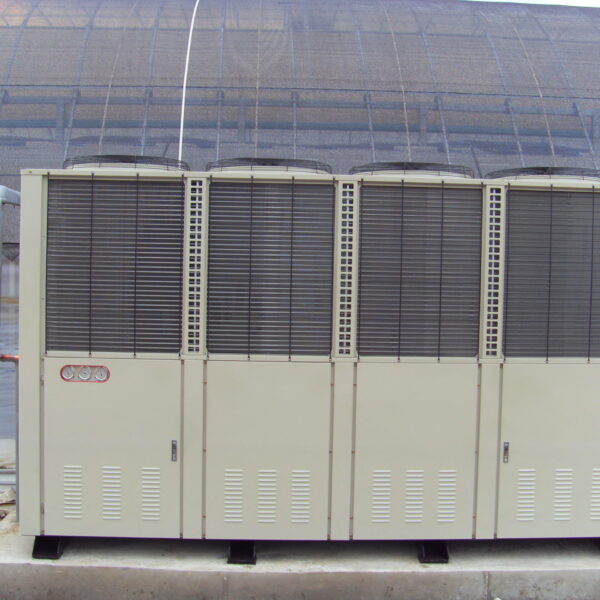
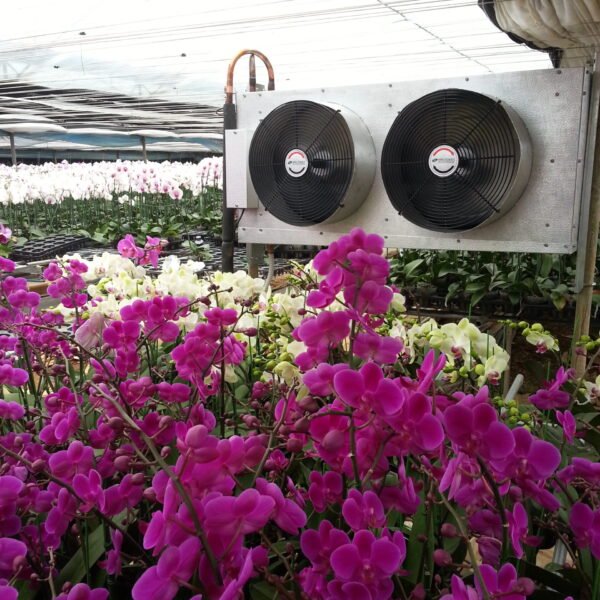
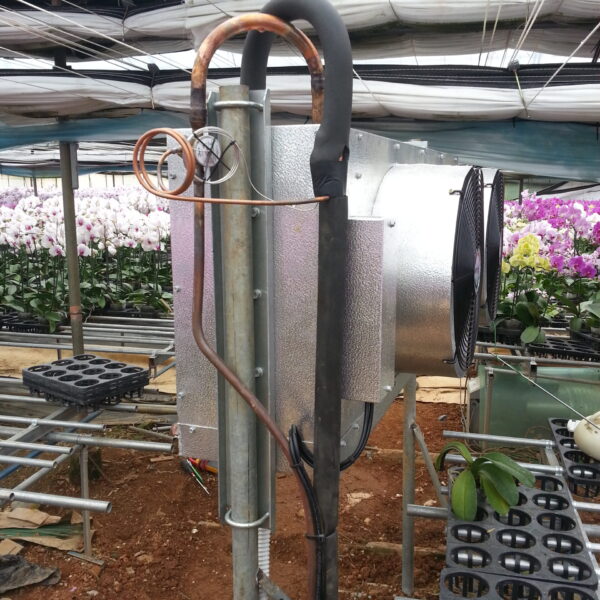
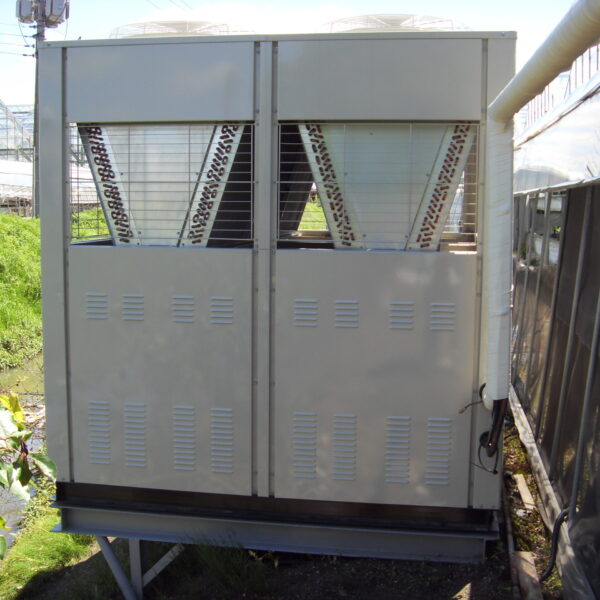
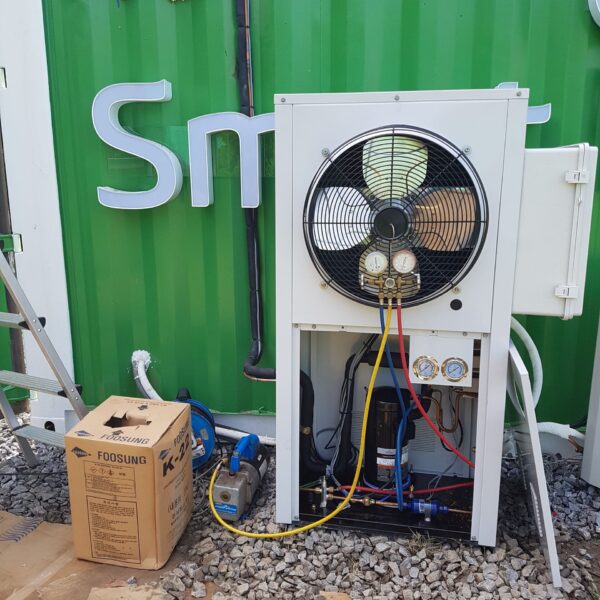
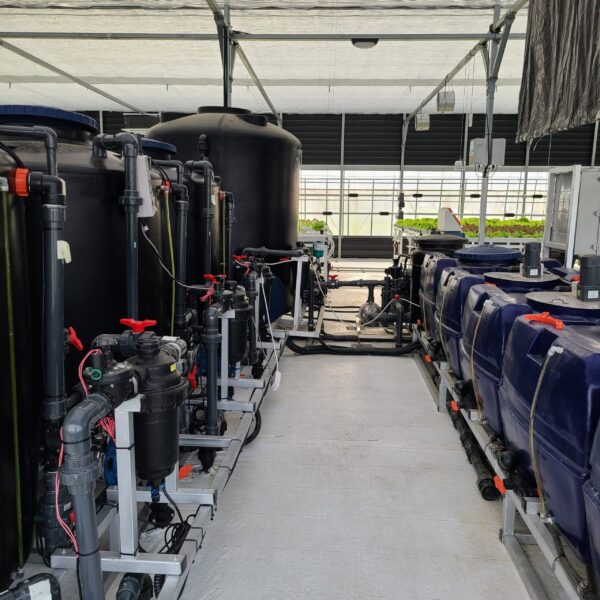
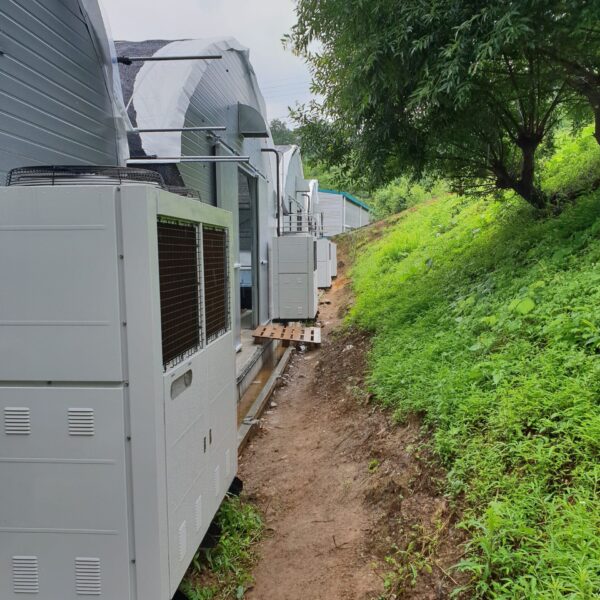
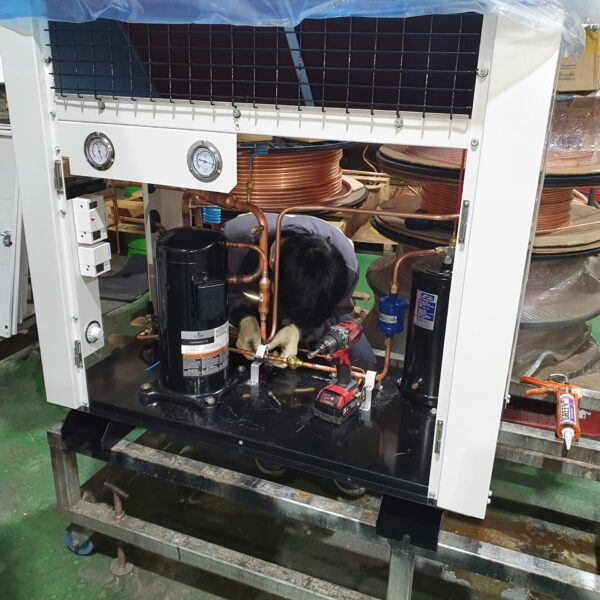
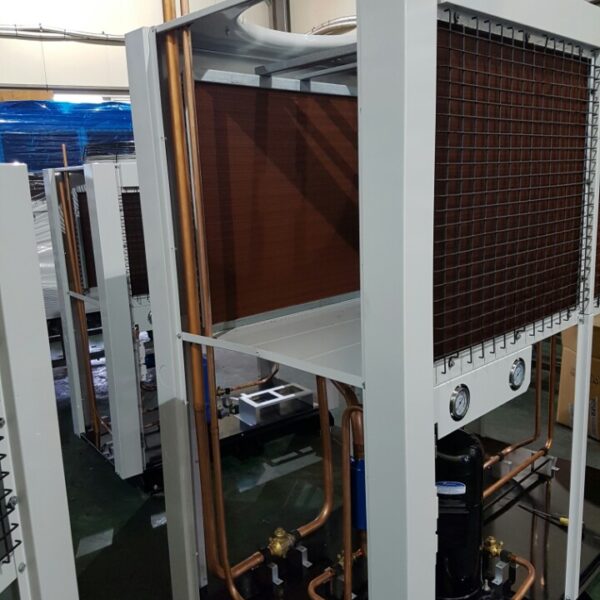
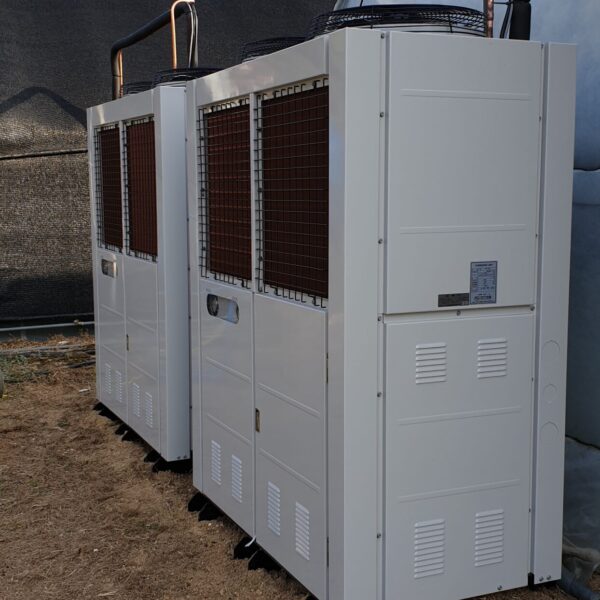
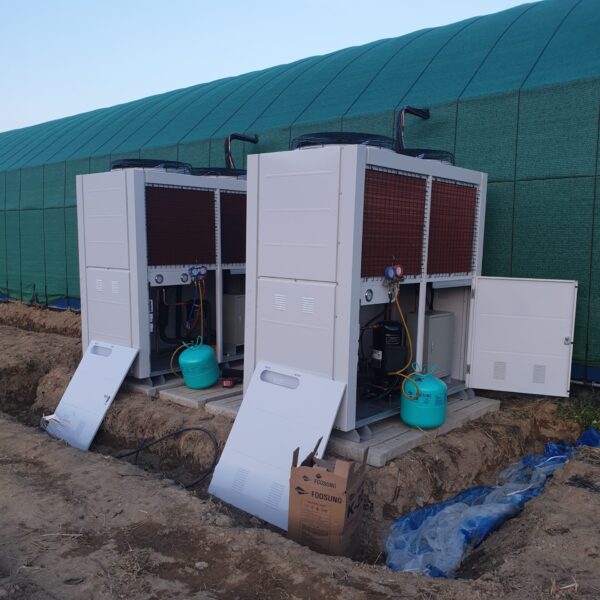
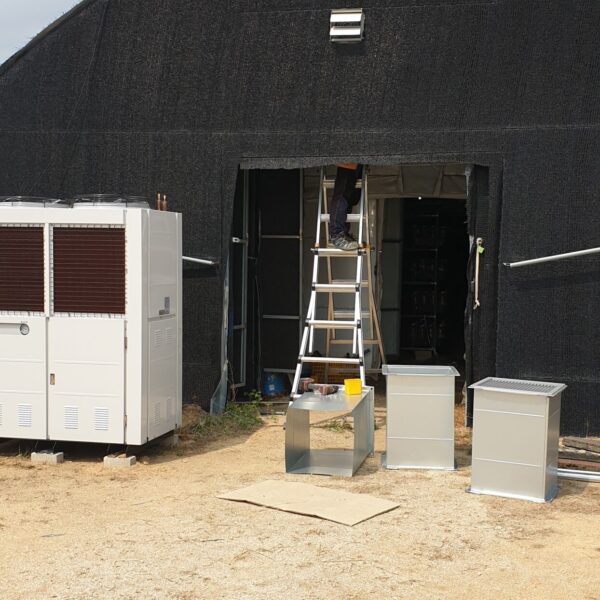
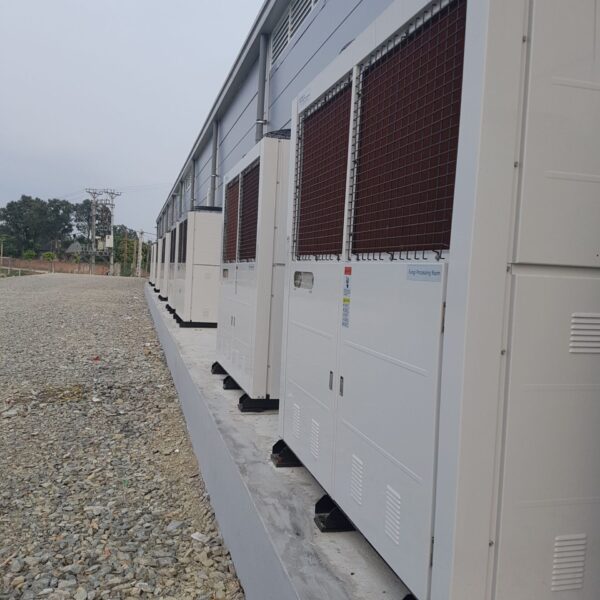
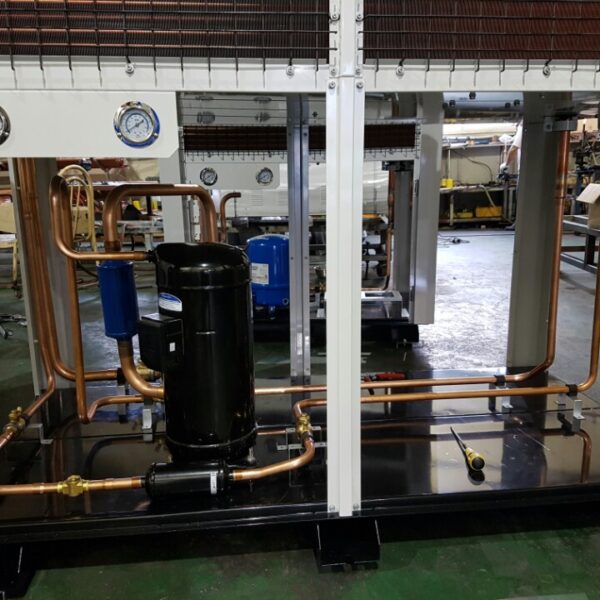
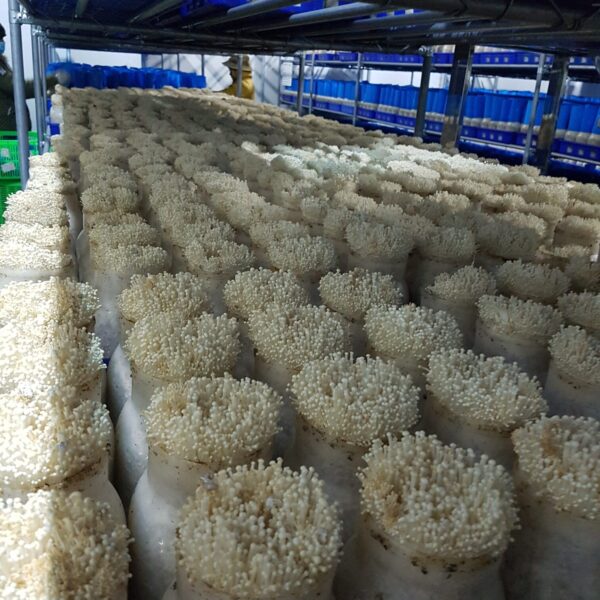
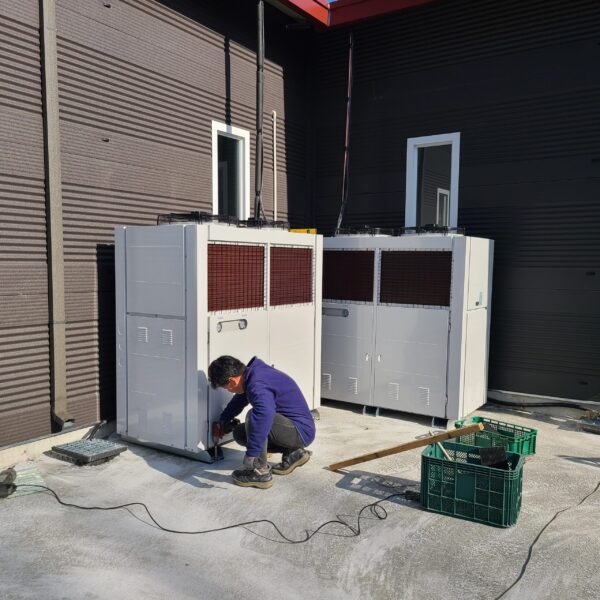
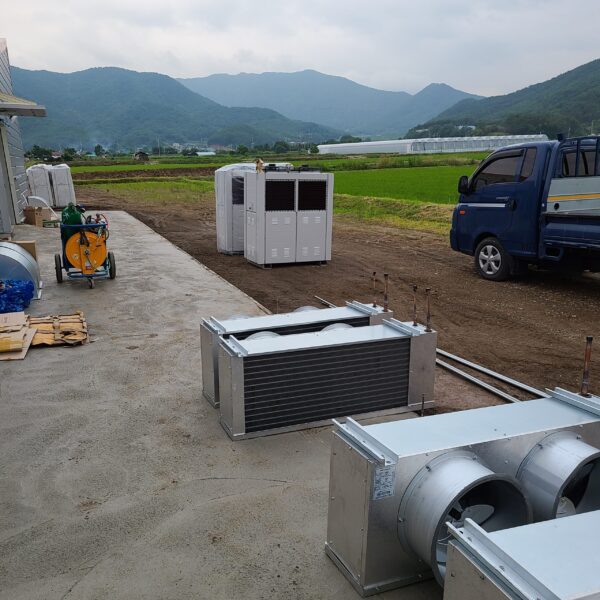
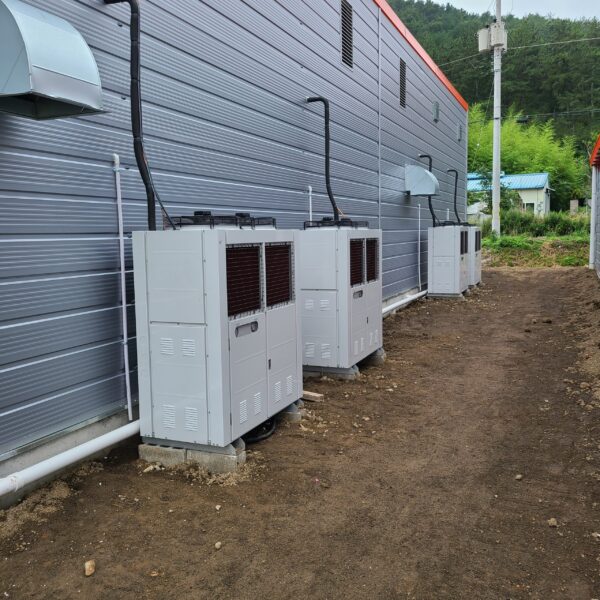
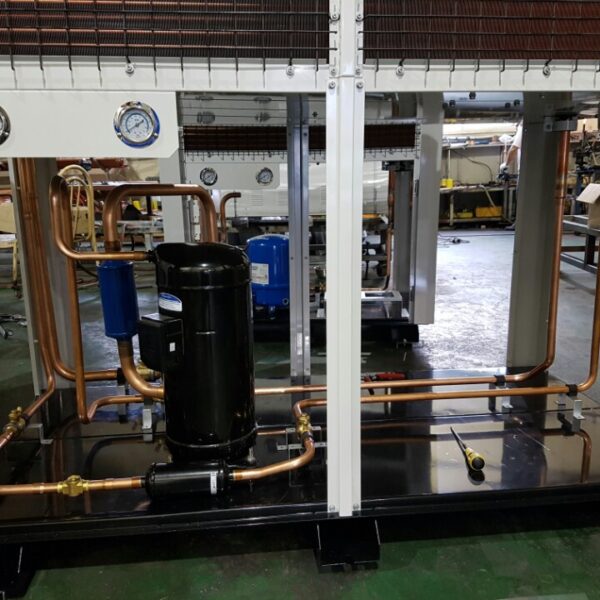
Lastly, in the case where sufficient cooling is not possible with evaporative cooling, continuous cooling is required, and in the case of cultivation of crops that are concerned about damage due to high humidity, there is a method using a refrigeration facility. There are various methods for cooling using such a refrigerator, and they are classified according to the type of heat source as a cooling/heating heat pump method using geothermal solar heat, hydrothermal heat, and air heat. Due to the high electricity consumption and high installation cost and occupying a large amount of space, there are many difficulties in installing the equipment.
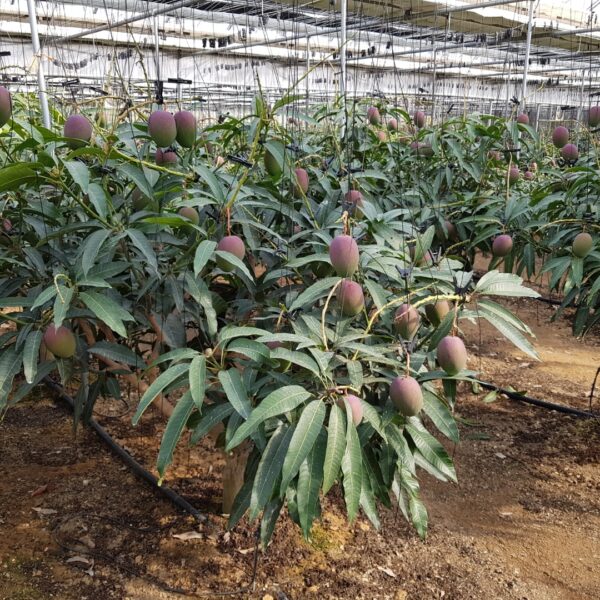
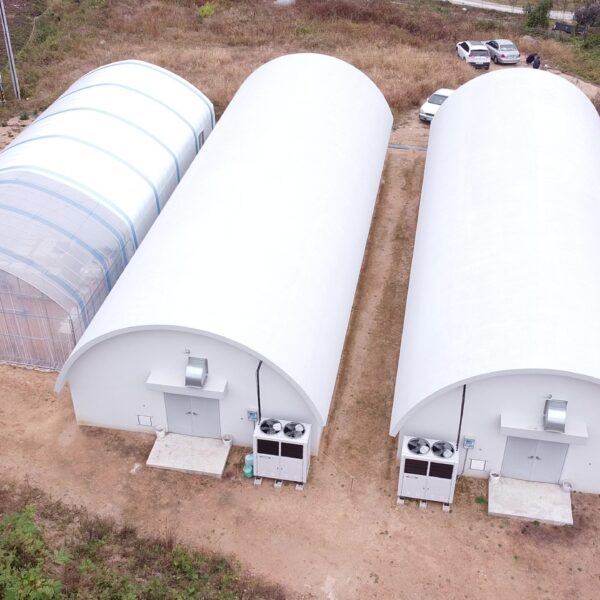
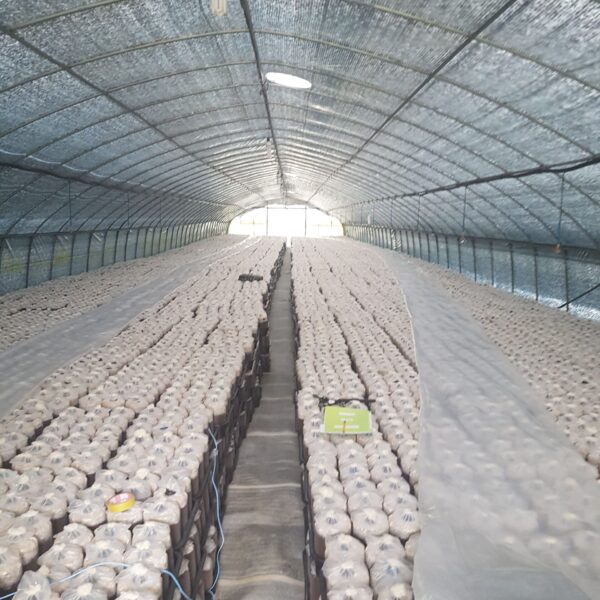
On a bright and sunny summer day, the amount of sunlight penetrating through the greenhouse is 8,000,000 kcal, which is a huge amount of 9,300 kw in a 14*25 m plastic greenhouse, that is, a 7 m 2 inter-dong 100 pyeong scale 1-2w standard greenhouse.
However, about 80% of such solar heat is blocked by a plastic shading film of structures such as steel, and 70% of the heat introduced into the greenhouse is used for transpiration and evaporation of plants. If the greenhouse is empty, that is, the internal temperature will rise by more than 65℃ and the cooling load will also increase that much. should install
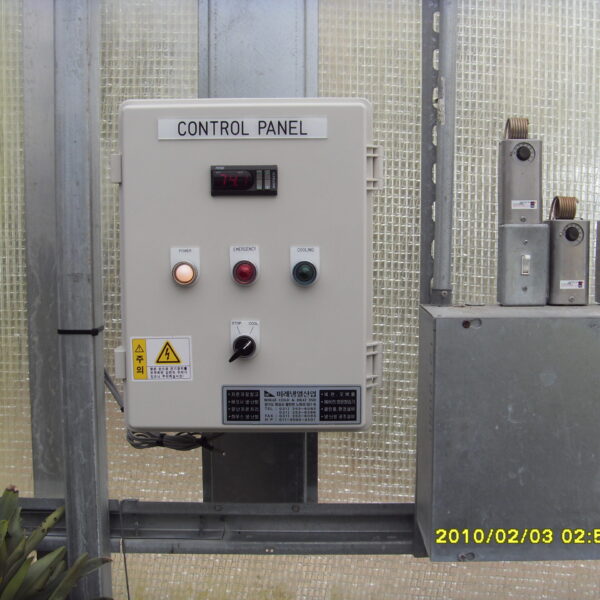
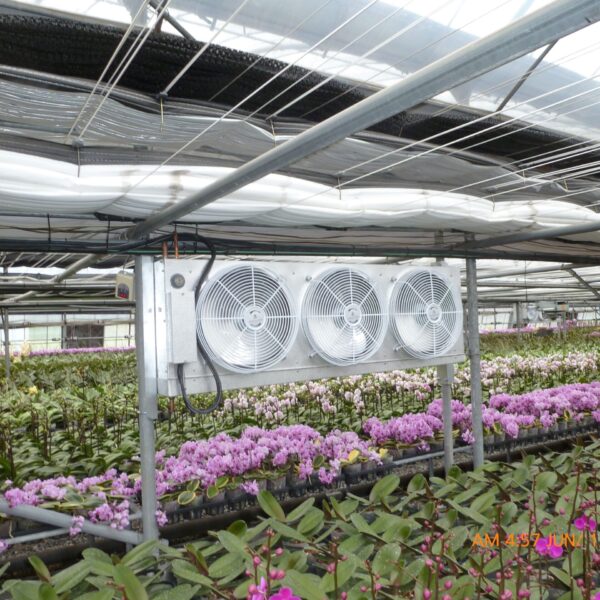
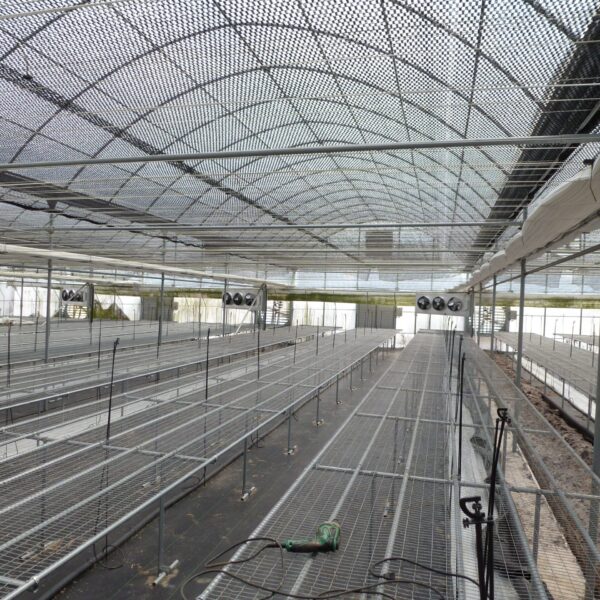
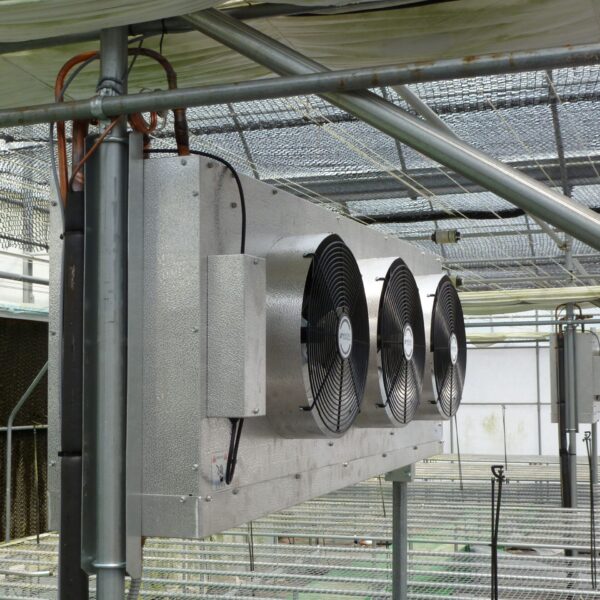
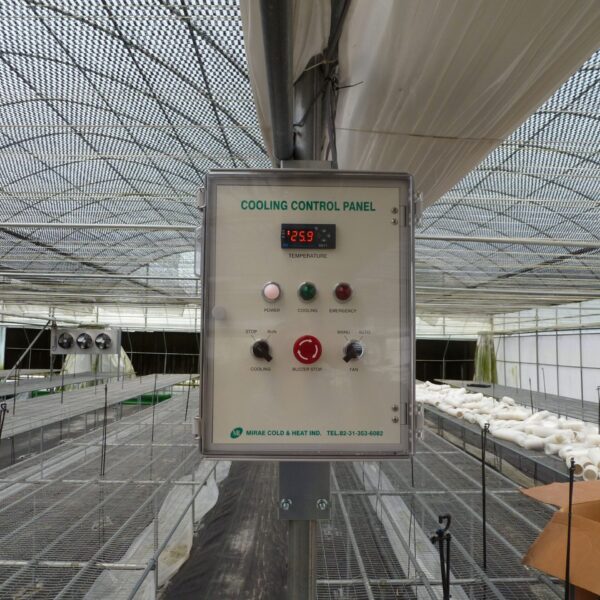
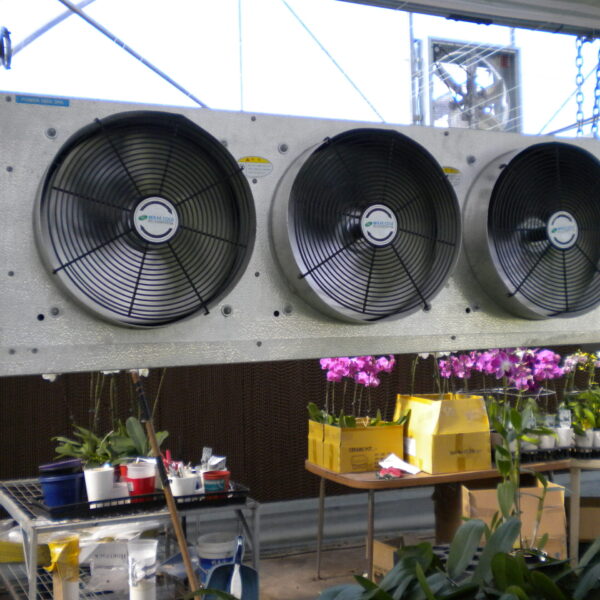
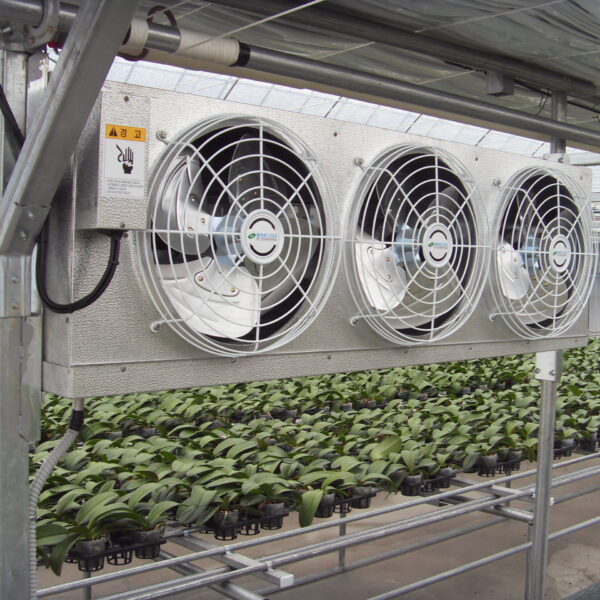
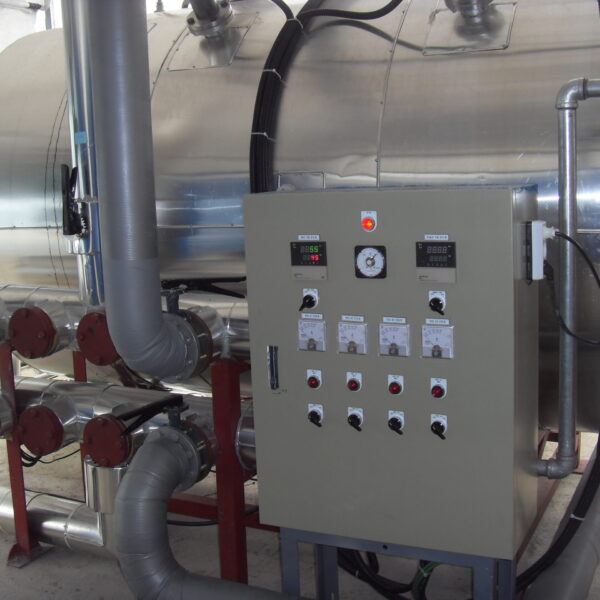
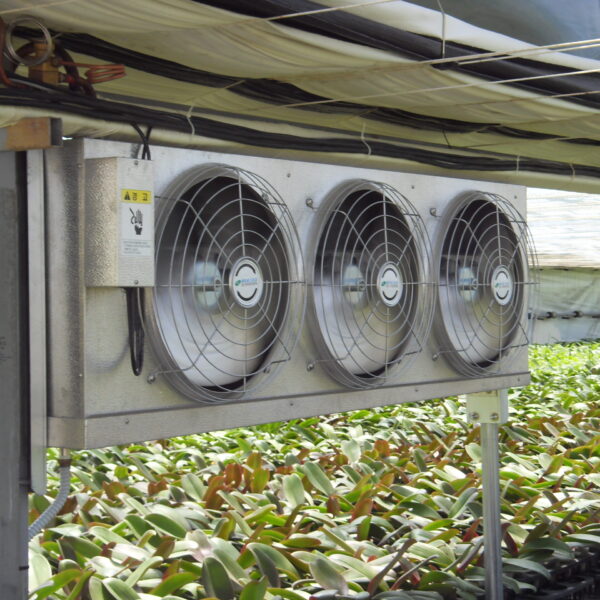
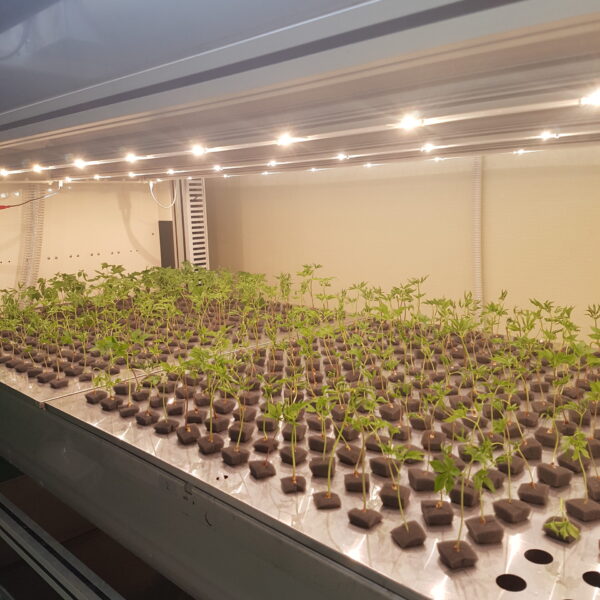
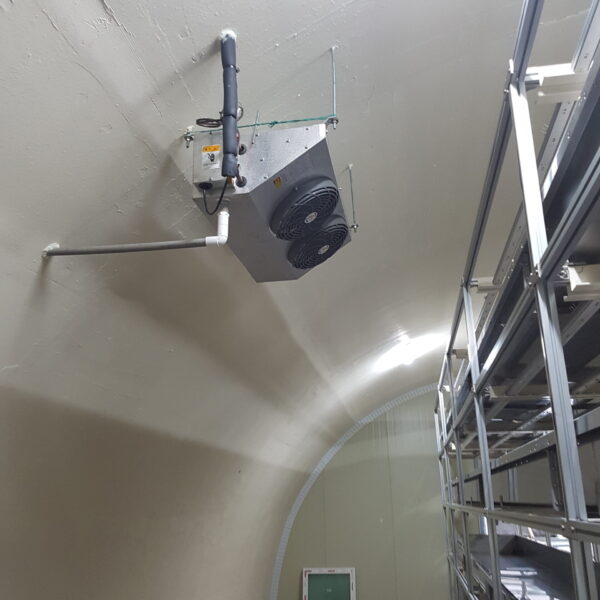
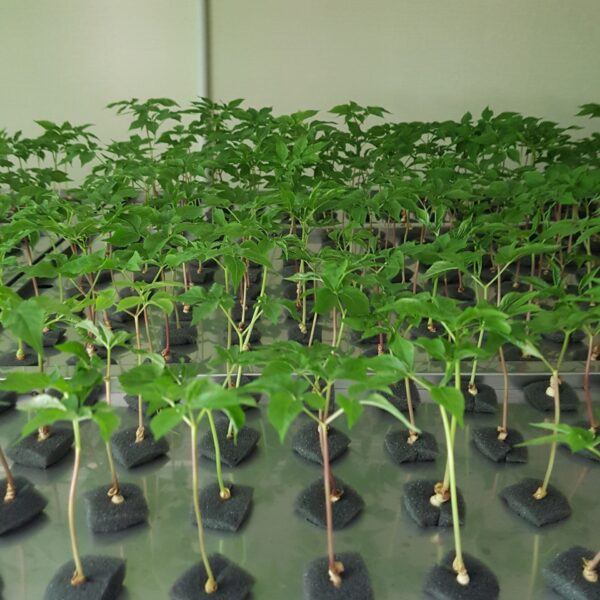
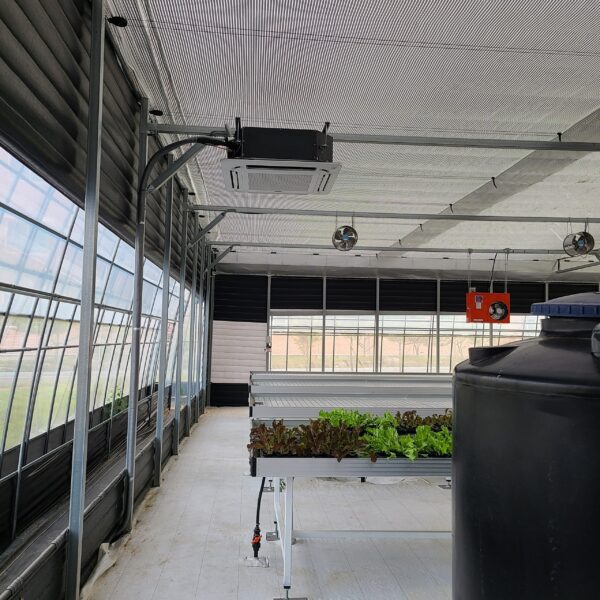
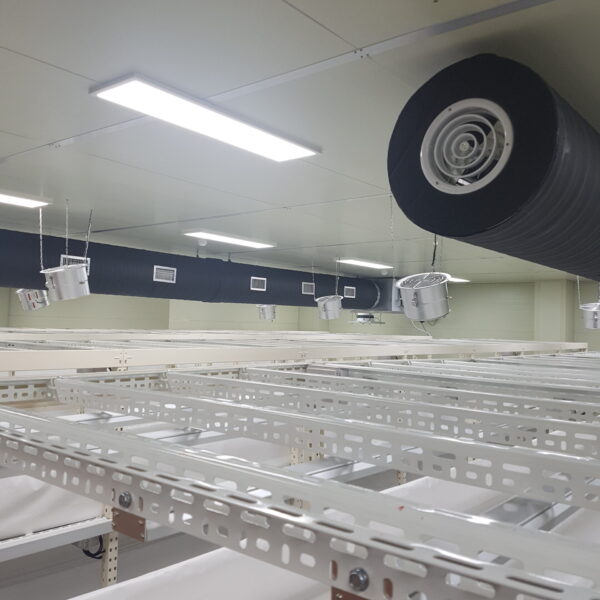
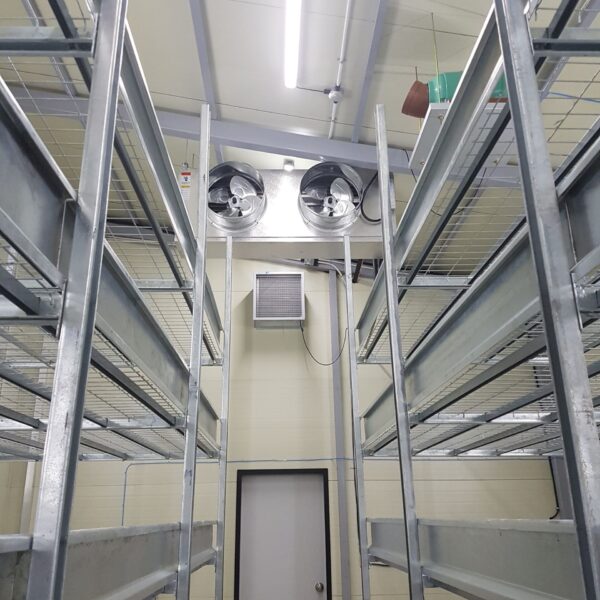
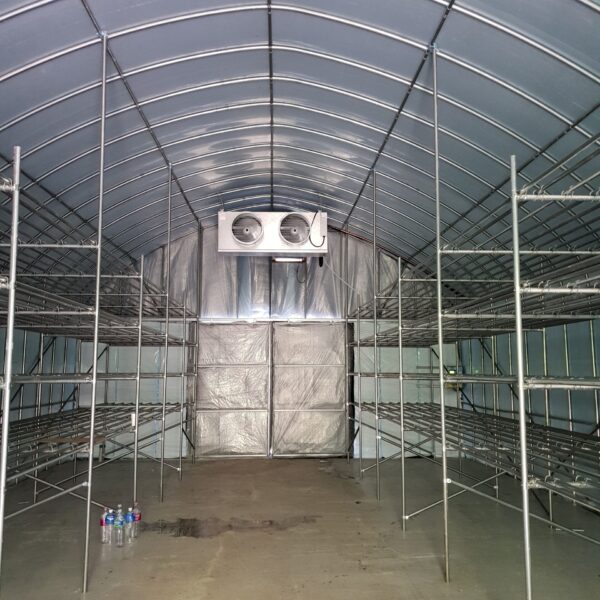
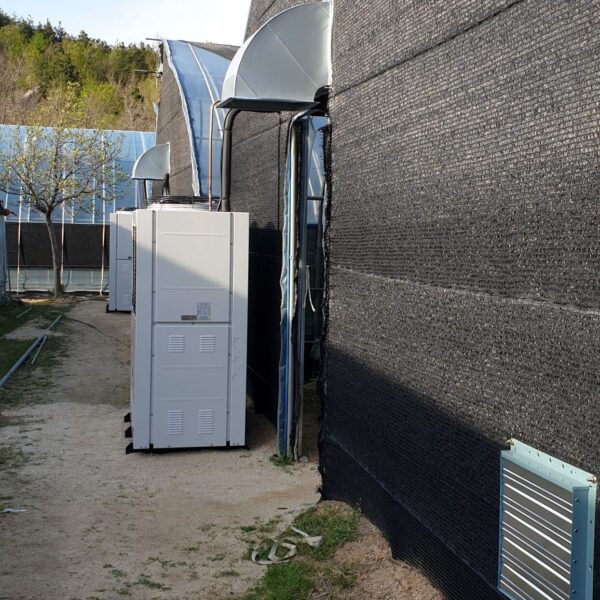
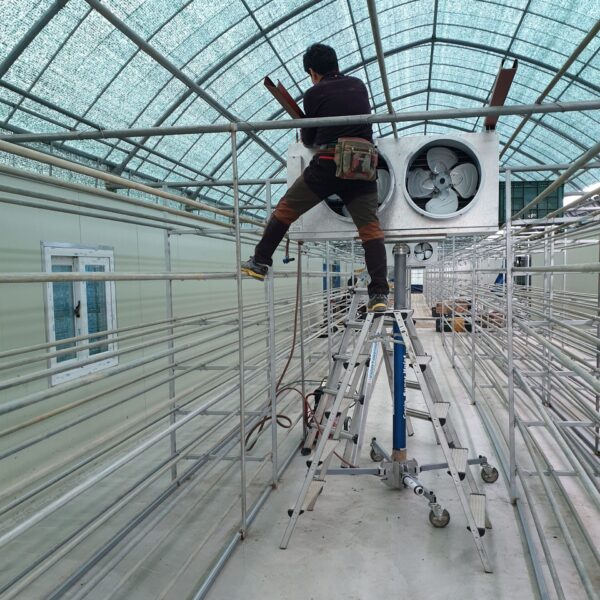
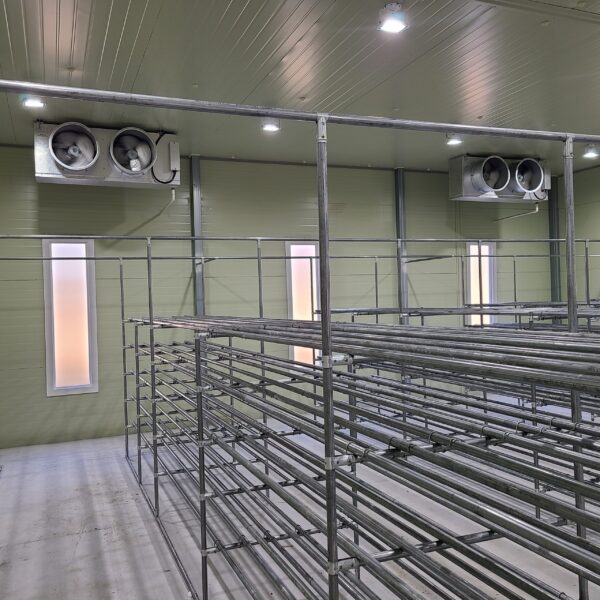
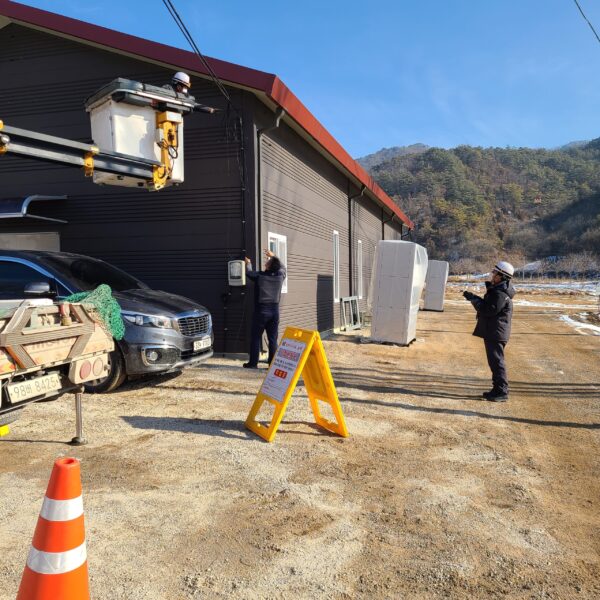
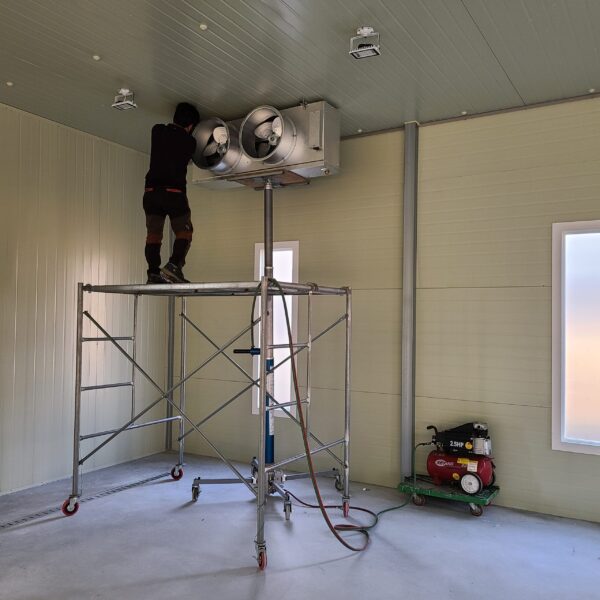
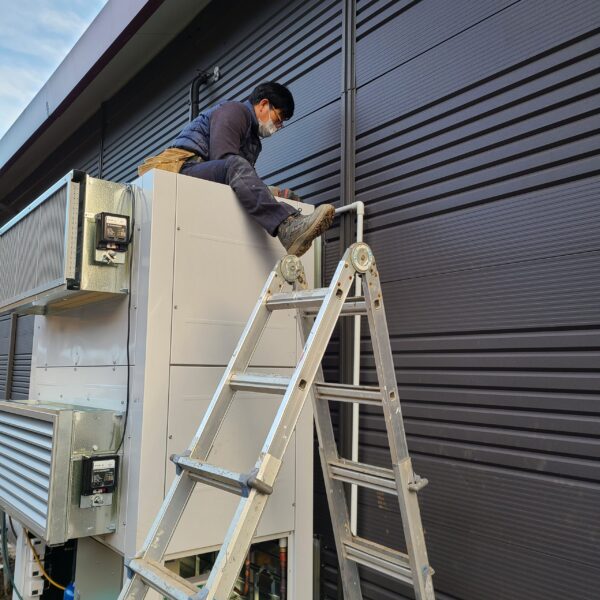
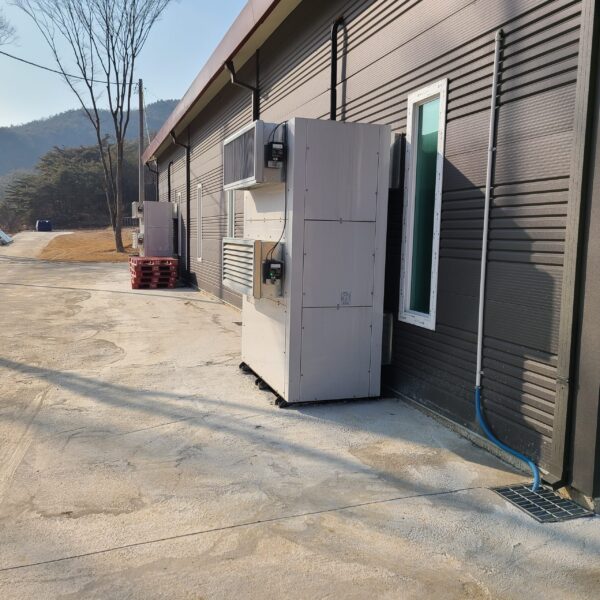
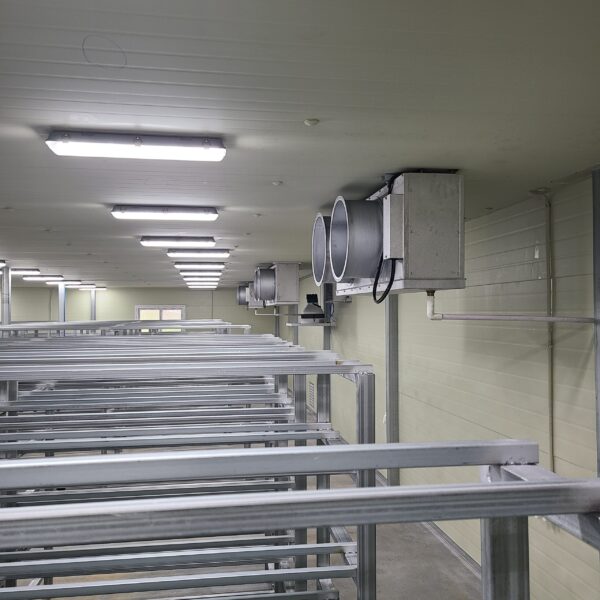
At this time, in order to uniformly remove the cooling load of the greenhouse, the internal evaporation unit, that is, the structure, capacity, quantity, installation location, etc. of the indoor unit, is a part that requires the consultation of an expert with experience and technology because there are many various variables.