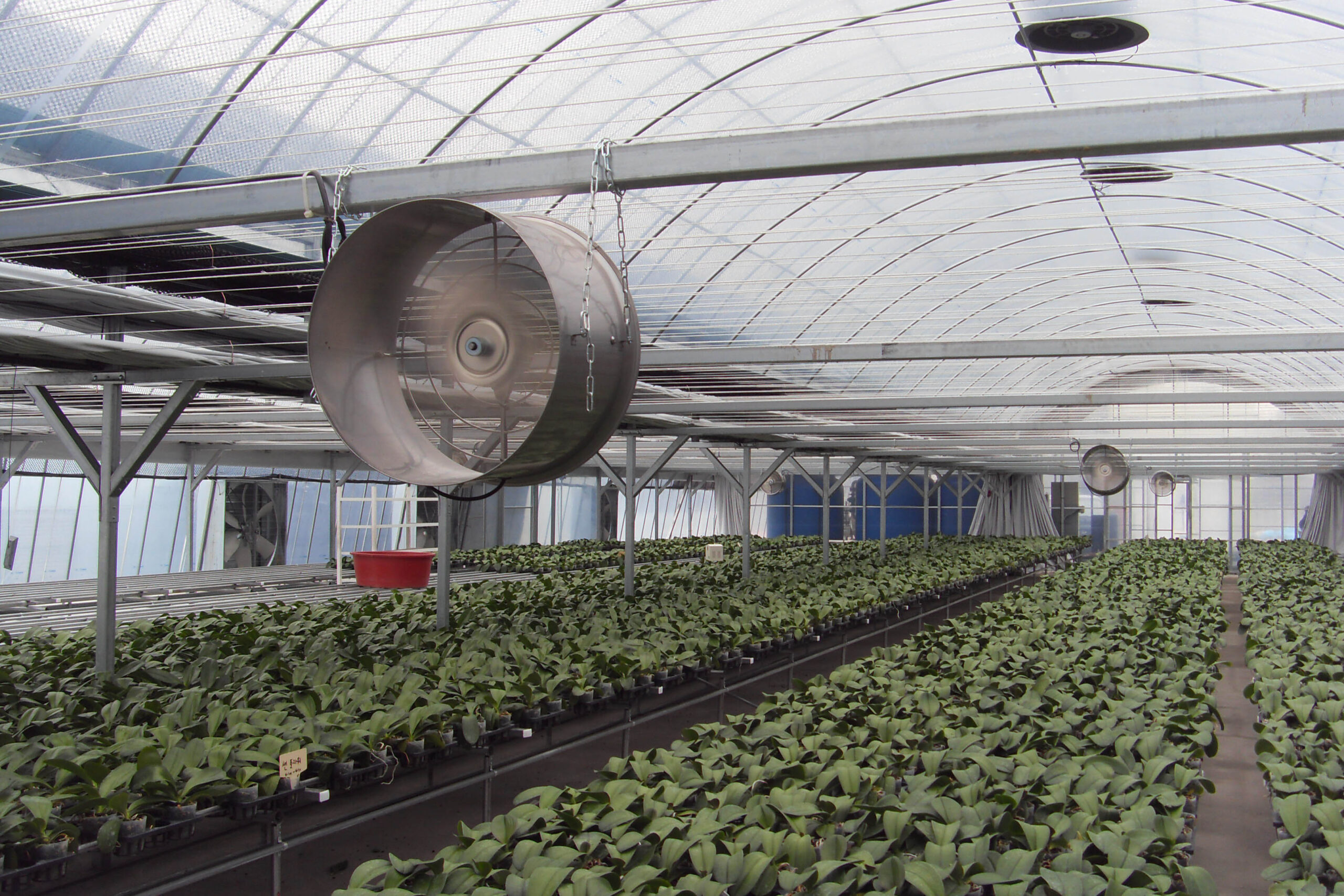
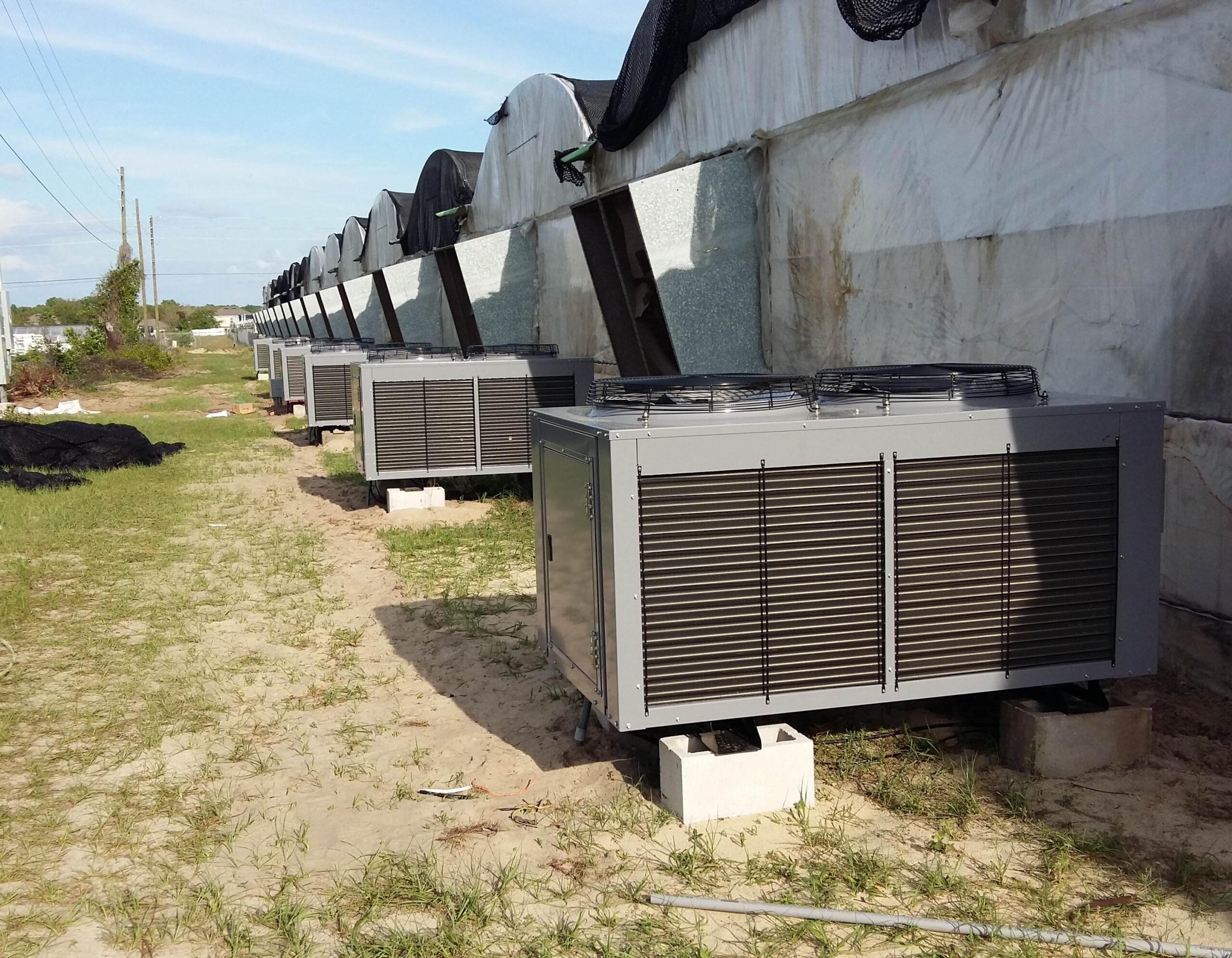
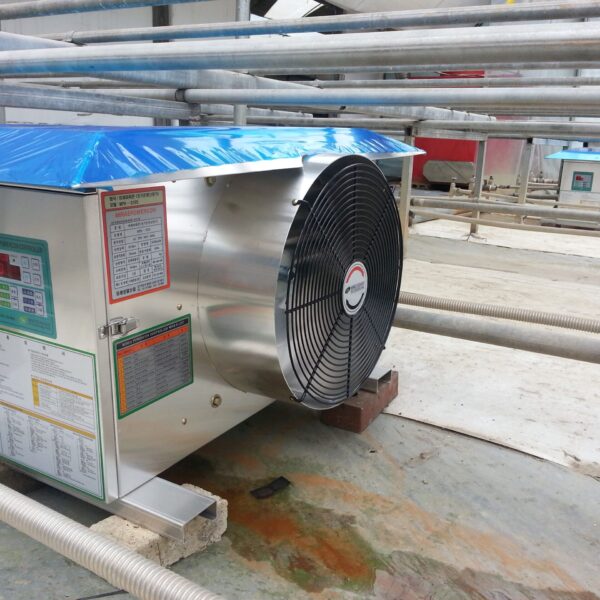
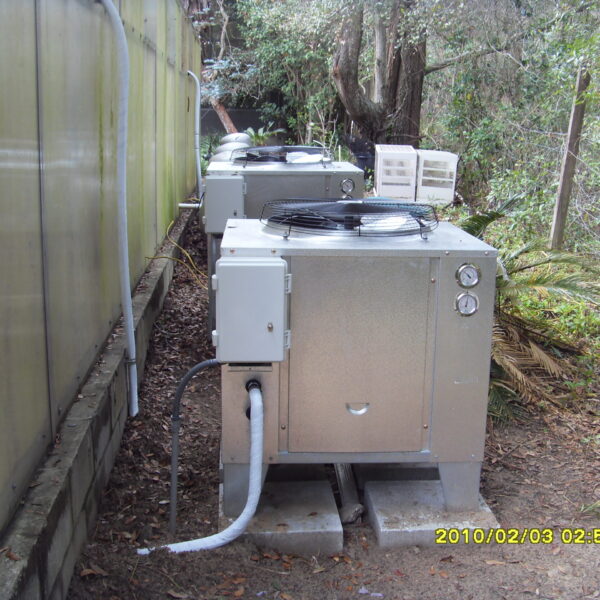
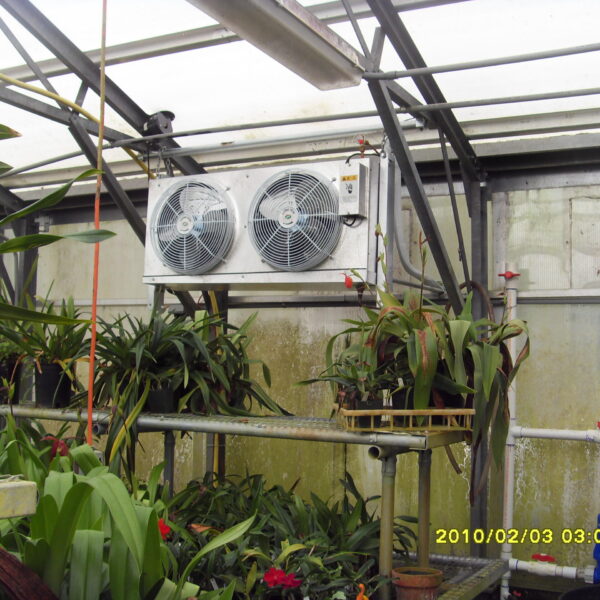
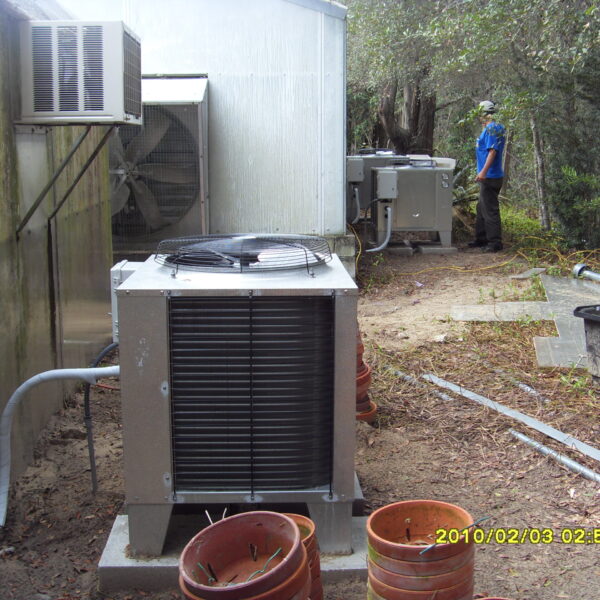
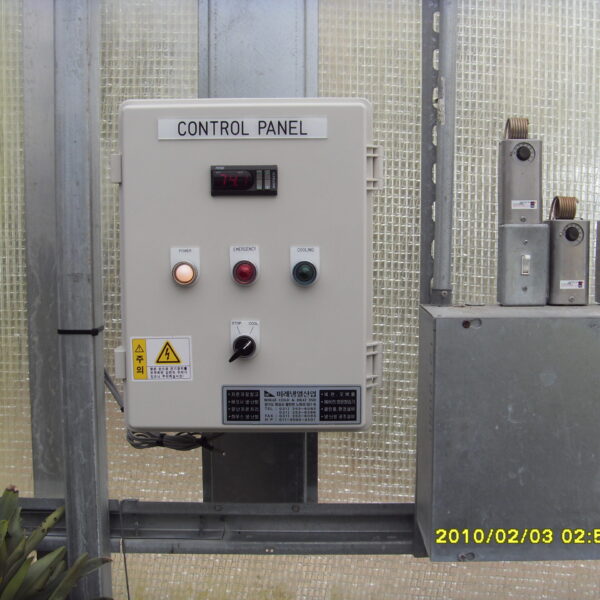
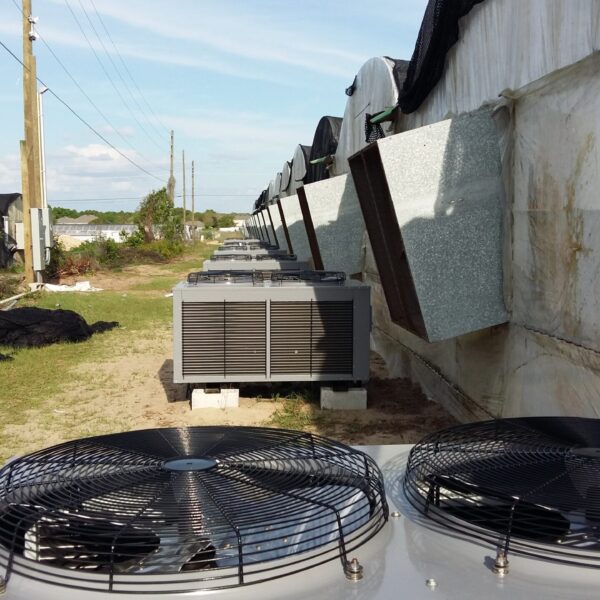
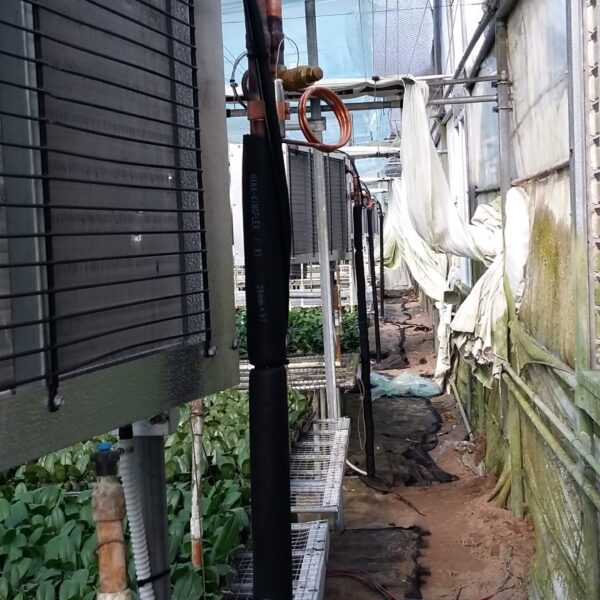
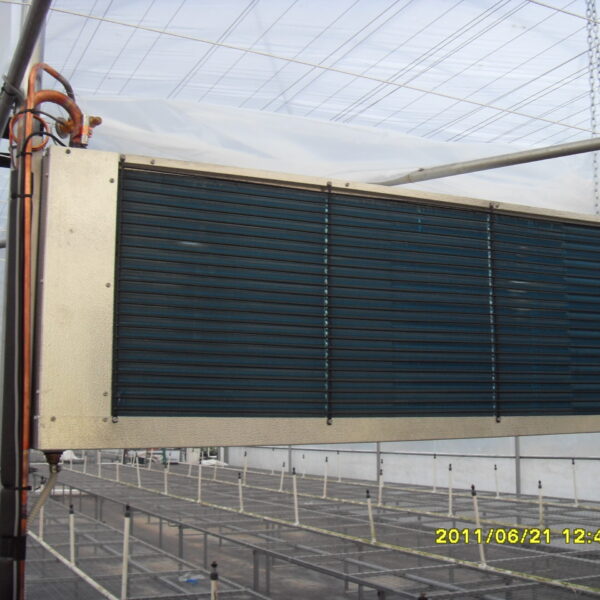
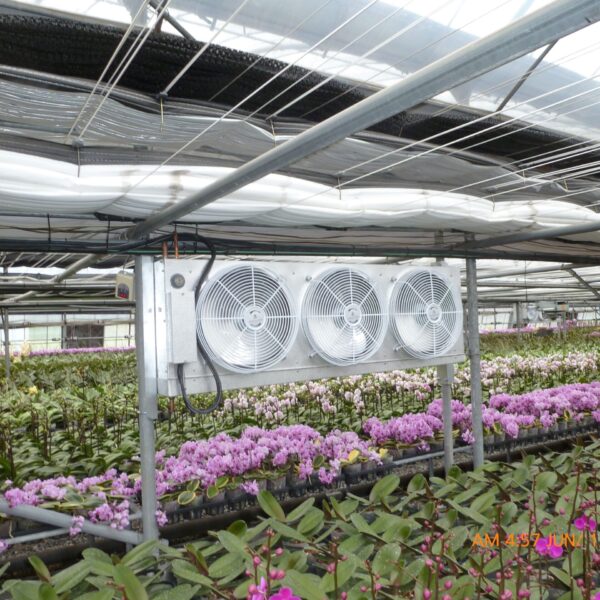
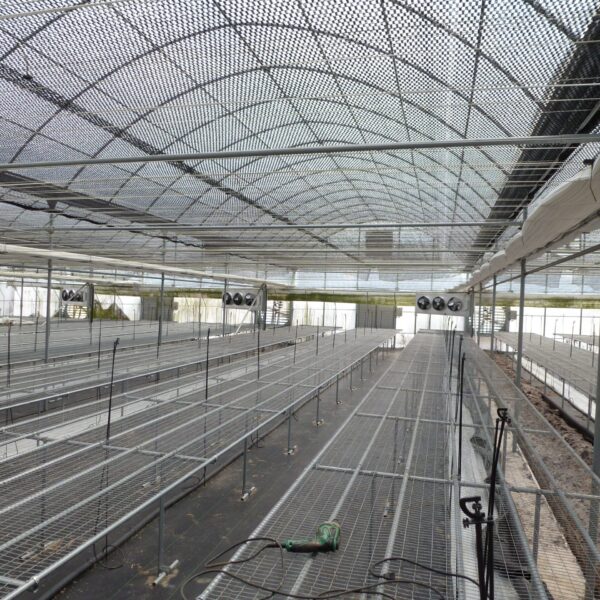
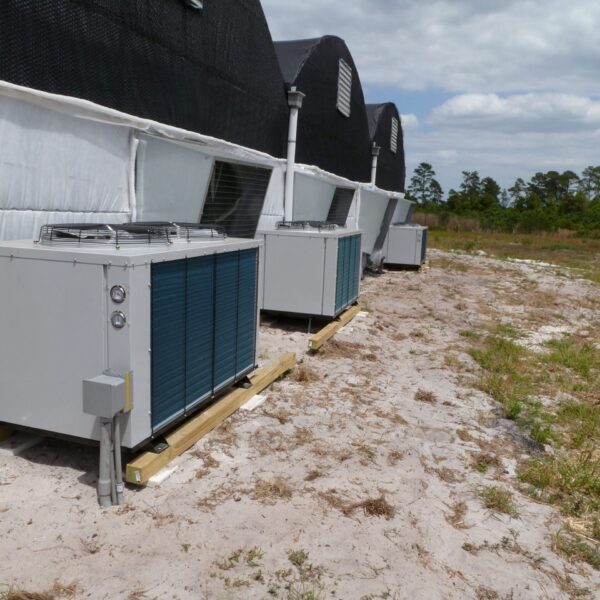
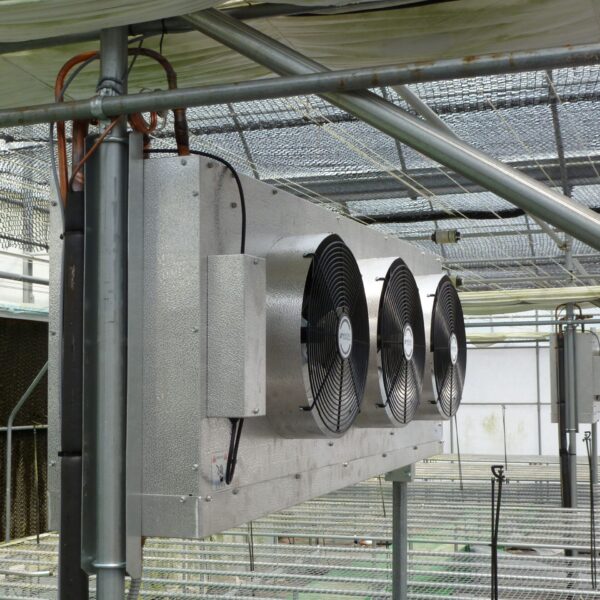
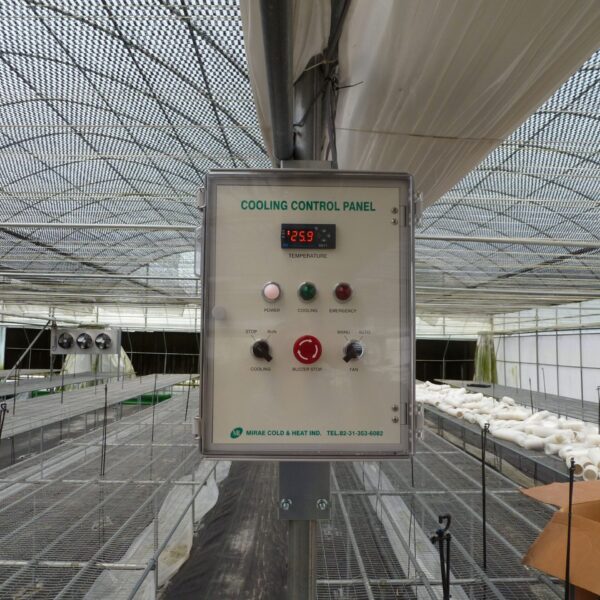
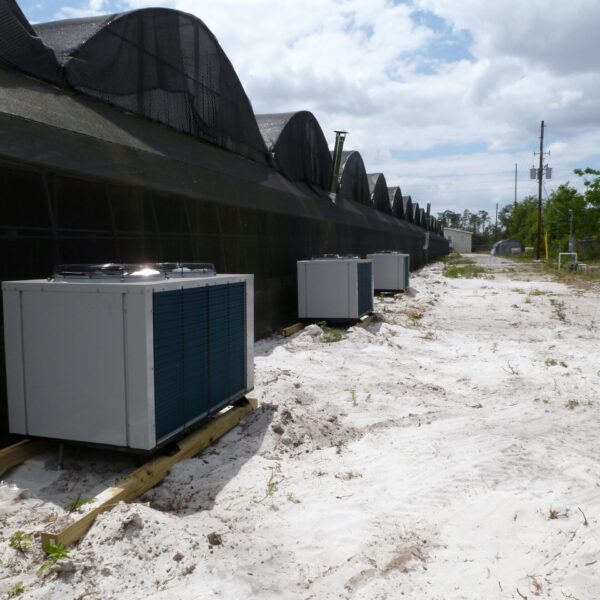
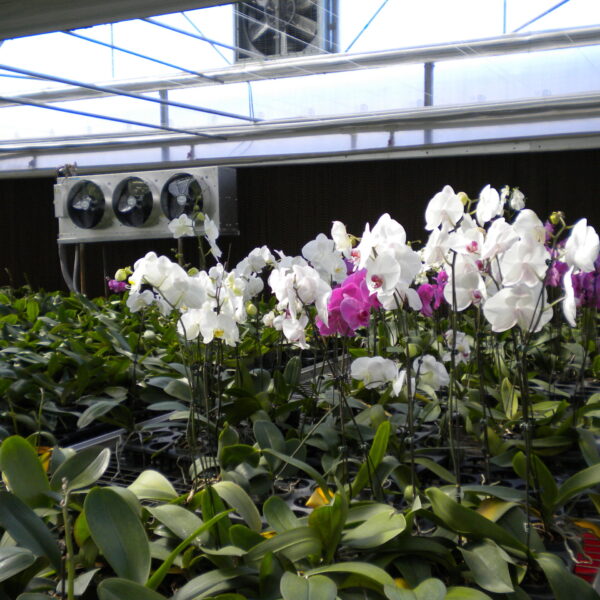
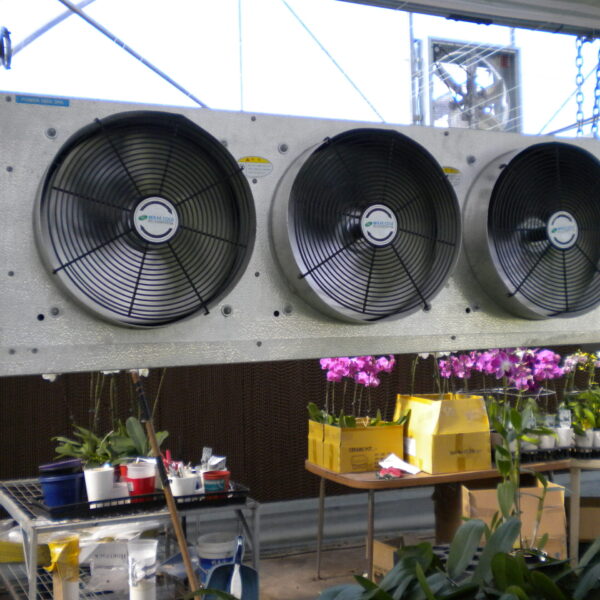
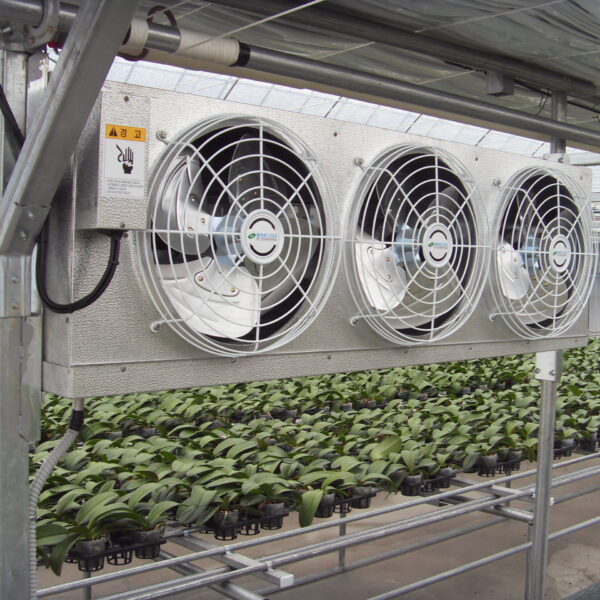
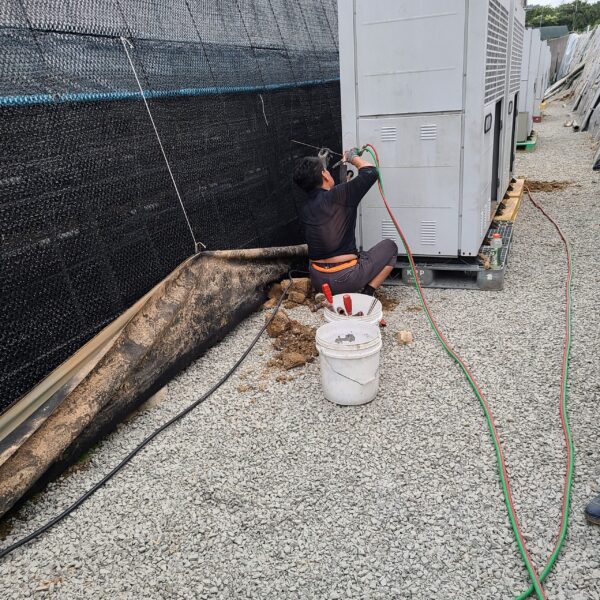
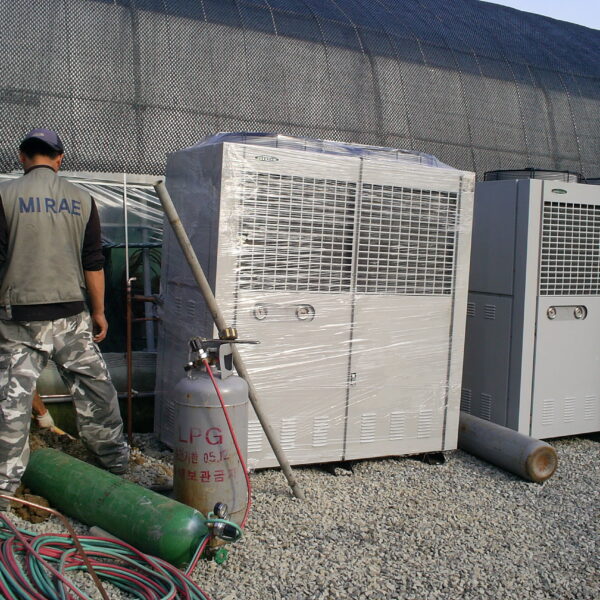
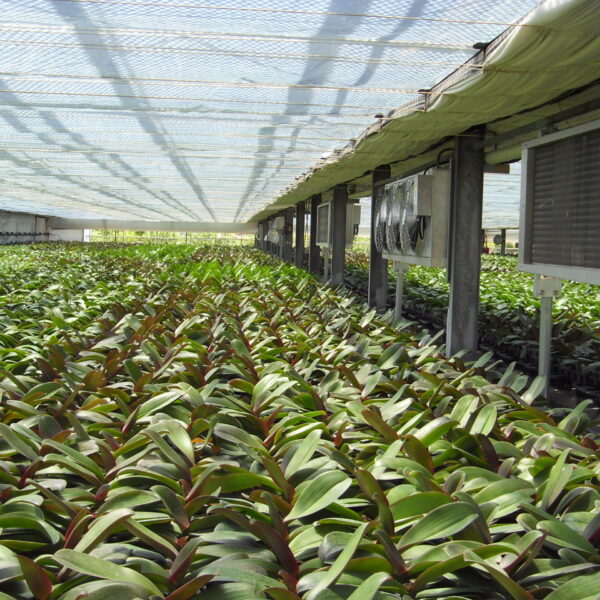
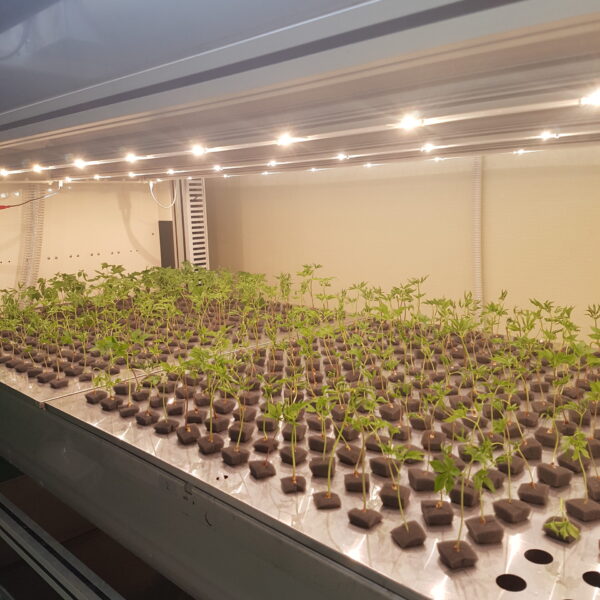
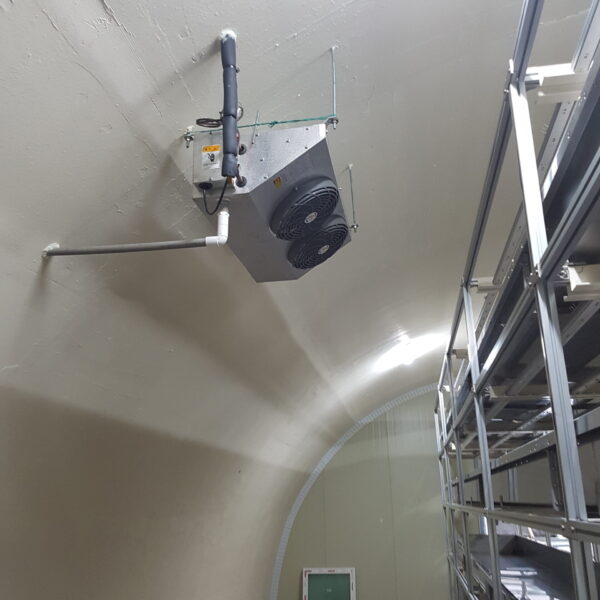
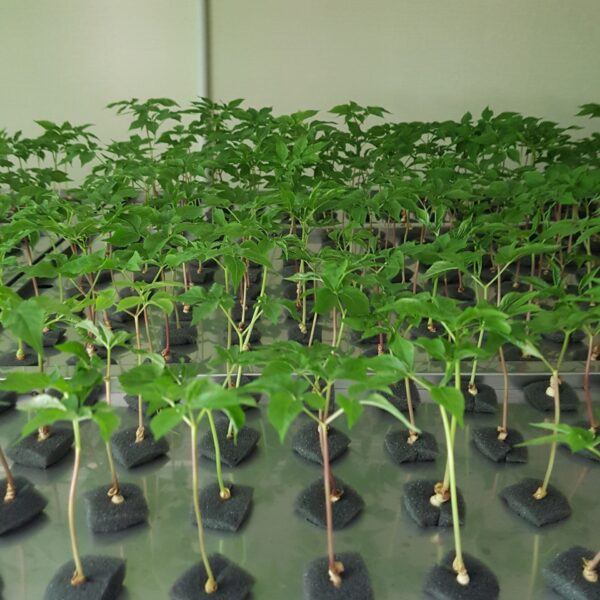
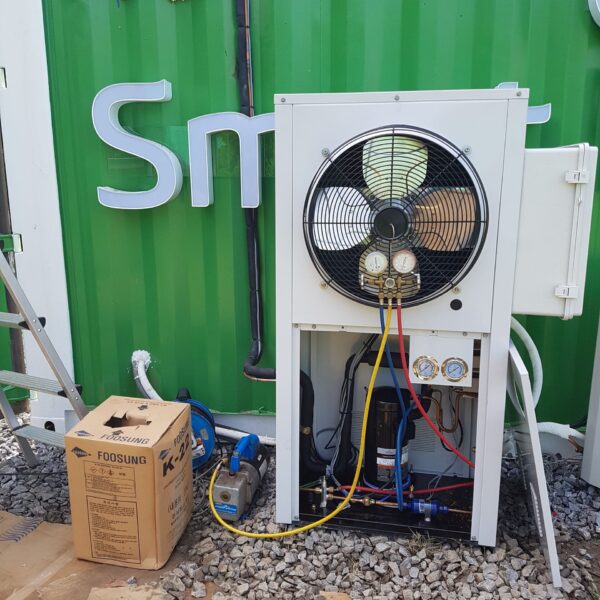
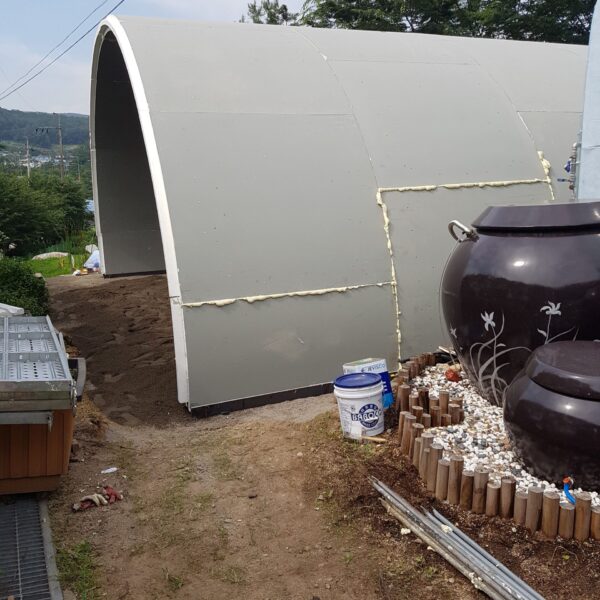
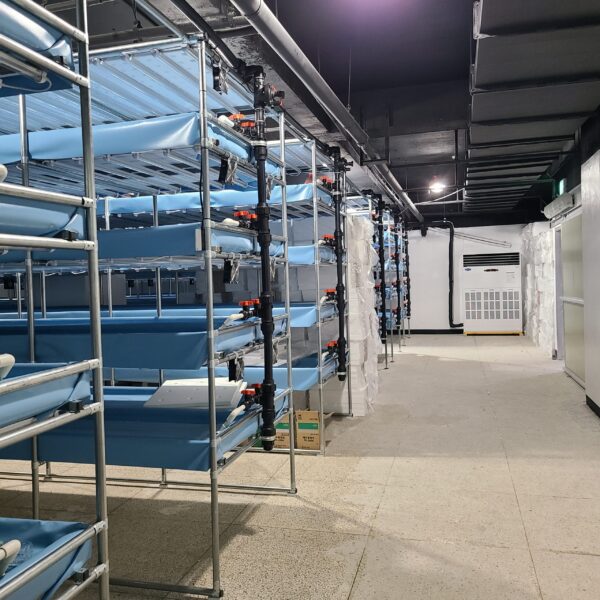
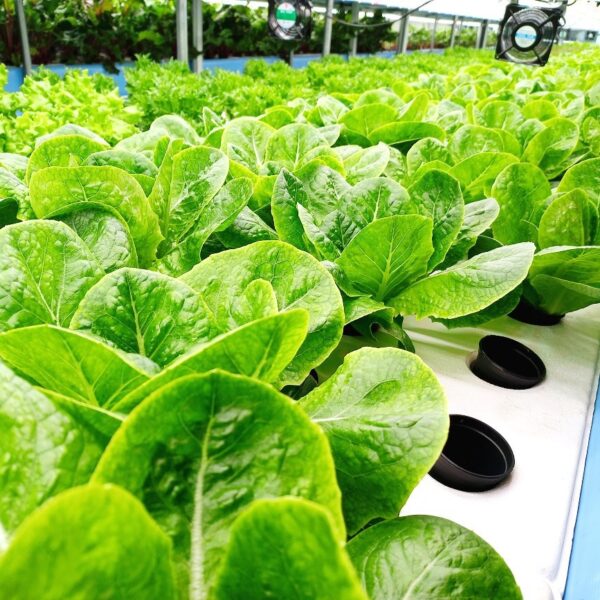
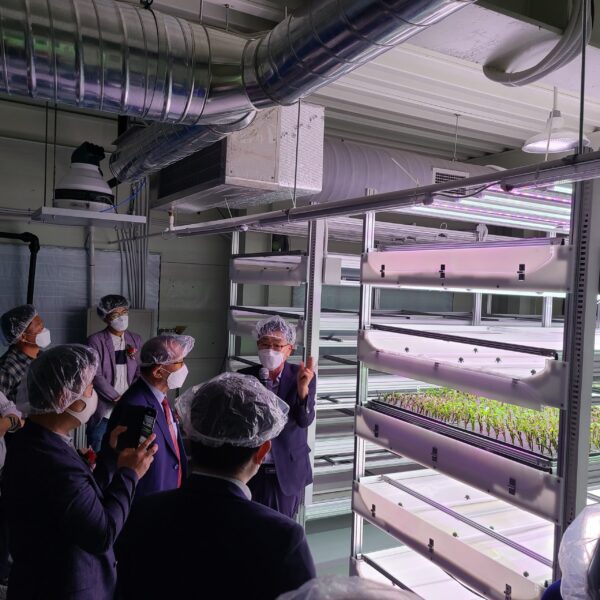
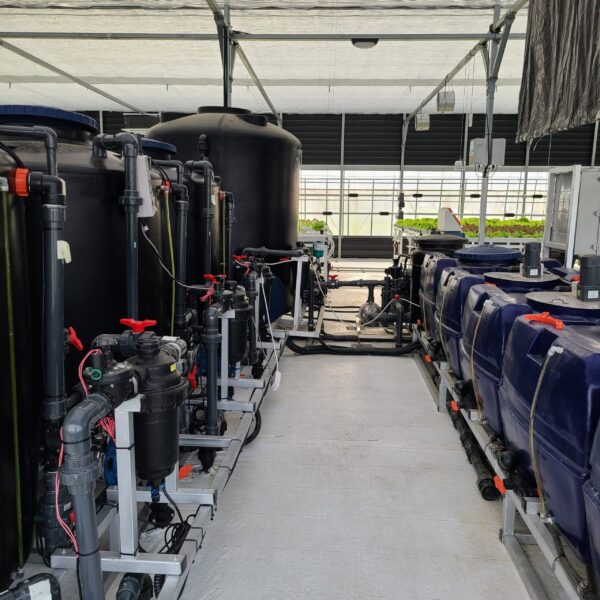
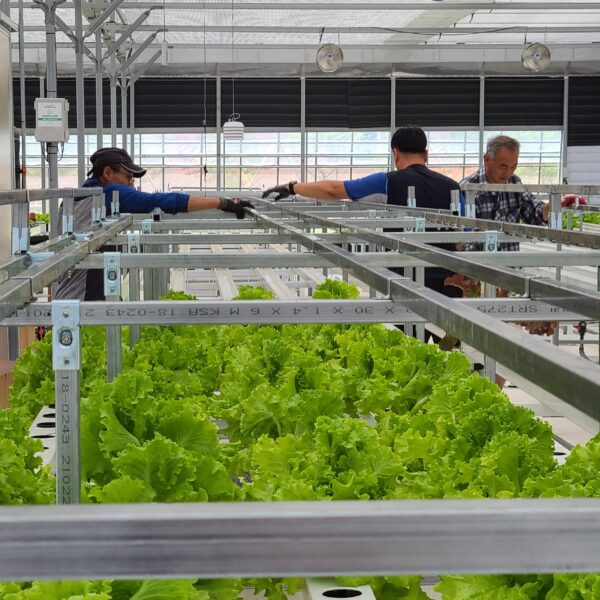
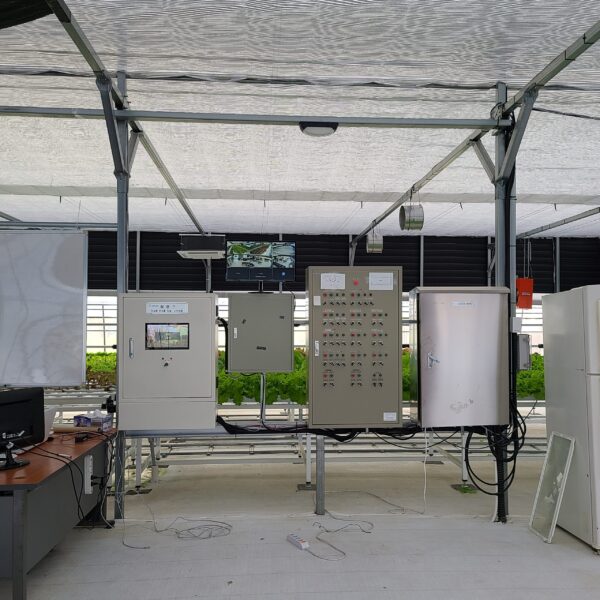
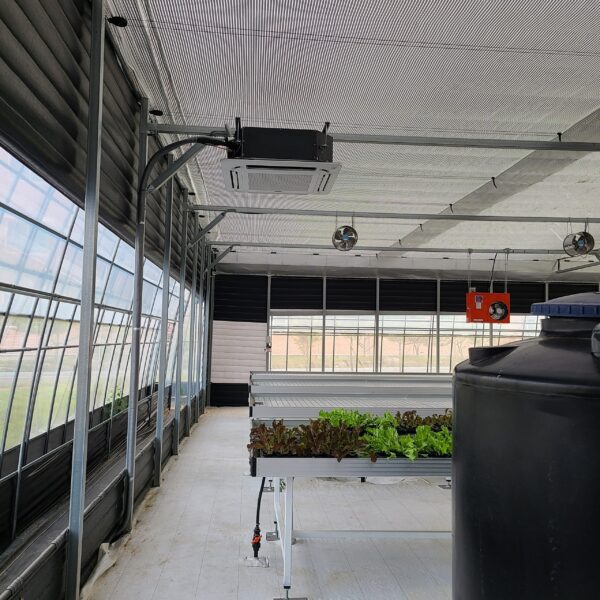
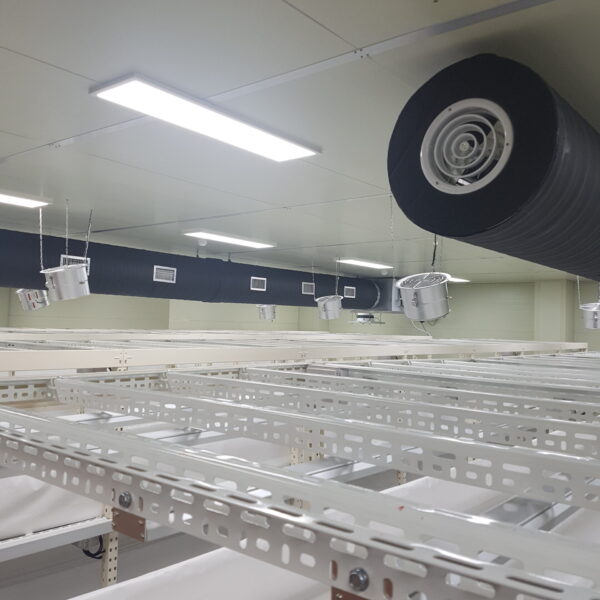
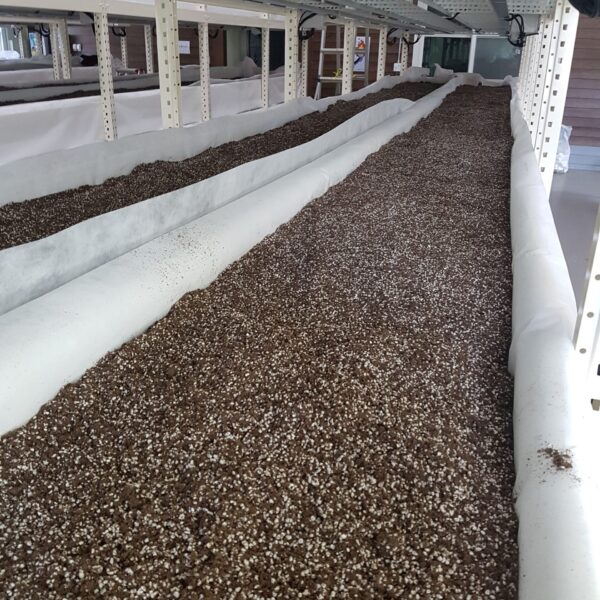
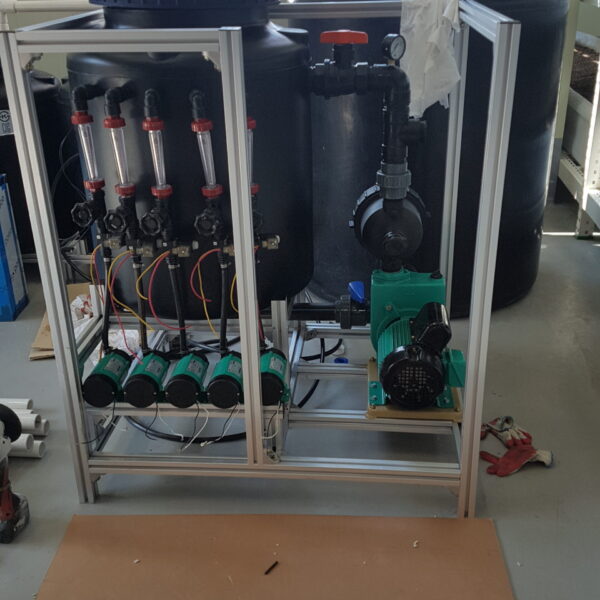
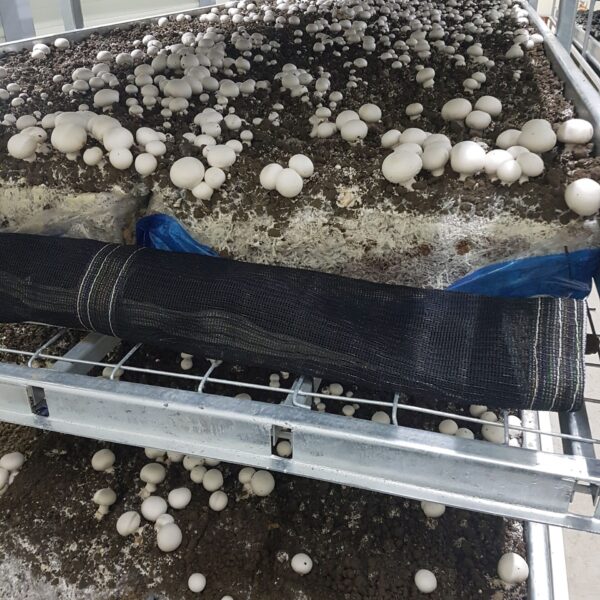
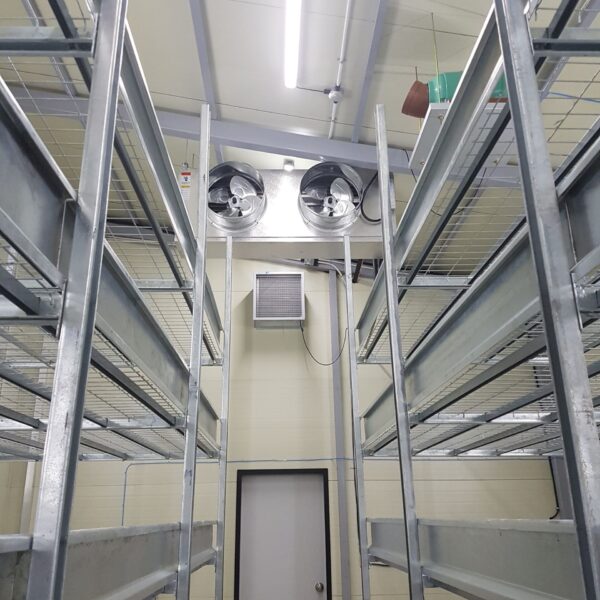
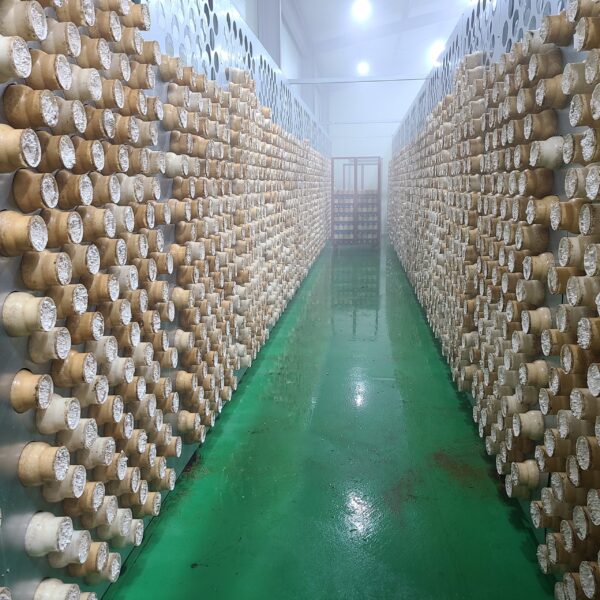
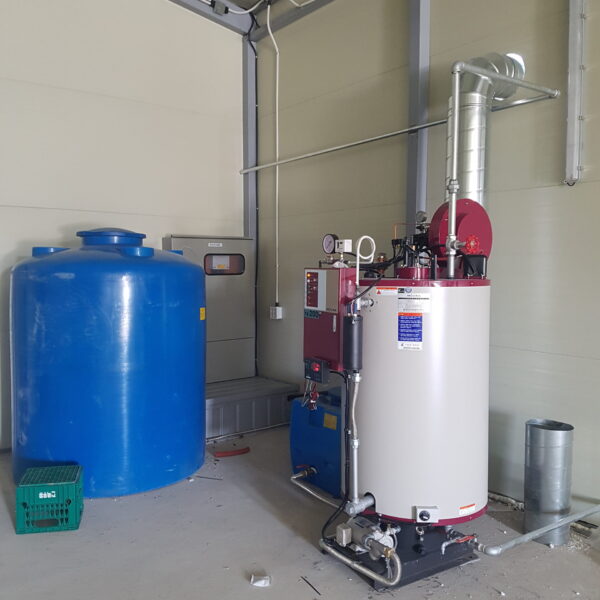
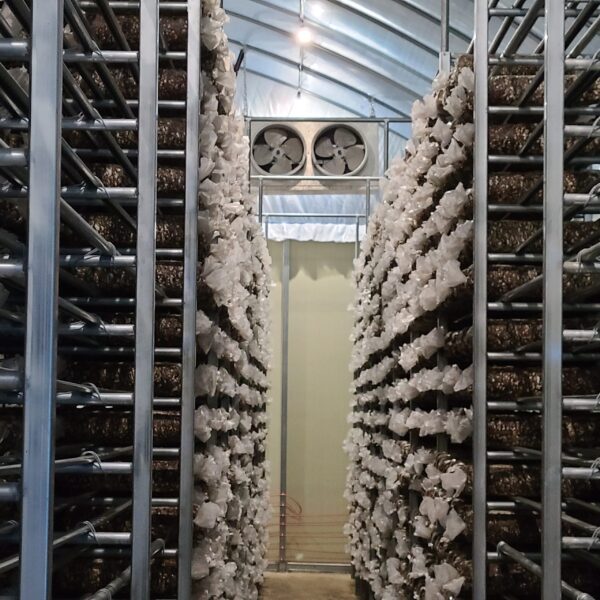
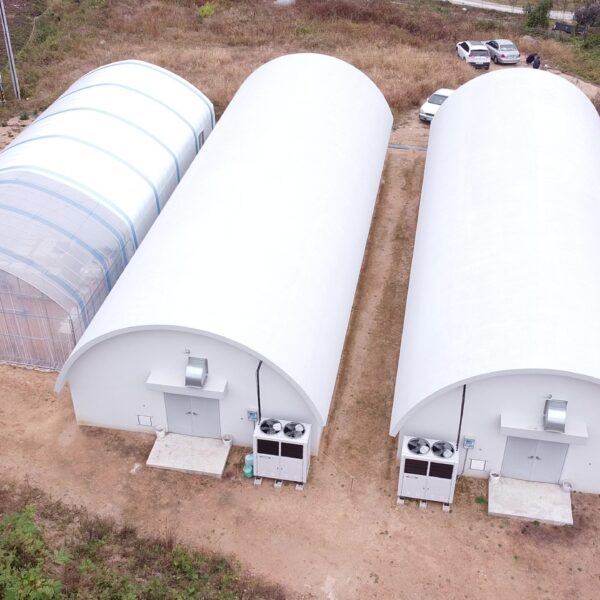
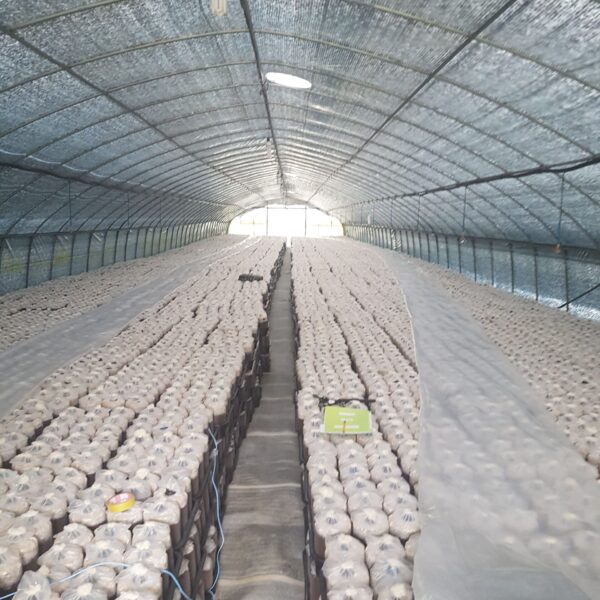
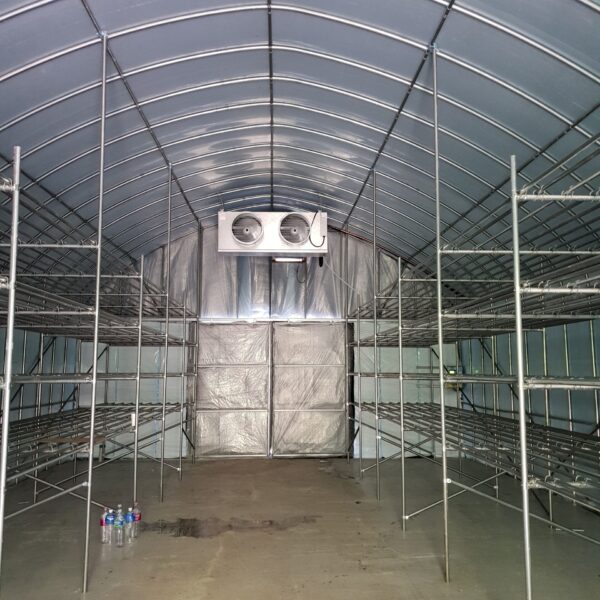
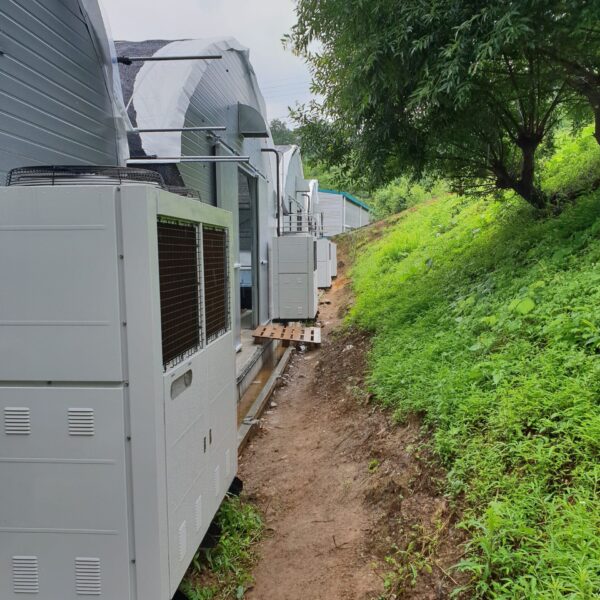
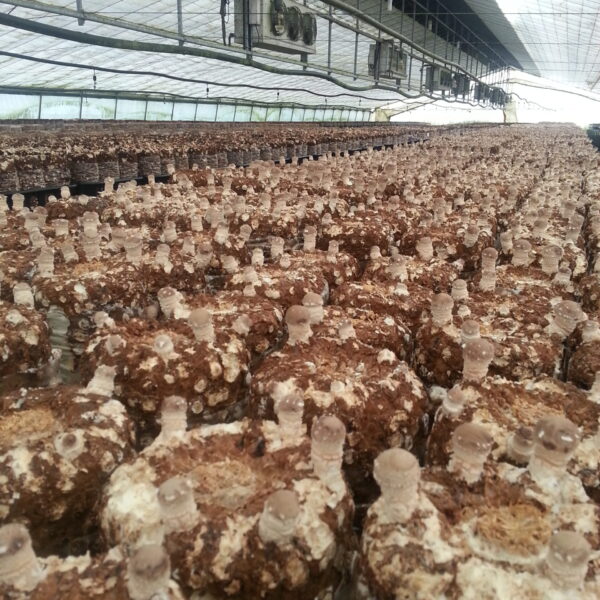
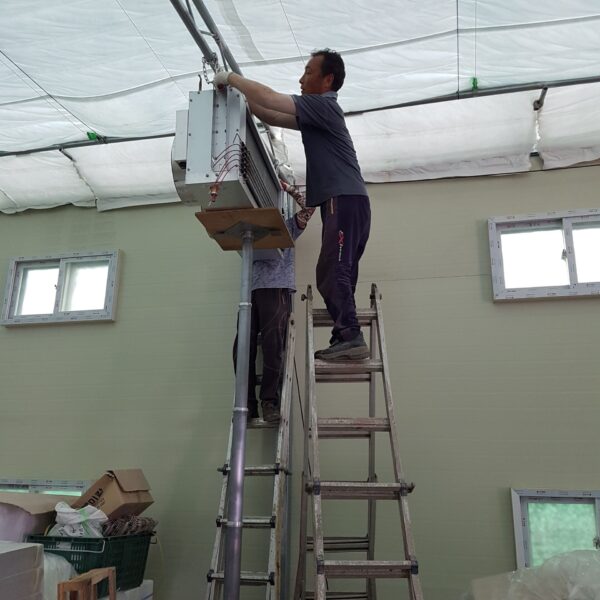
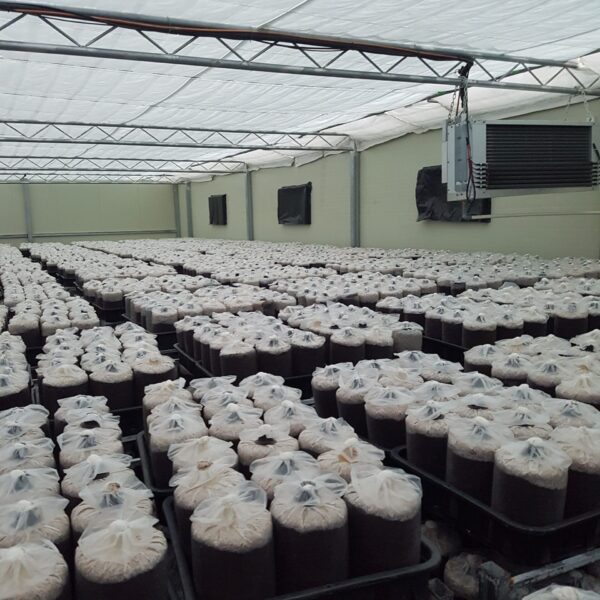
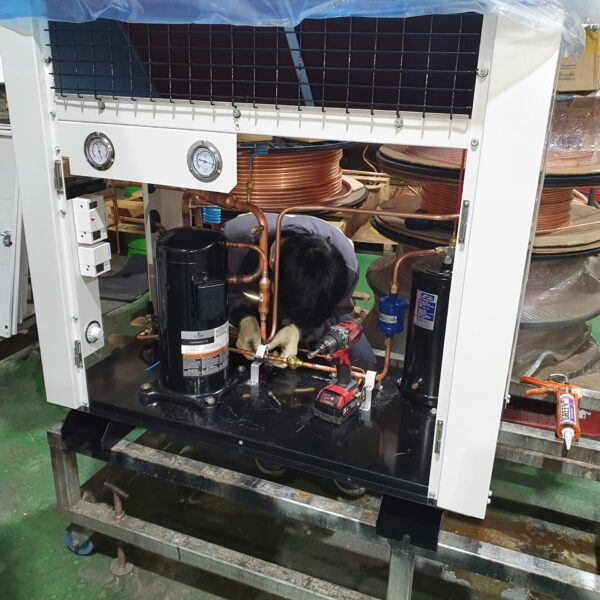
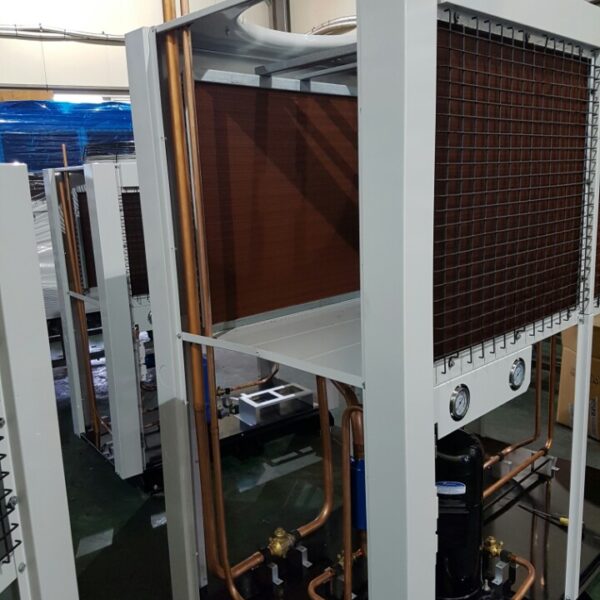
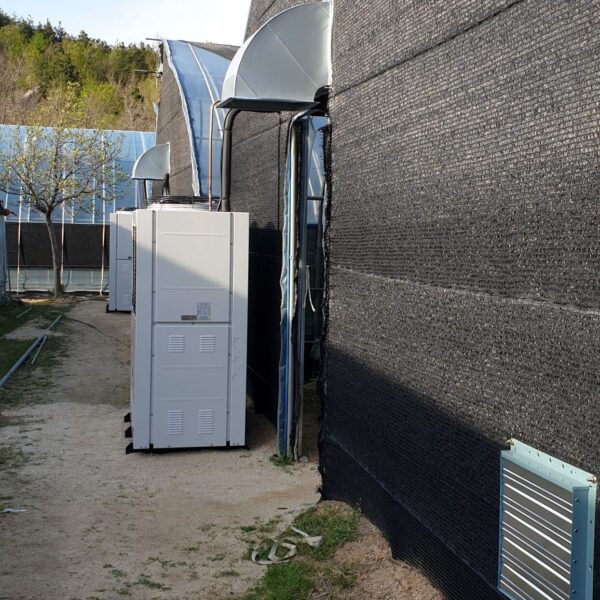
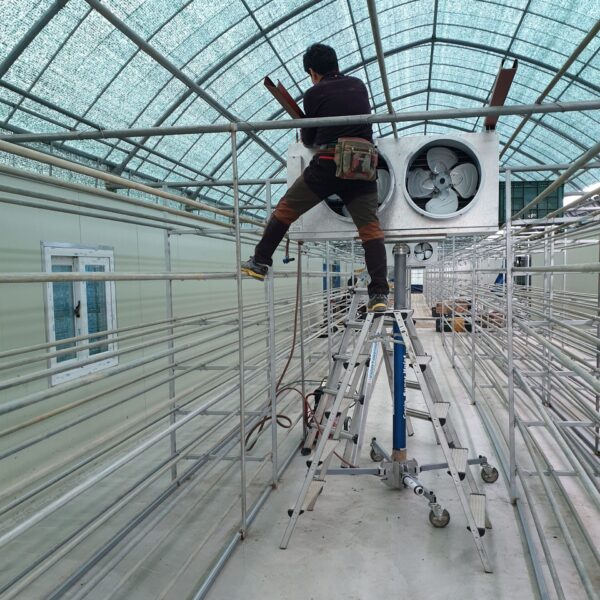
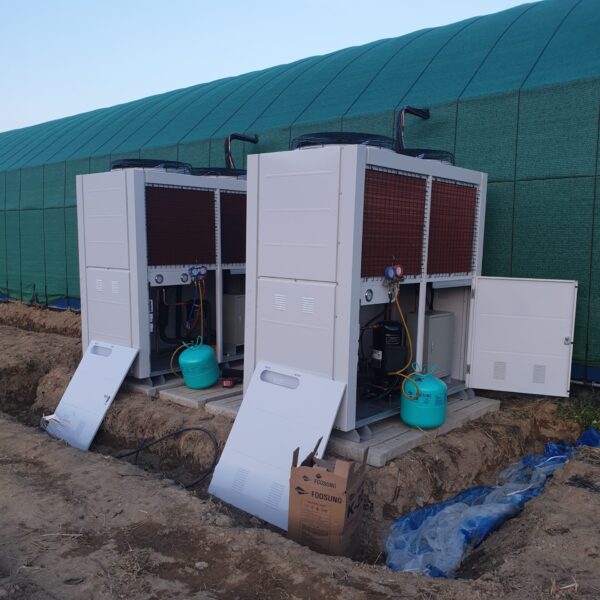
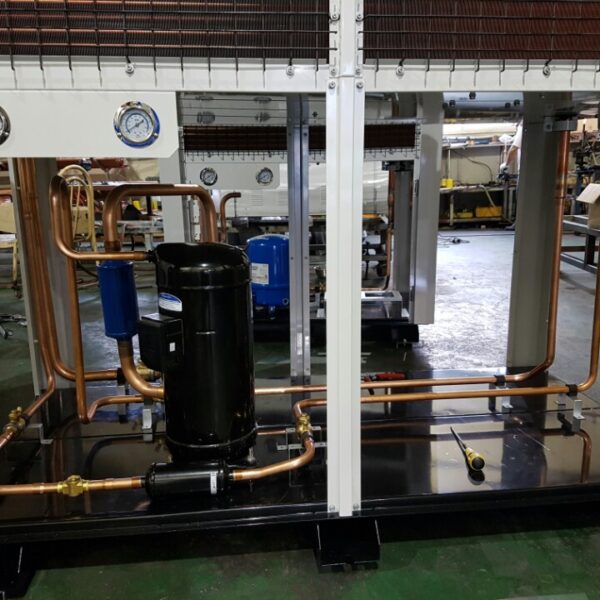
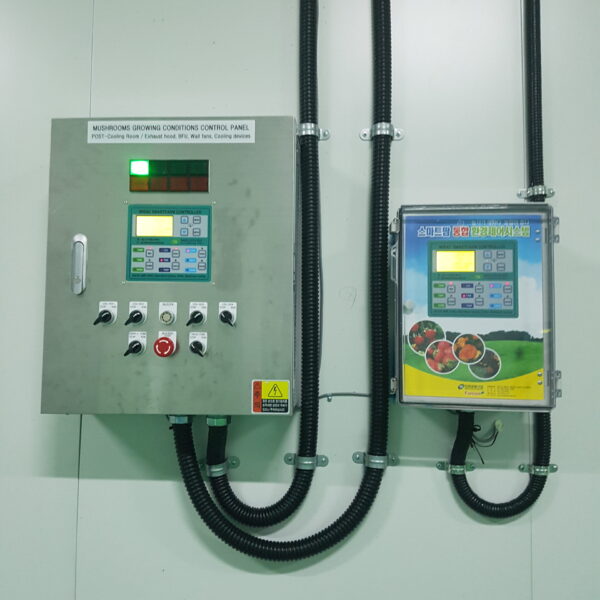
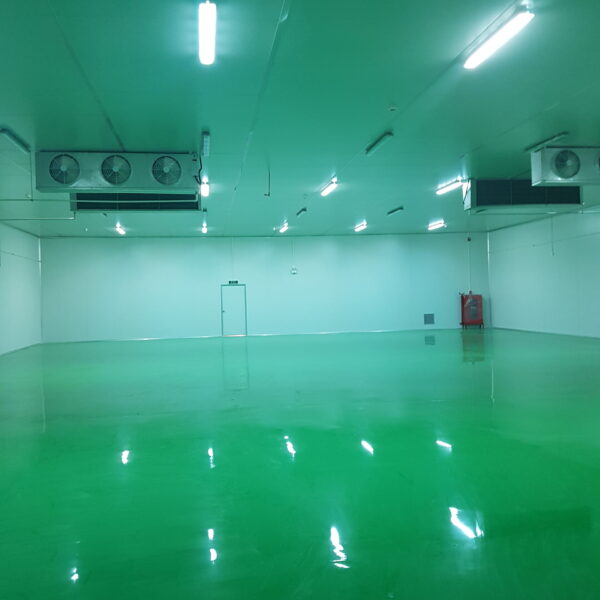
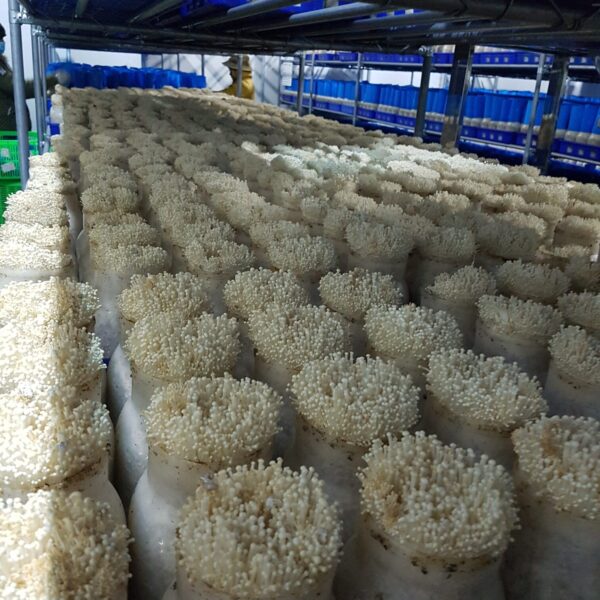
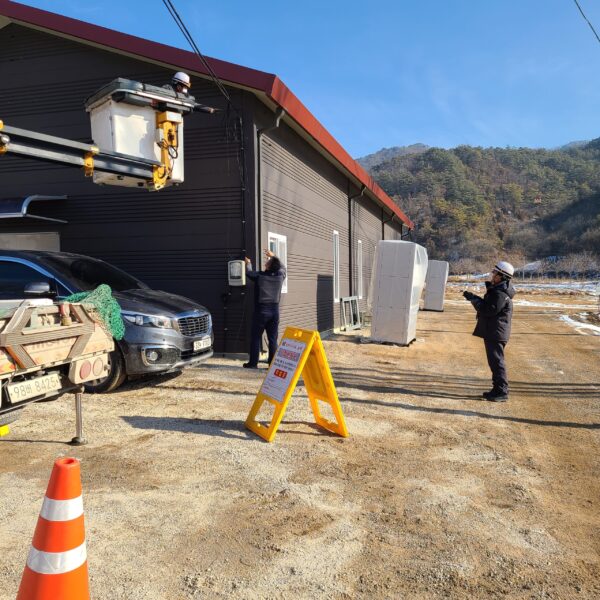
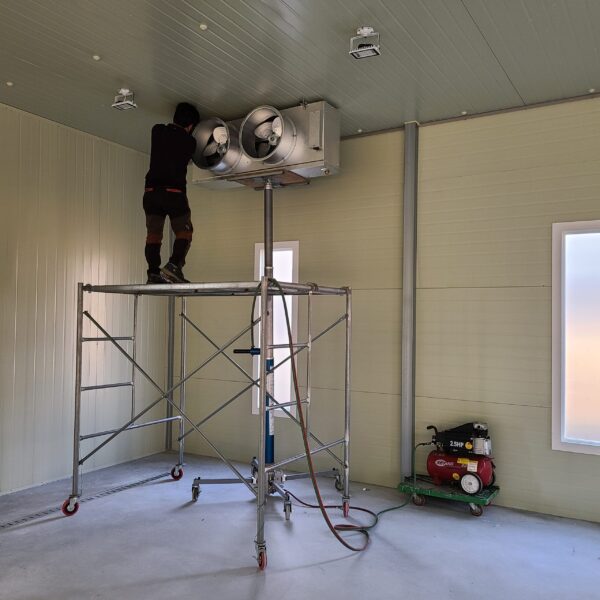
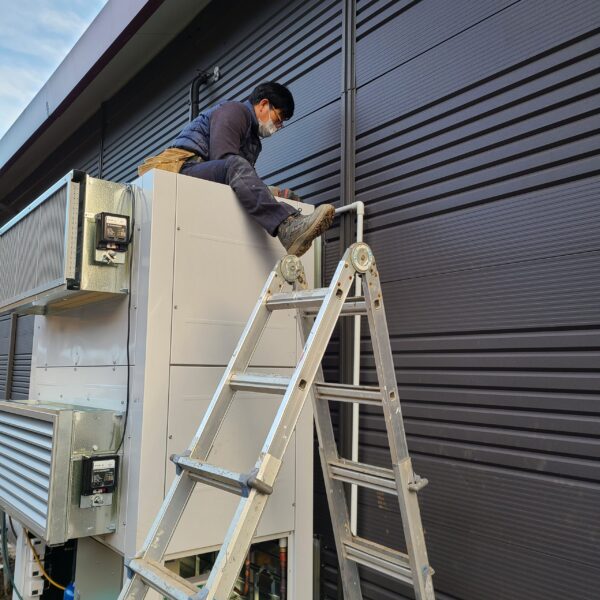
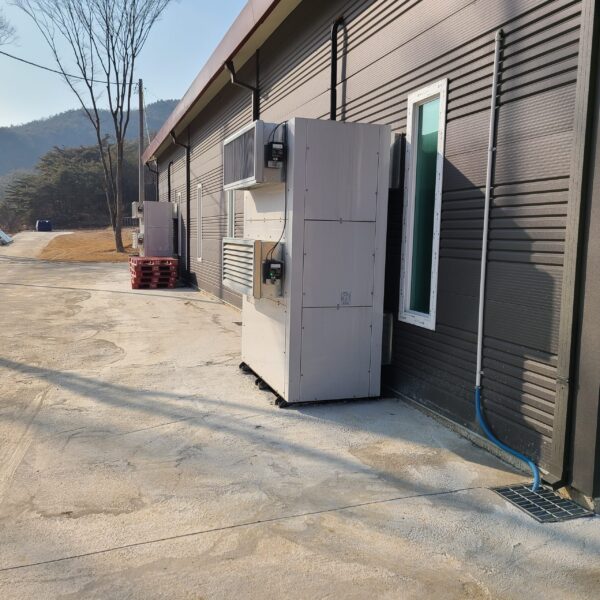
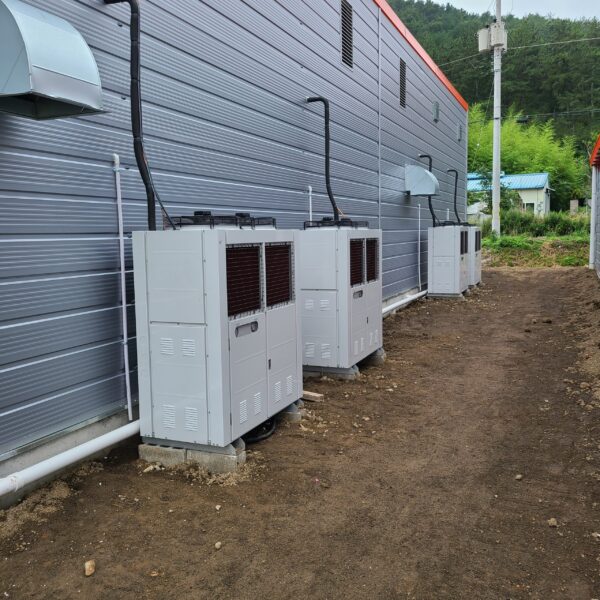
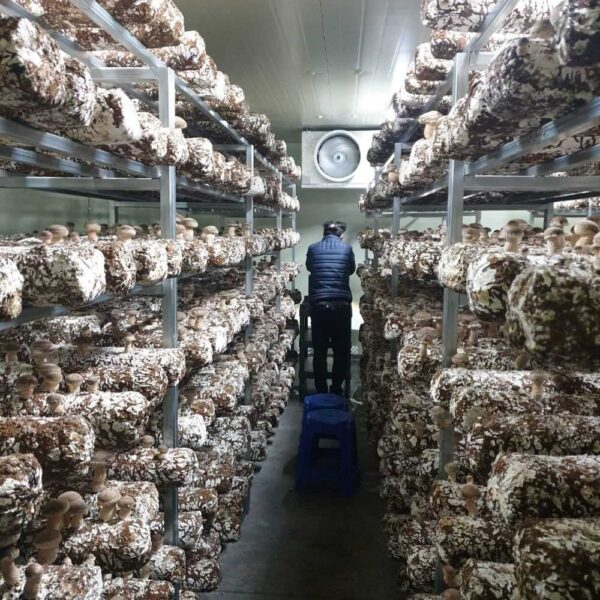
The greenhouse has a severe temperature rise due to solar heat in its structure and characteristics, which not only damages crop growth but also adversely affects the quality, so cooling is required at an appropriate time and through an appropriate method. When ventilation is properly combined with a shading facility that blocks sunlight by cooling through ventilation, the most common method of cooling is sufficient ventilation for indoor air to maintain the outdoor temperature level.
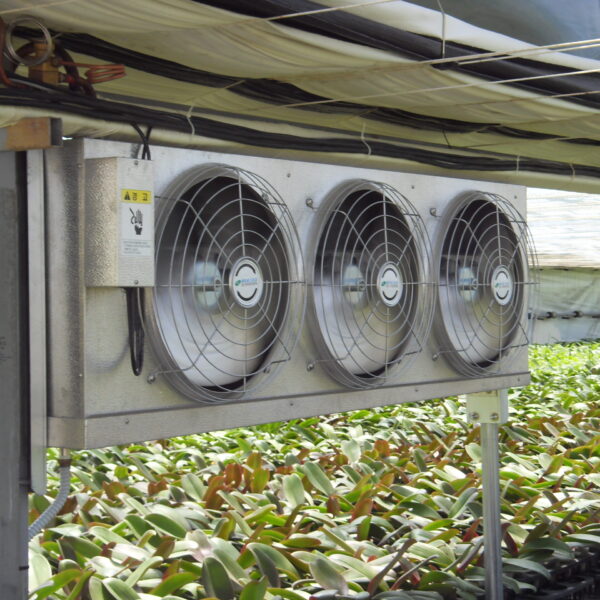
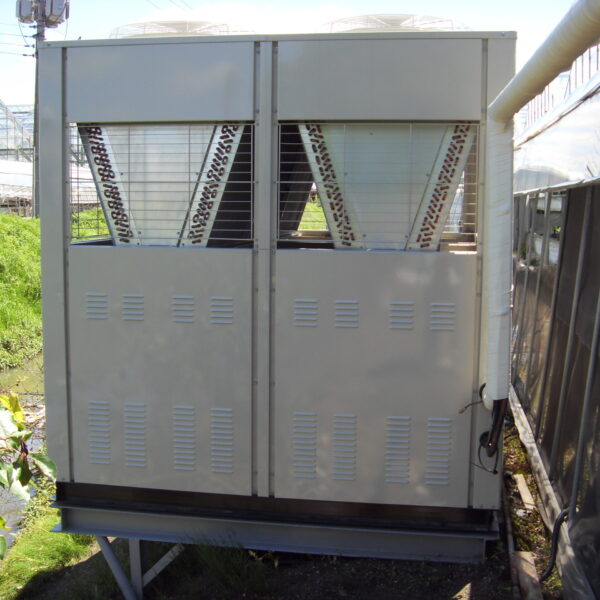
Such ventilation can be divided into natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation. Natural ventilation is a method of ventilating by partially opening and closing the vinyl covering the greenhouse. The air goes out through the upper skylight and the outside air flows in through the lower side window, so that ventilation is achieved. In this way, ventilation using the temperature difference of the air by properly opening and closing the windows of the greenhouse is called natural ventilation. However, there are many areas where it is difficult to install windows due to the nature of the greenhouse structure in the greenhouses in windy areas. Greenhouses in these regions are designed to act as a buffer against strong winds such as typhoons by injecting air into double vinyl with an air layer. It is impossible to install a skylight. If opening and closing of the skylight is not possible, the side window alone has no ventilation effect. Therefore, such a greenhouse must be ventilated by a ventilation fan.