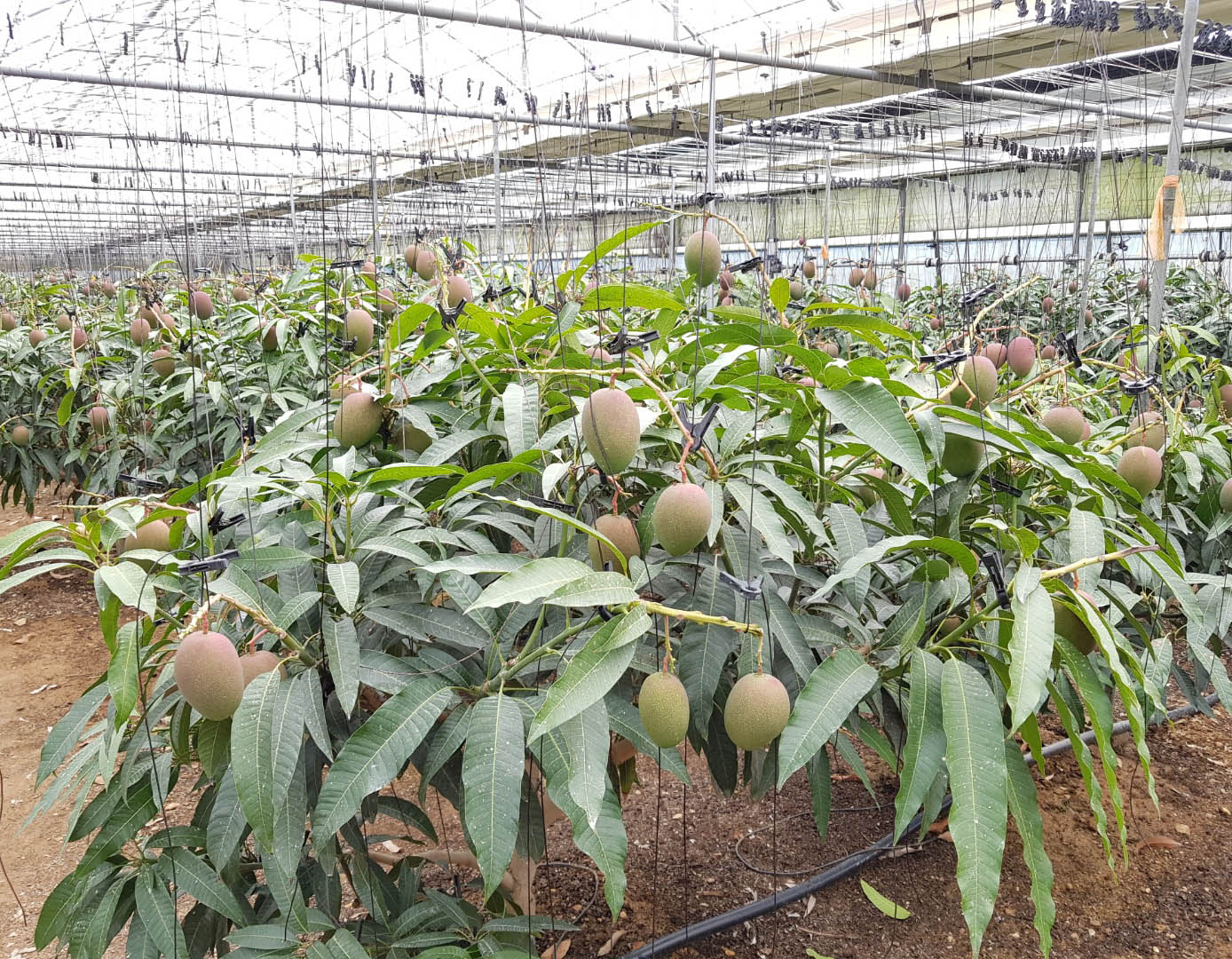
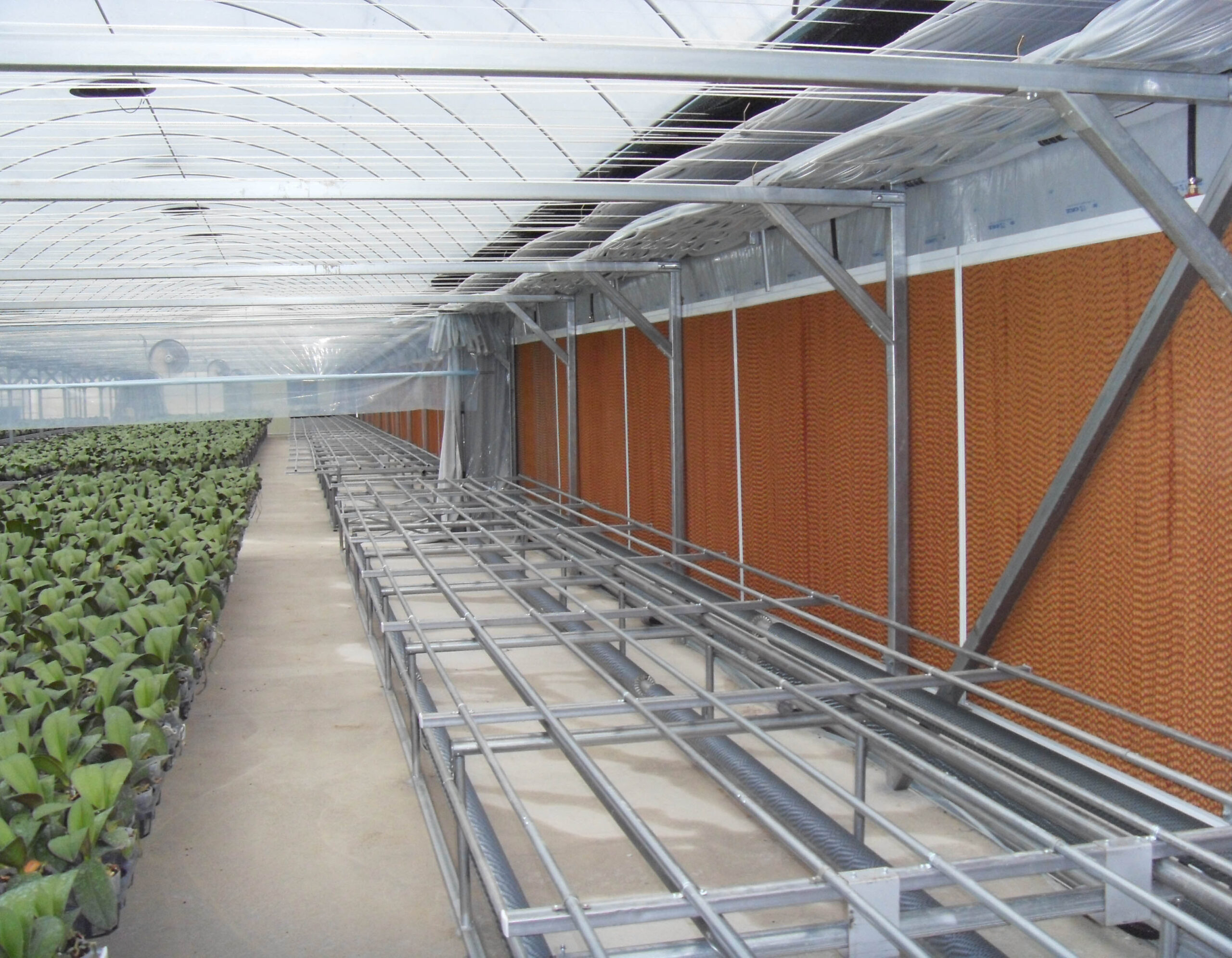
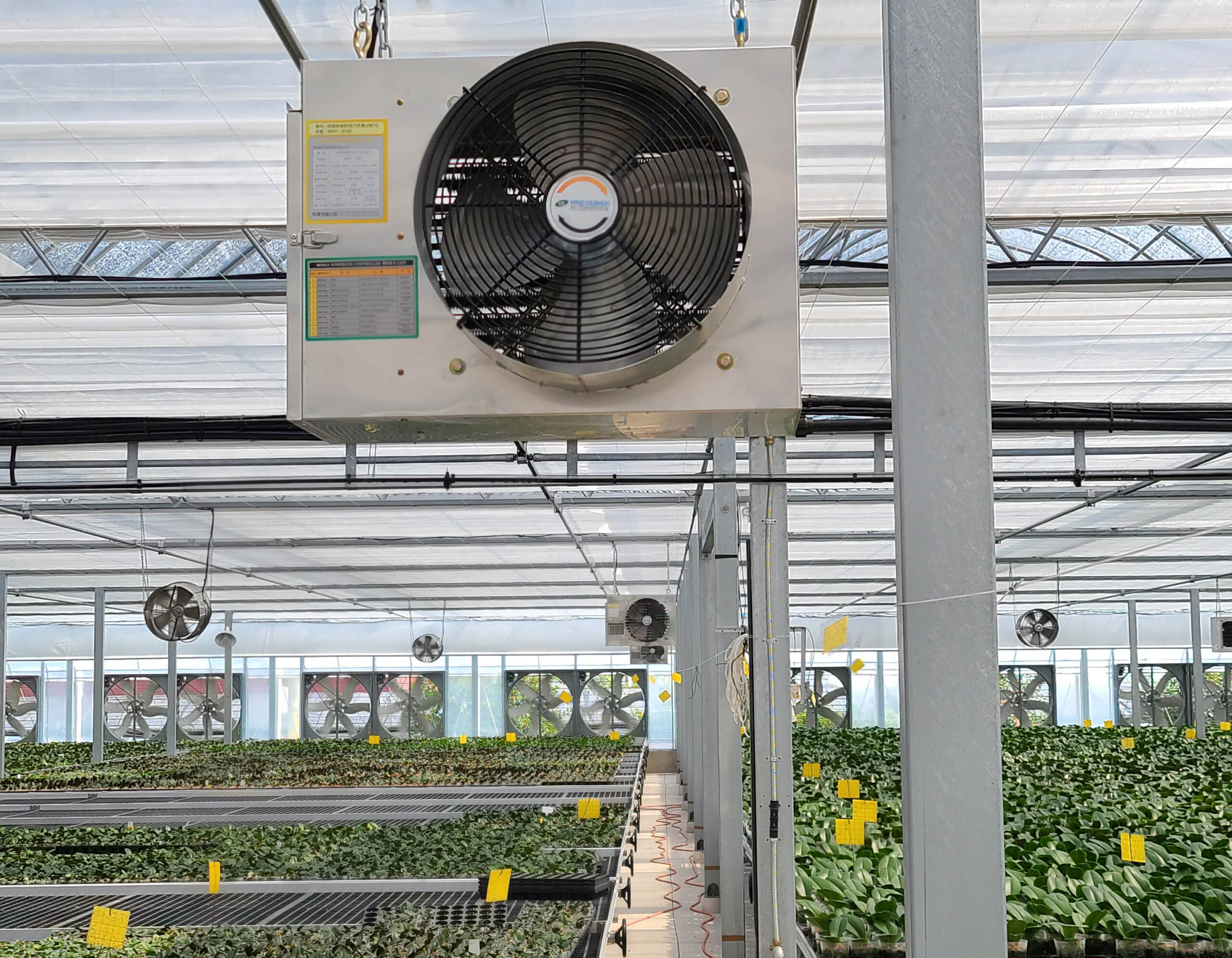
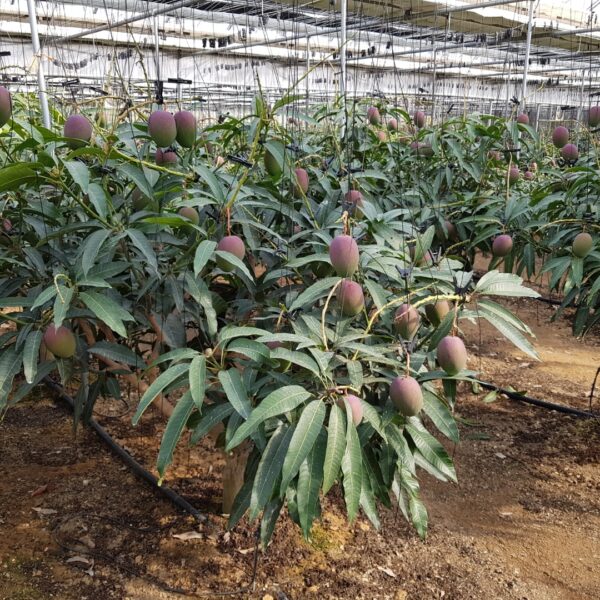
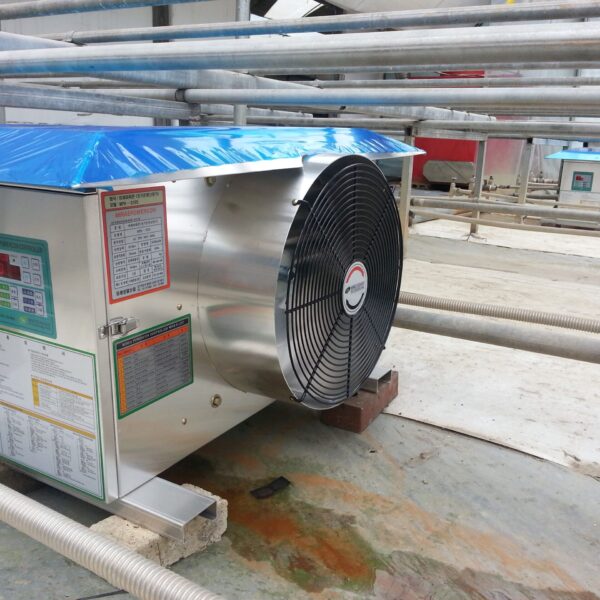
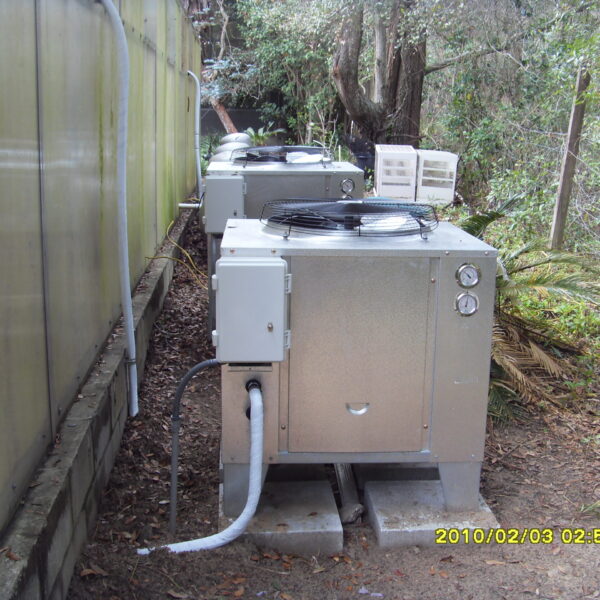
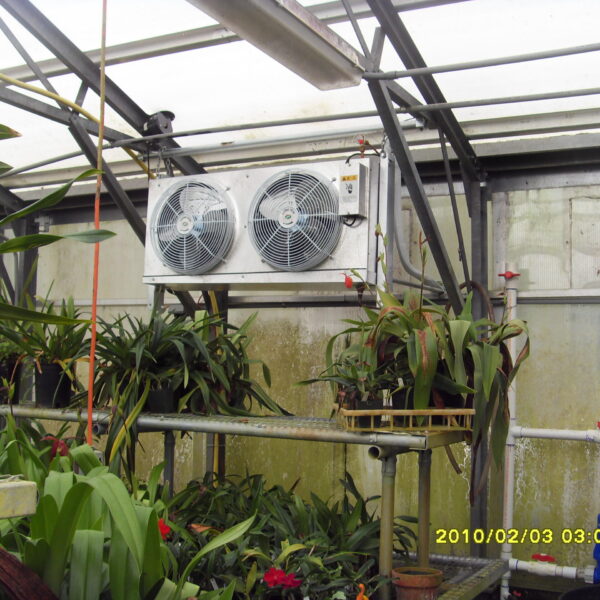
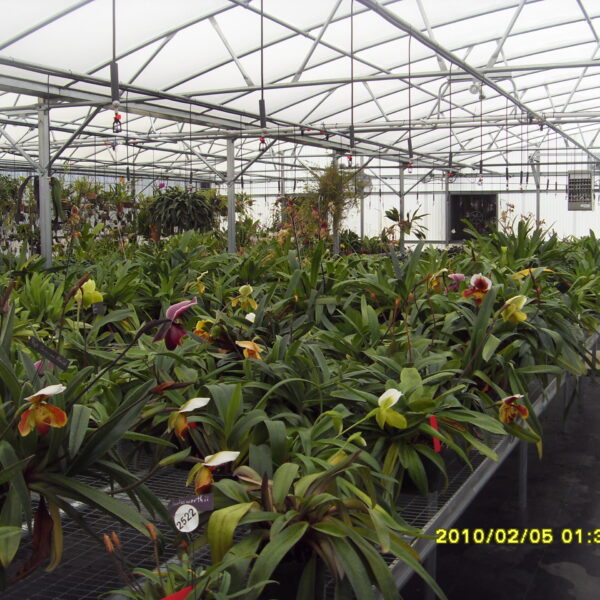
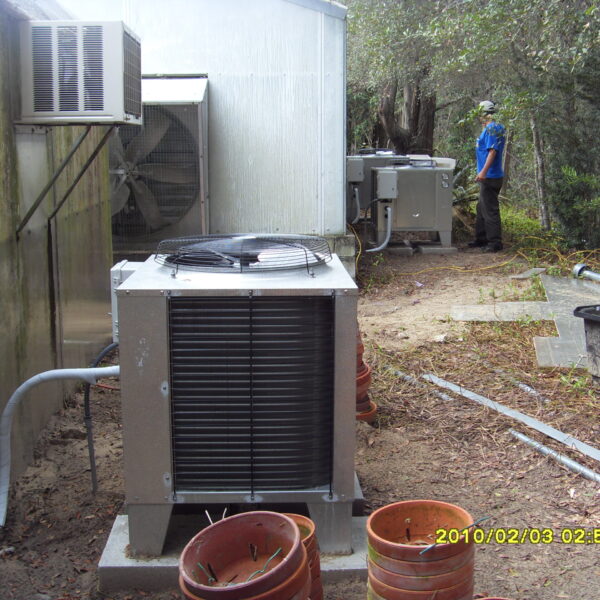
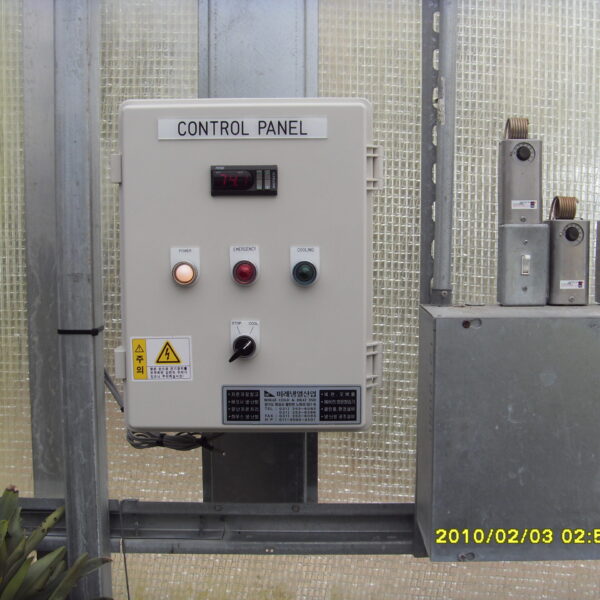
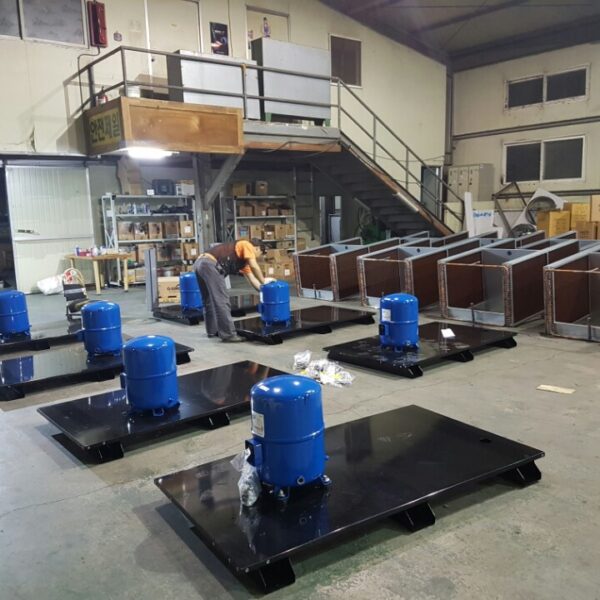
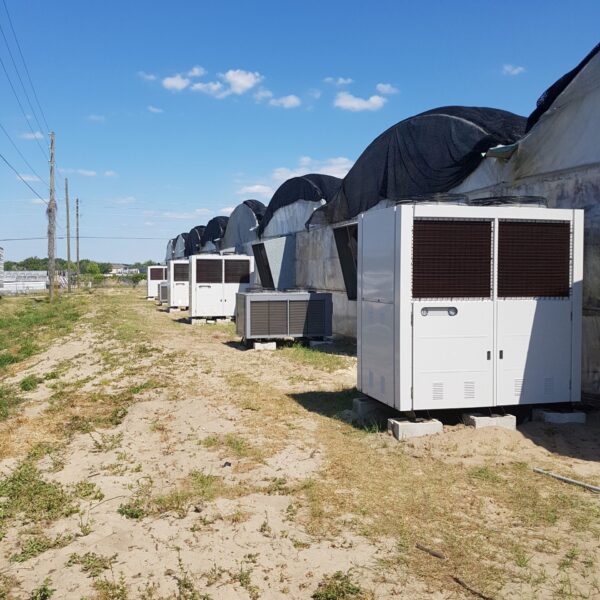
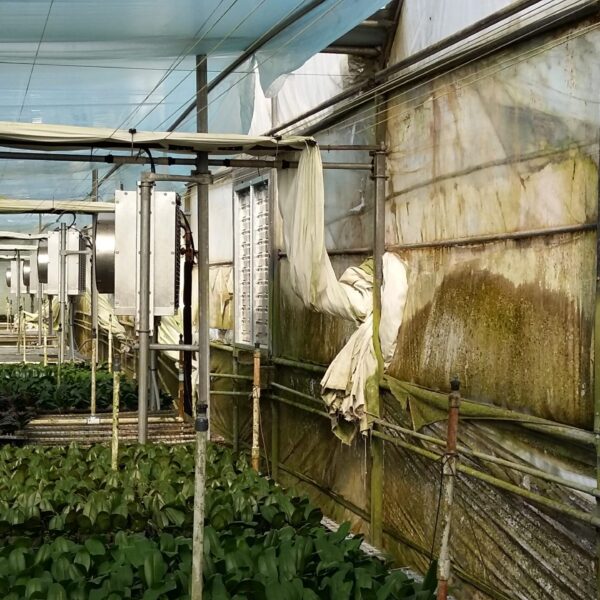
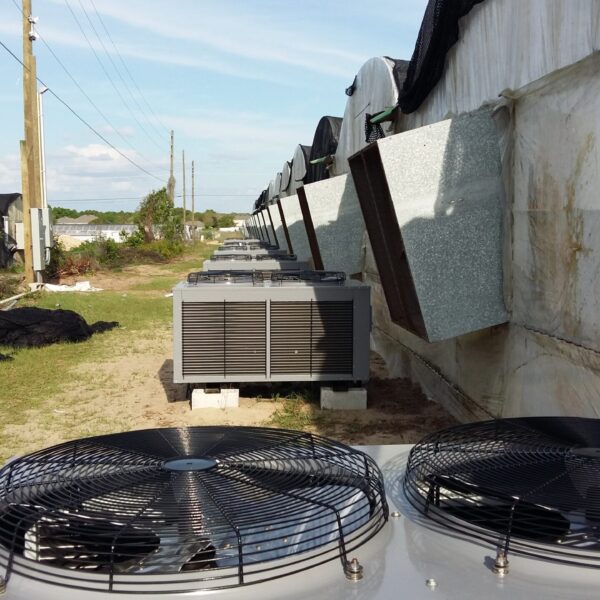
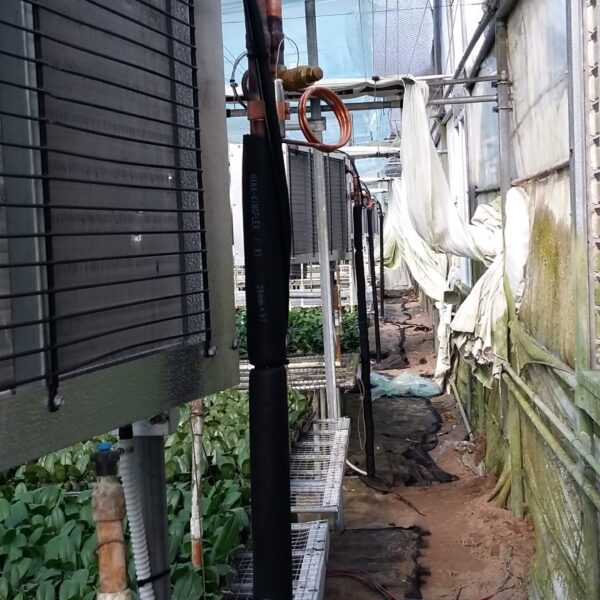
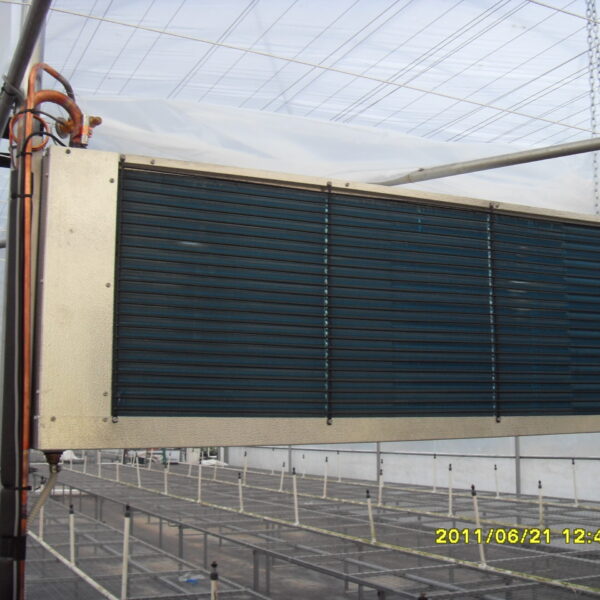
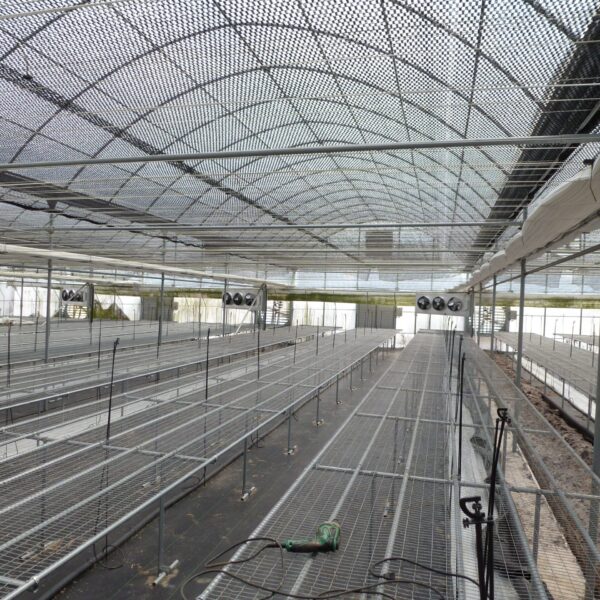
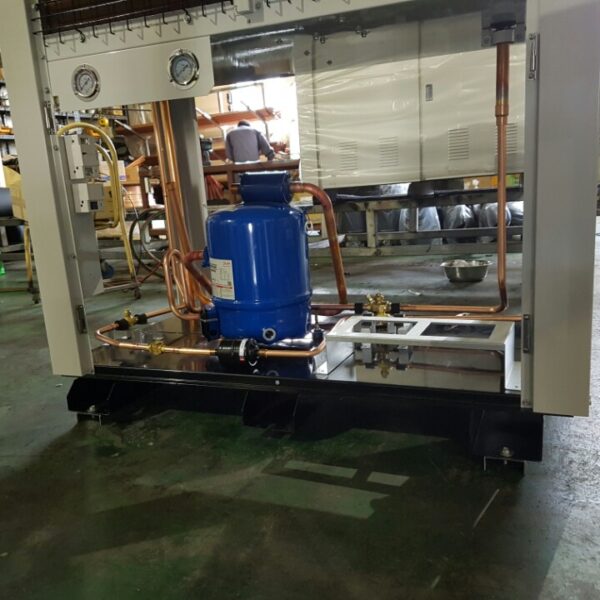
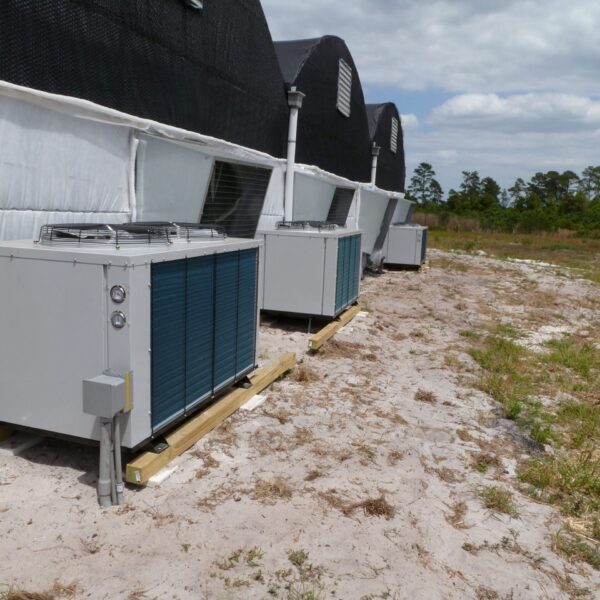
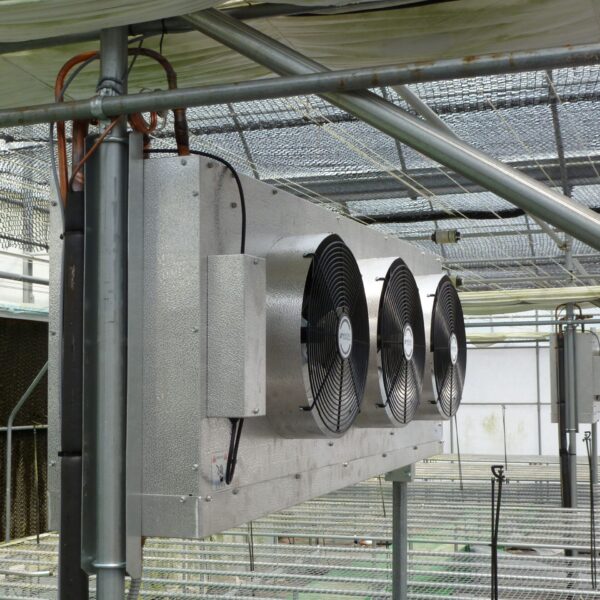
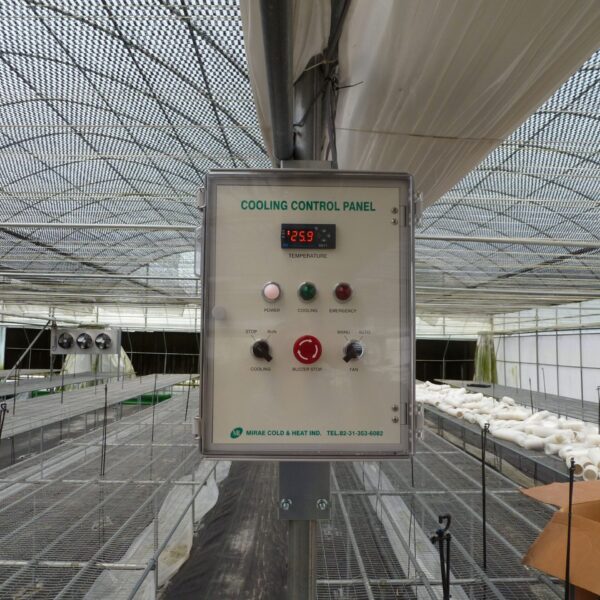
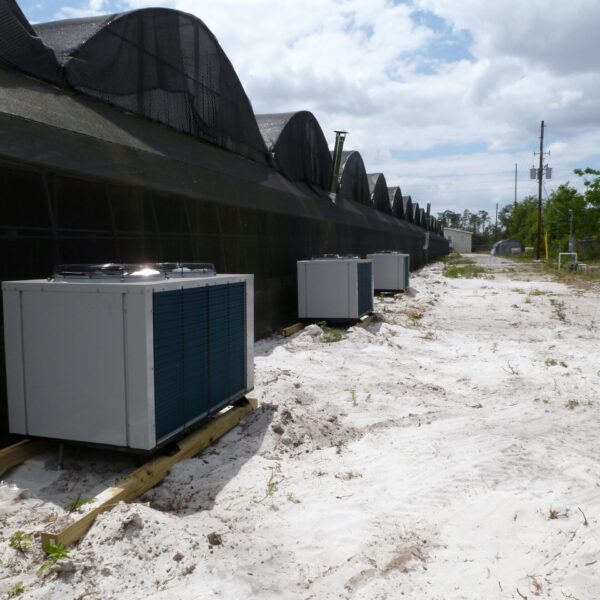
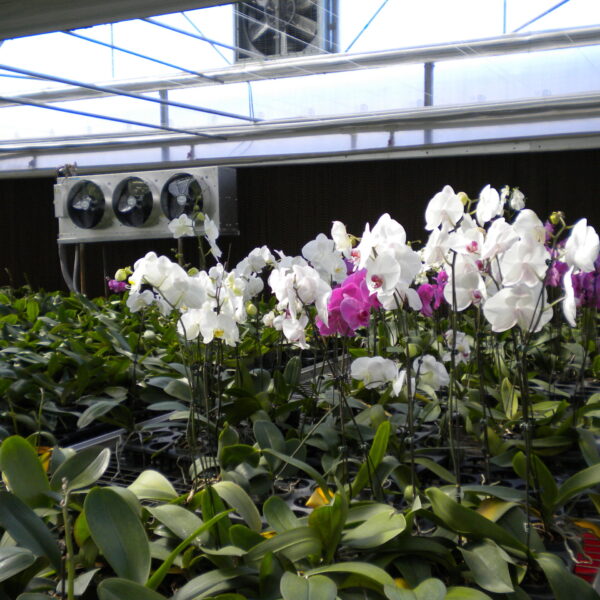
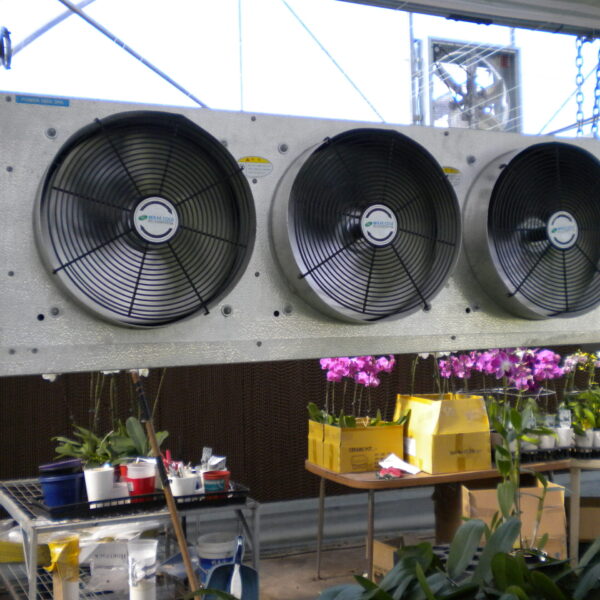
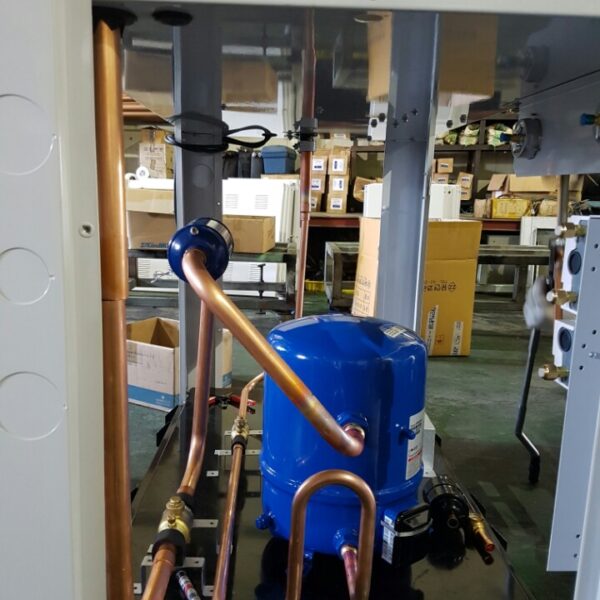
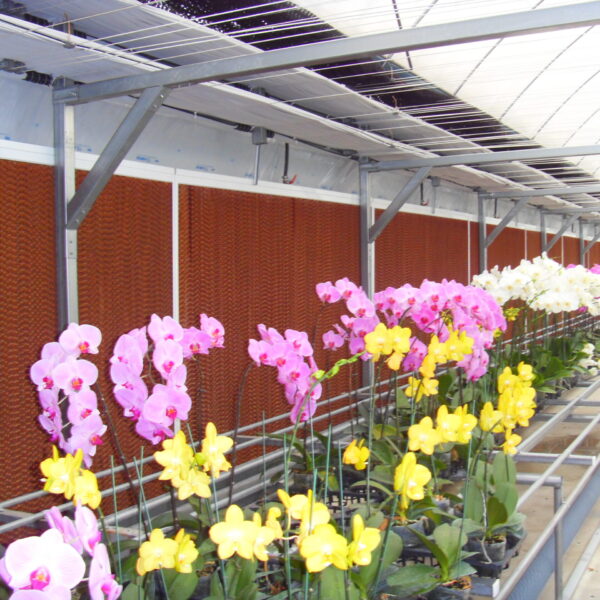
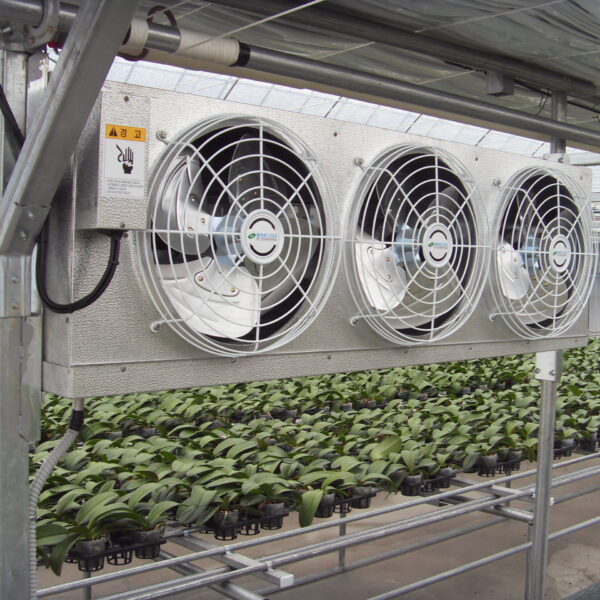
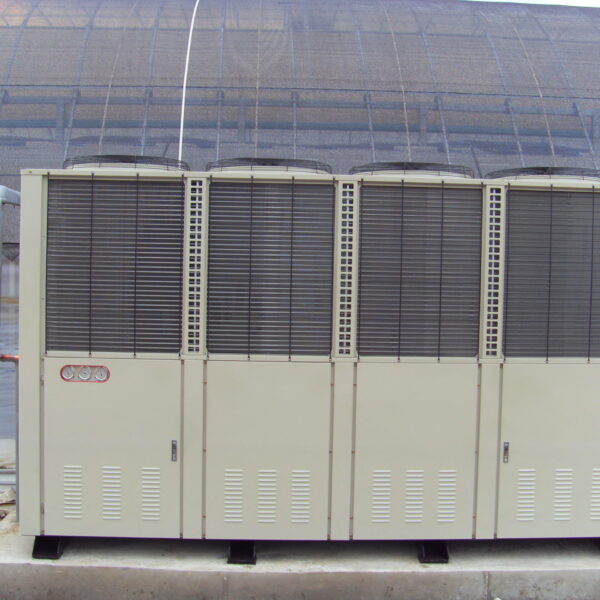
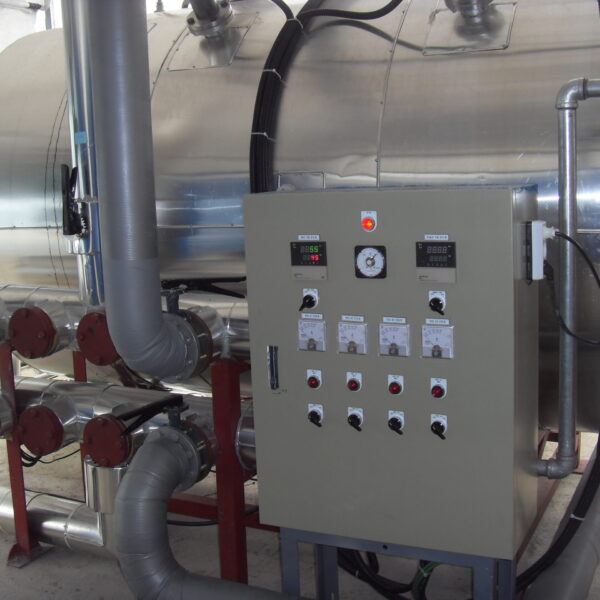
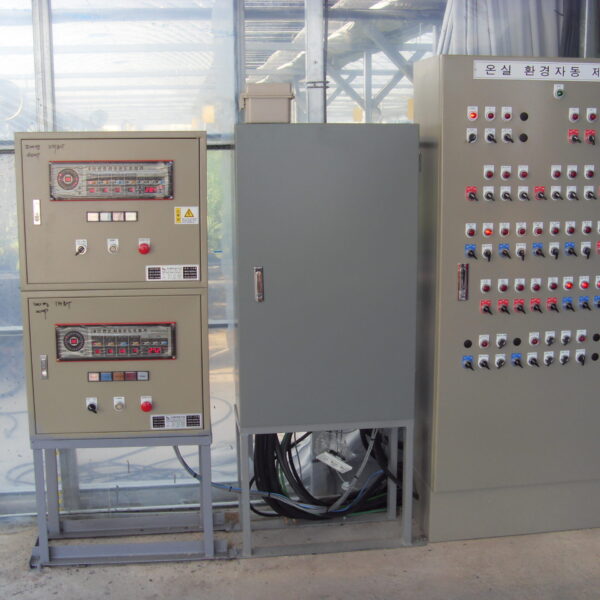
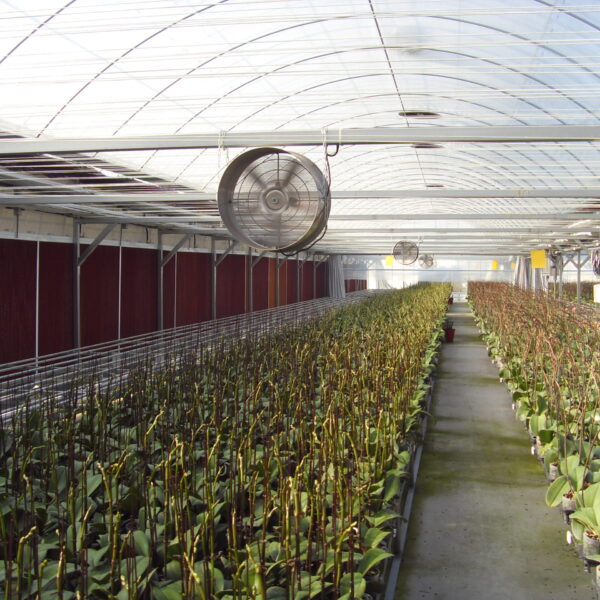
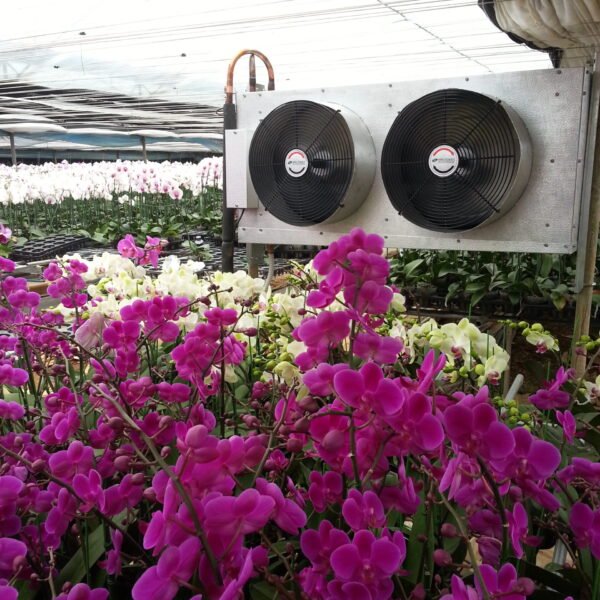
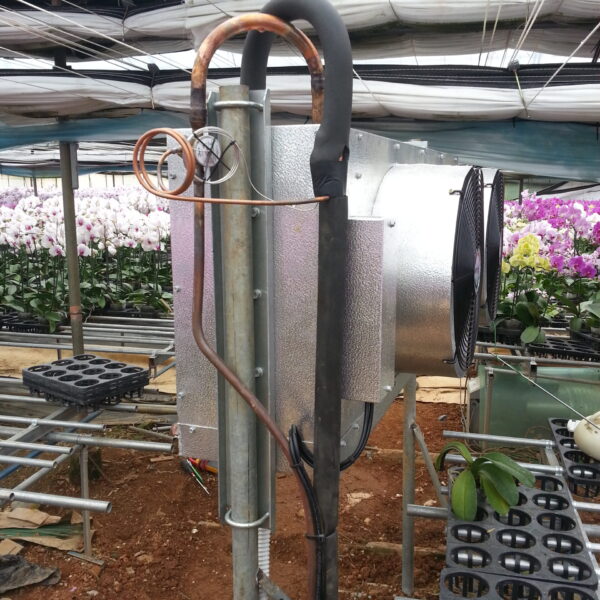
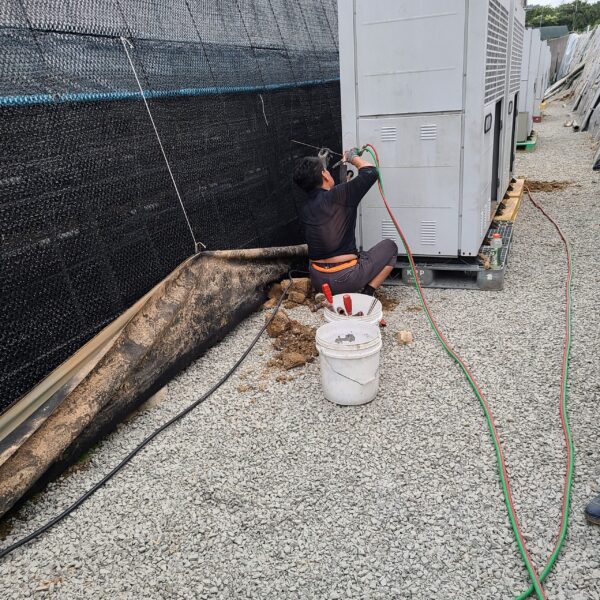
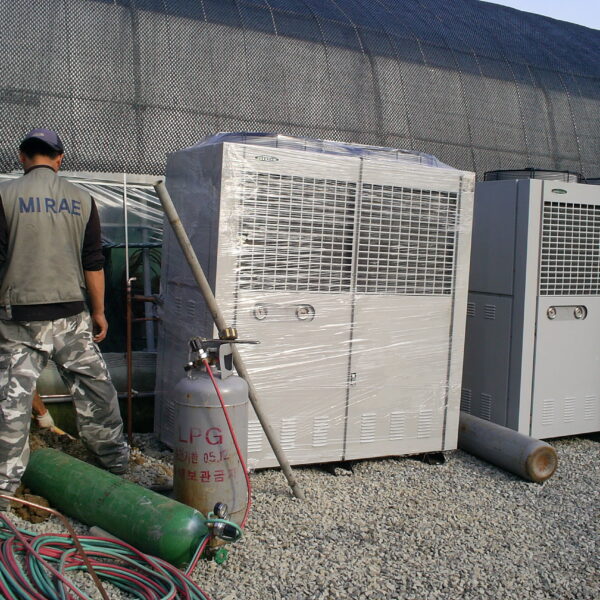
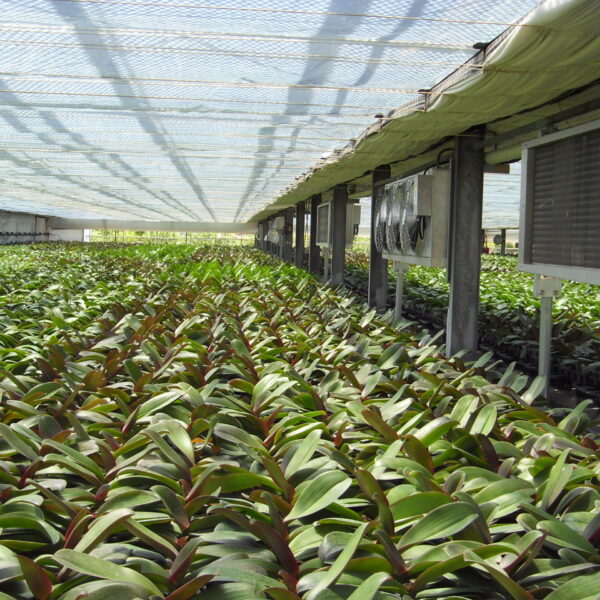
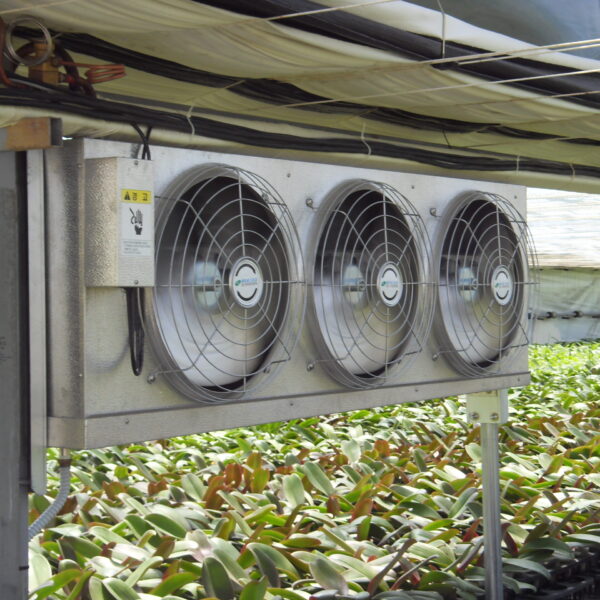
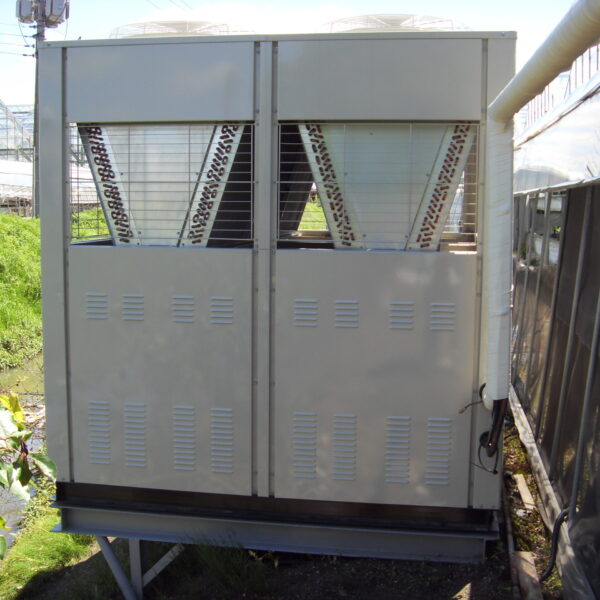
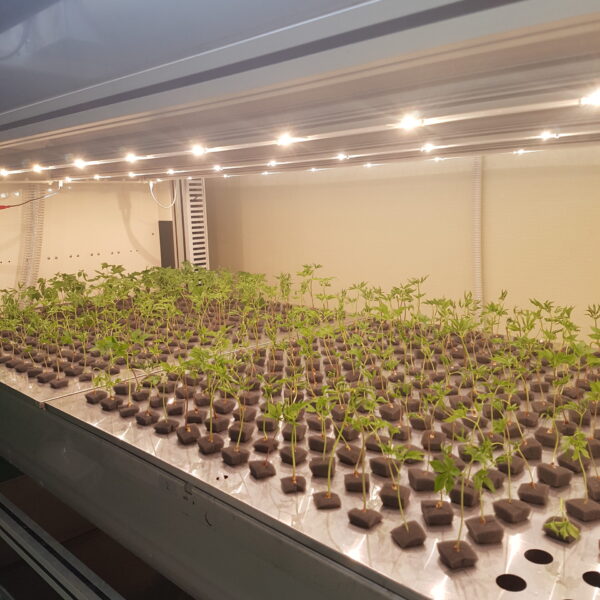
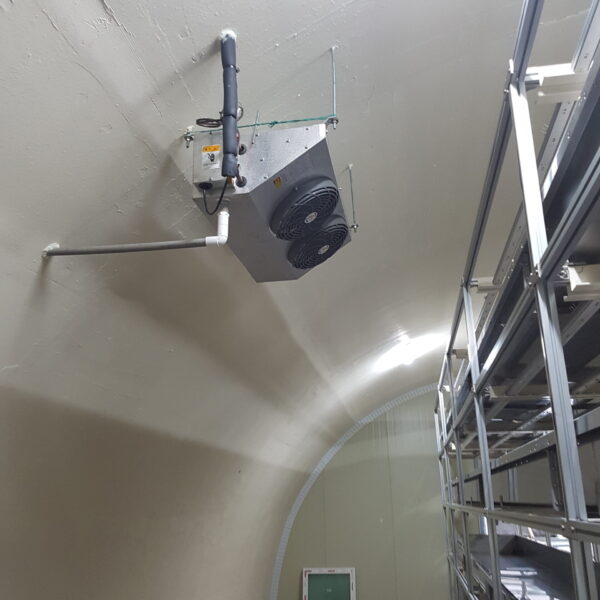
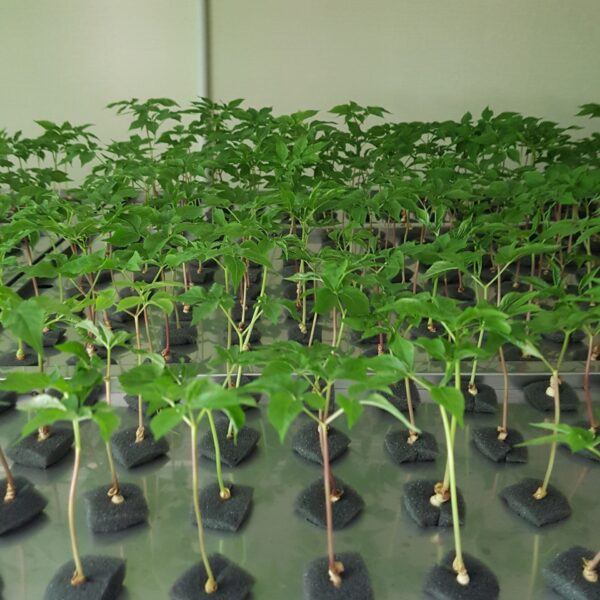
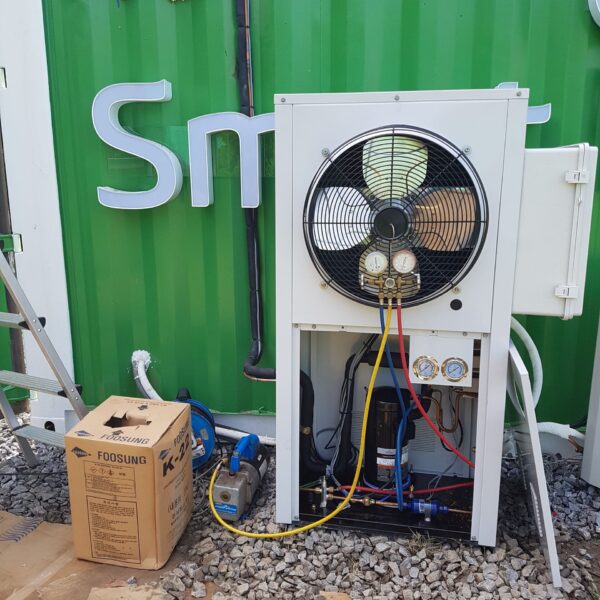
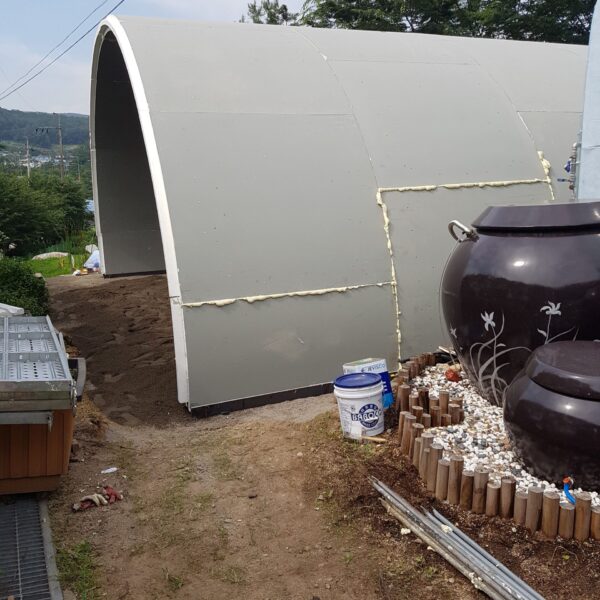
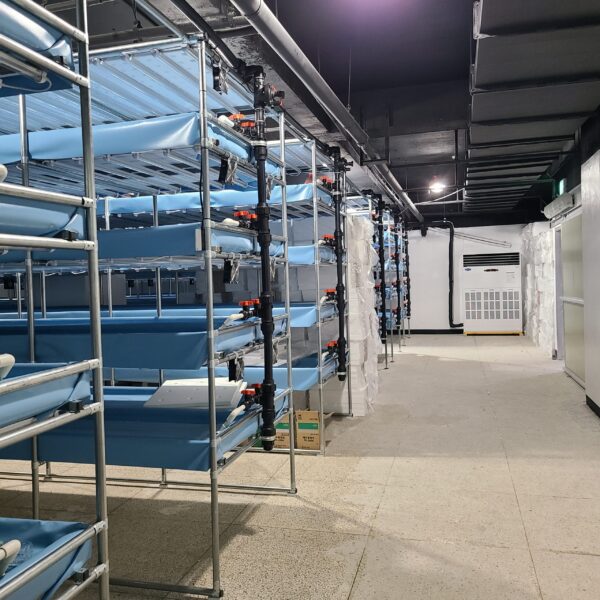
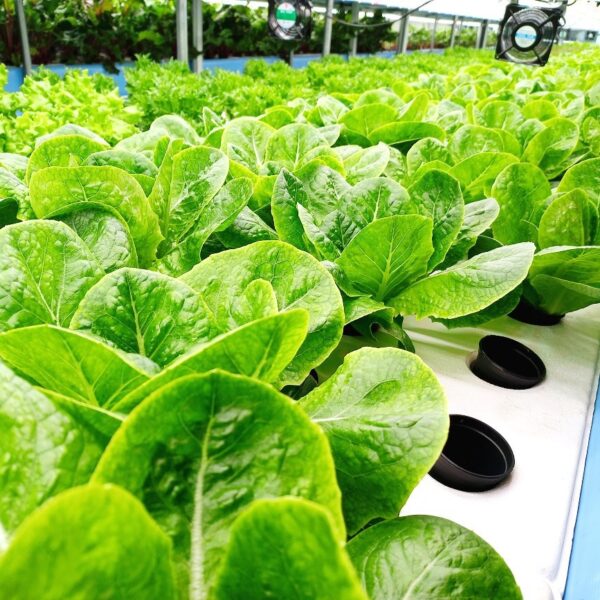
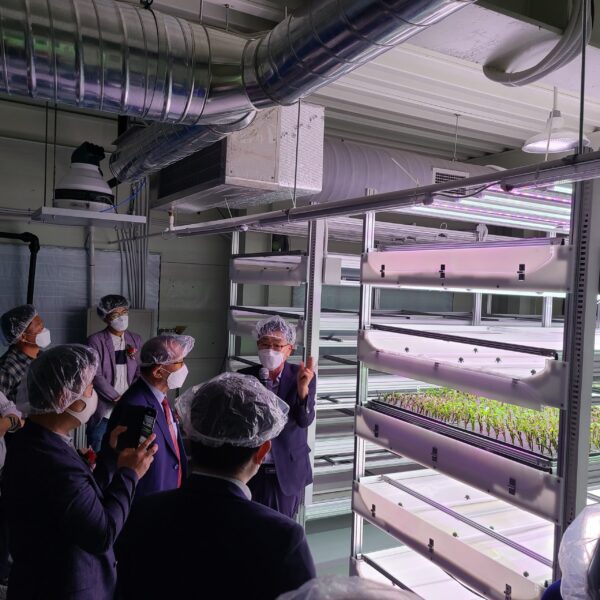
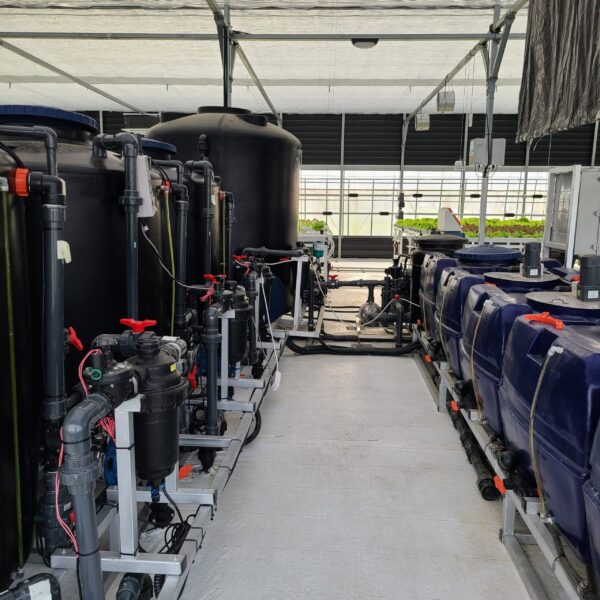
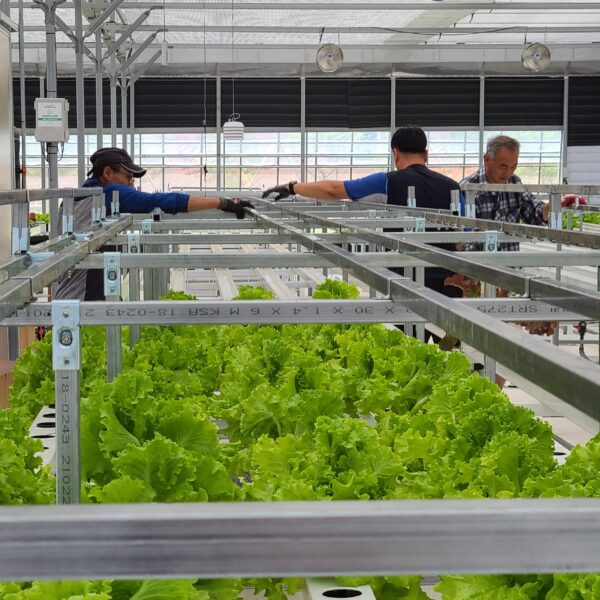
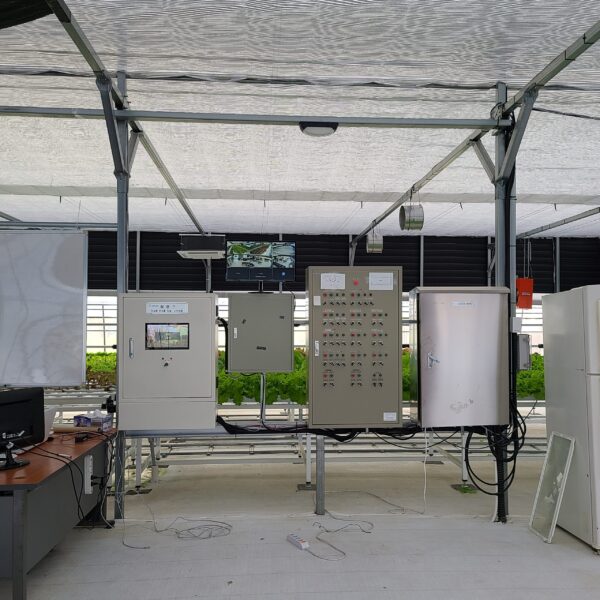
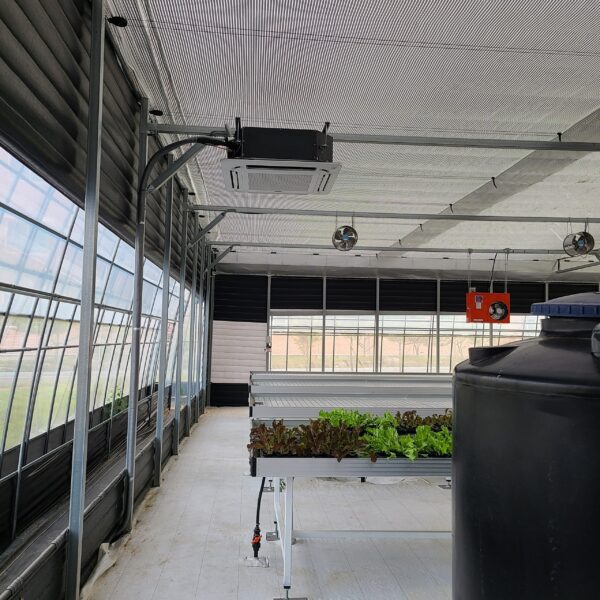
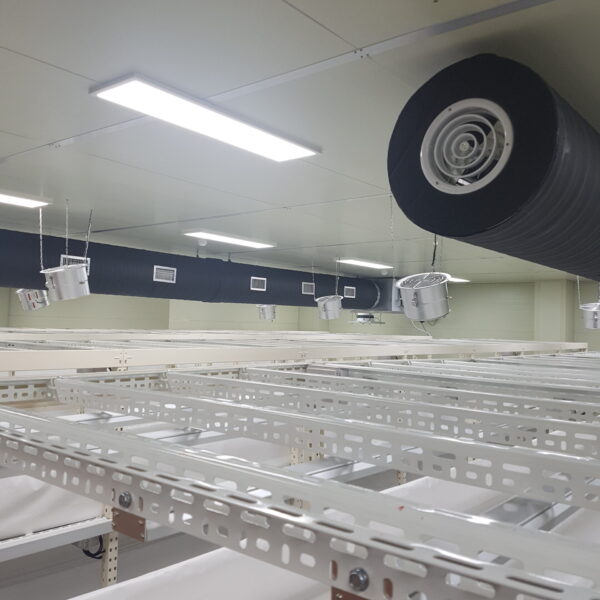
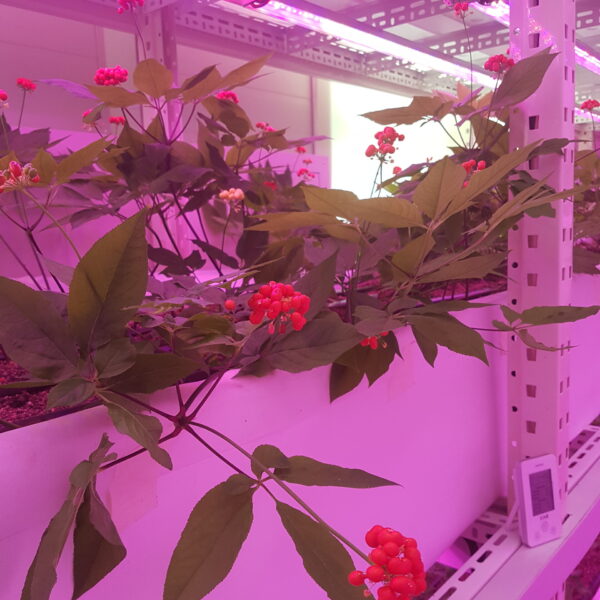
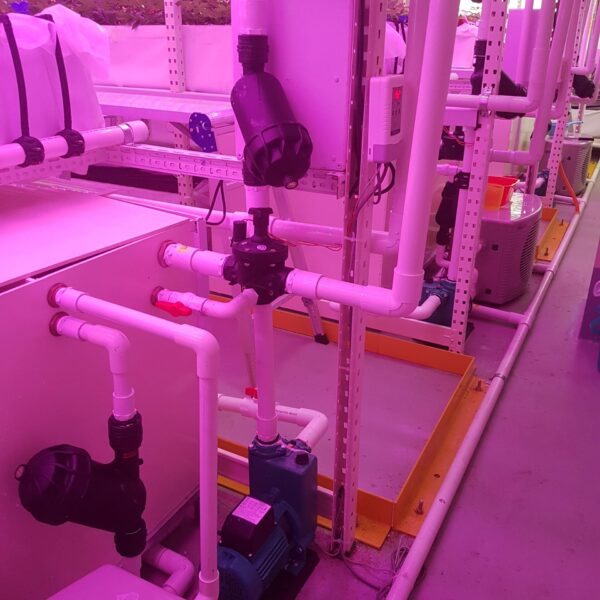
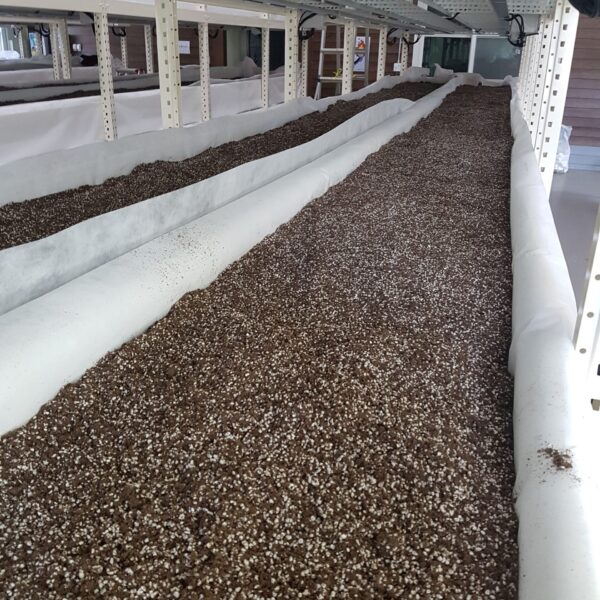
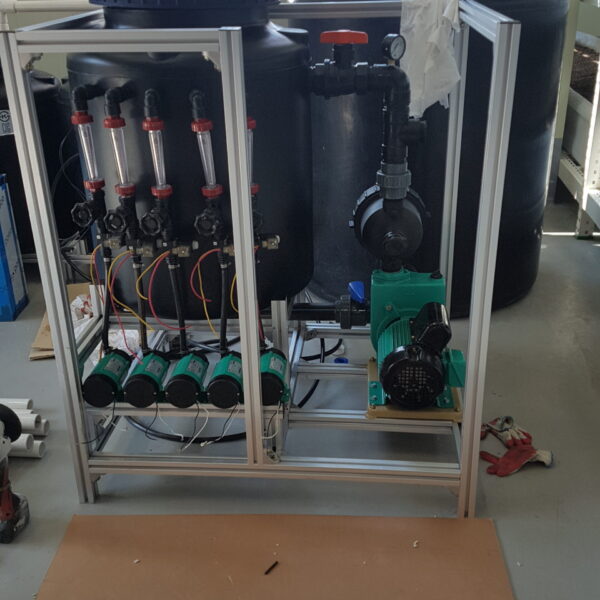
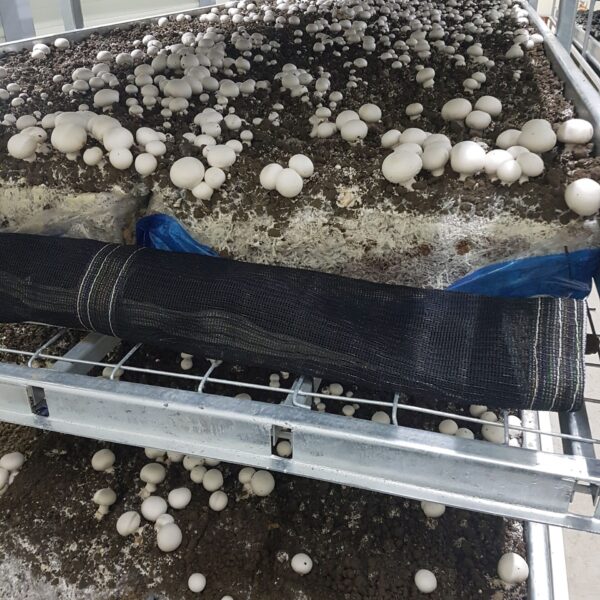
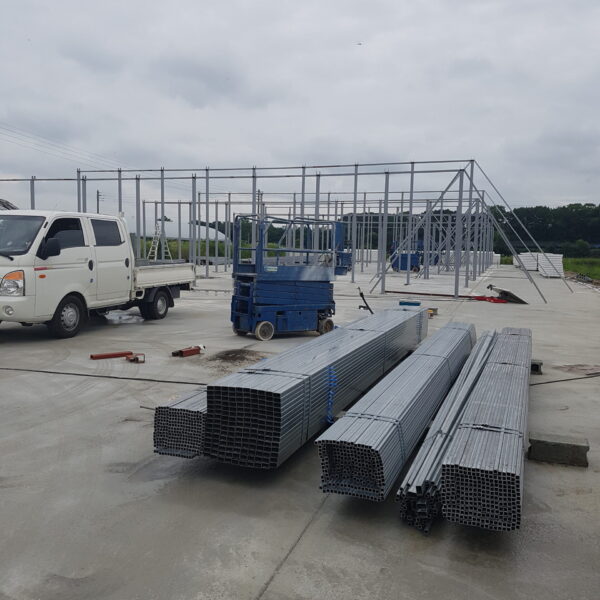
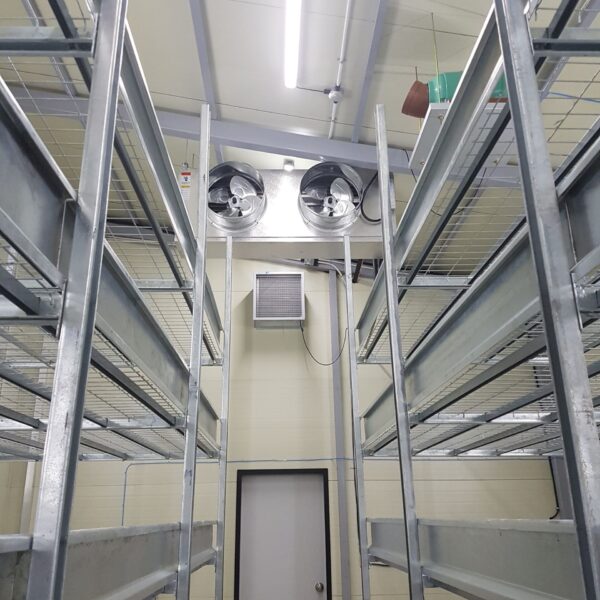
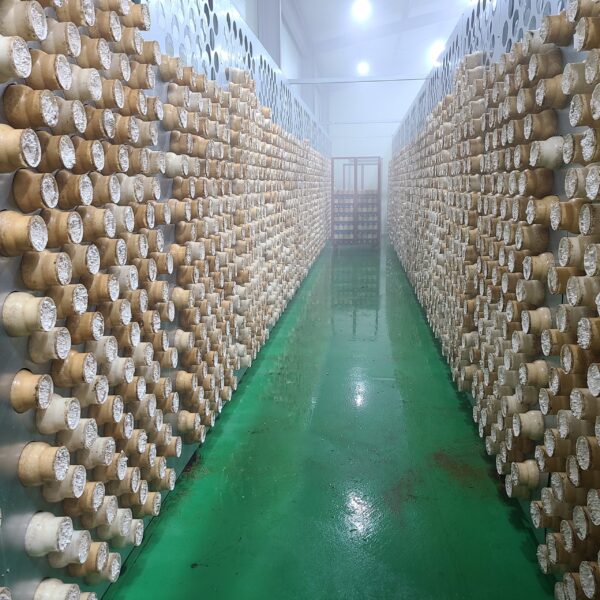
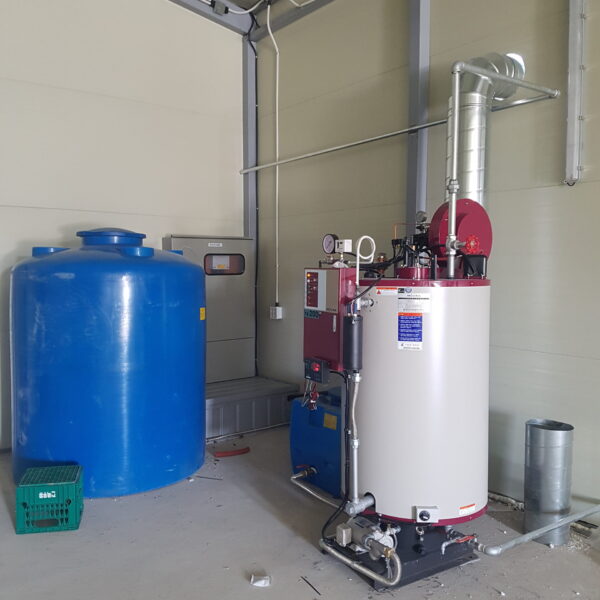
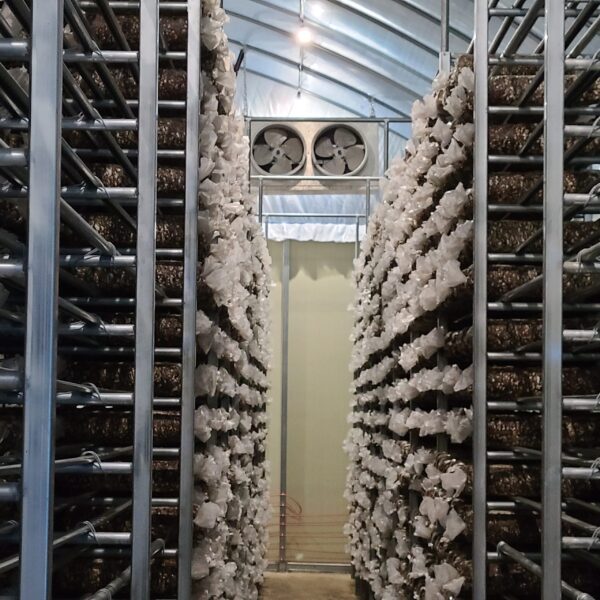
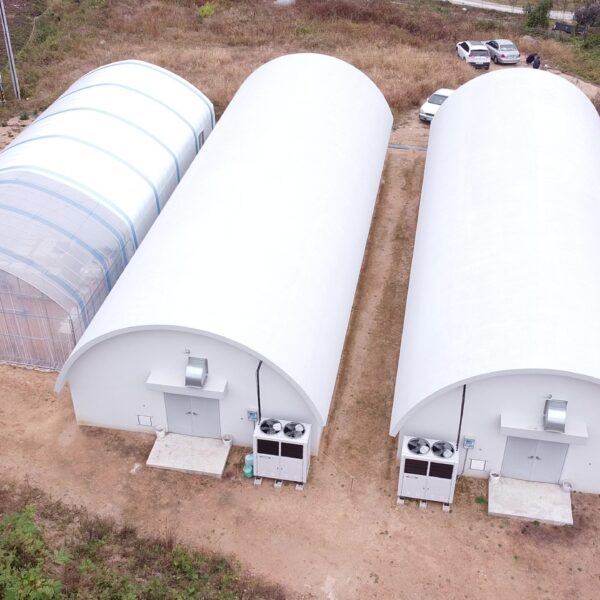
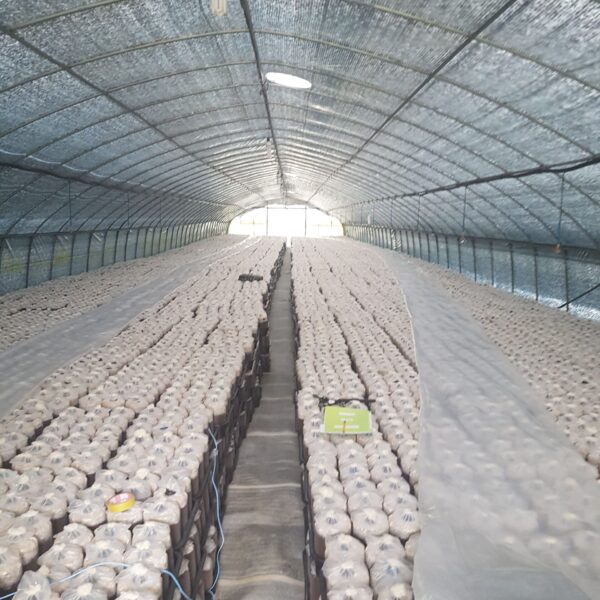
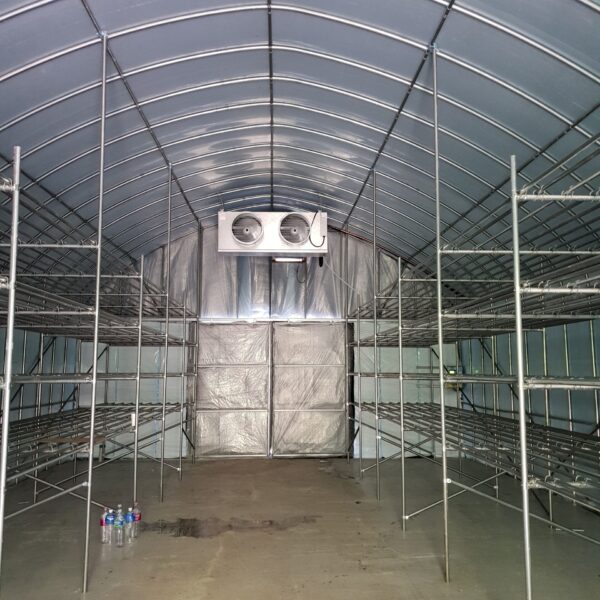
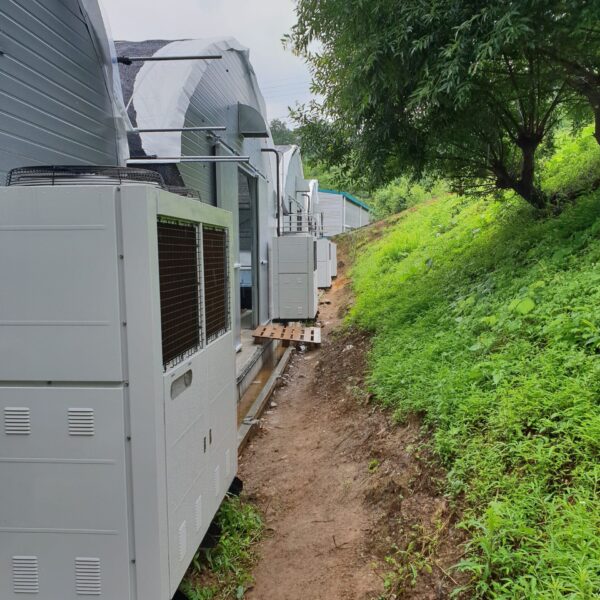
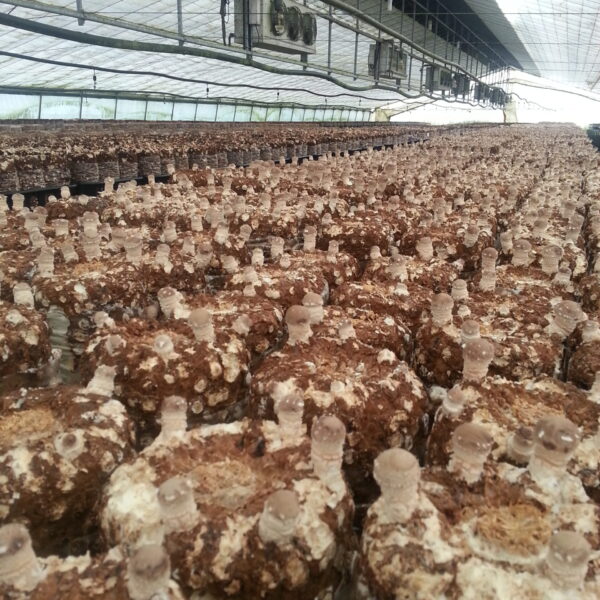
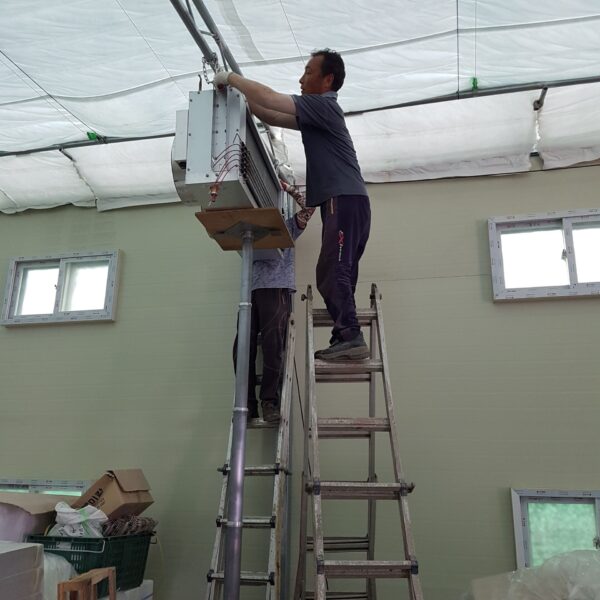
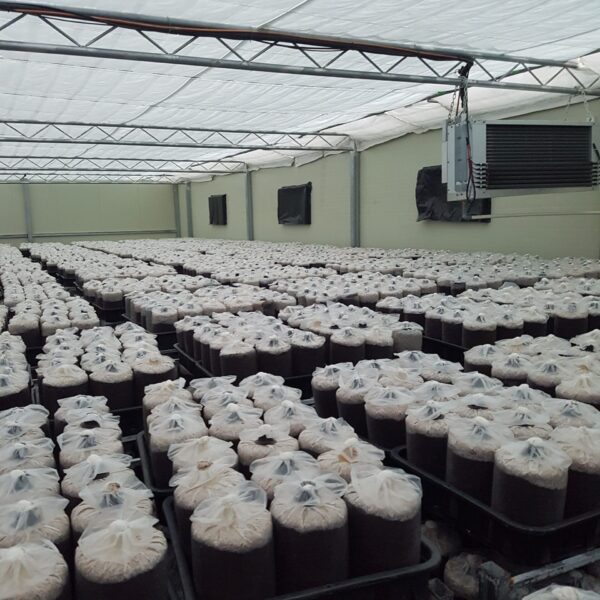
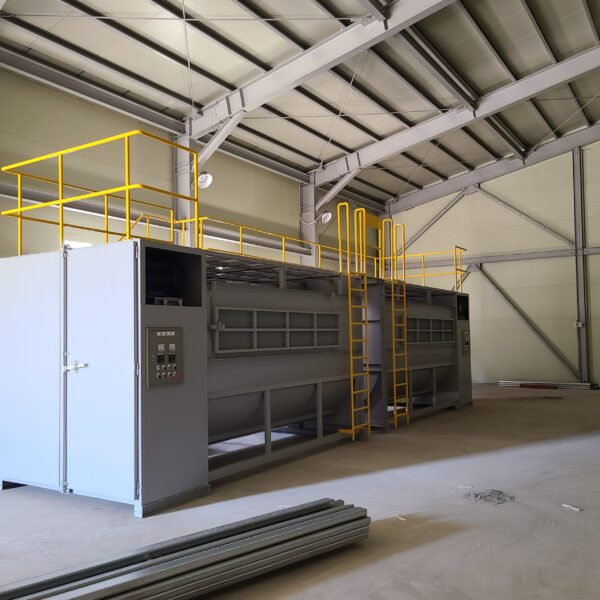
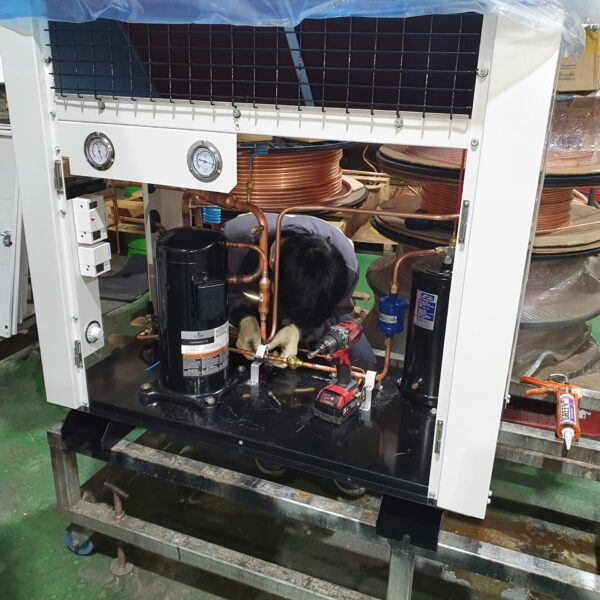
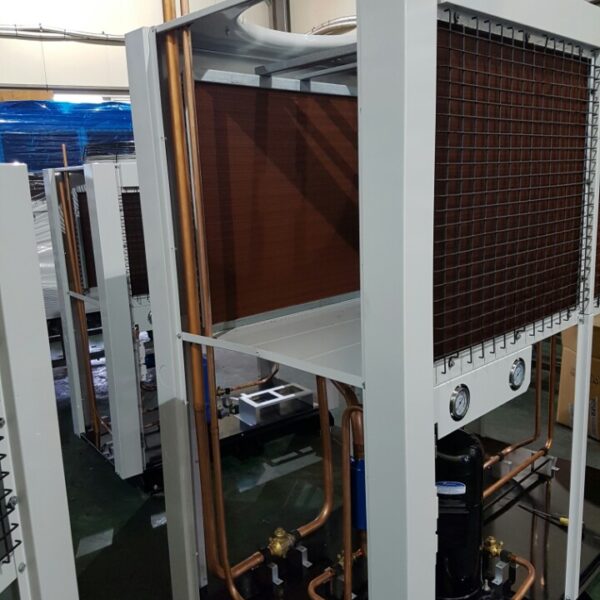
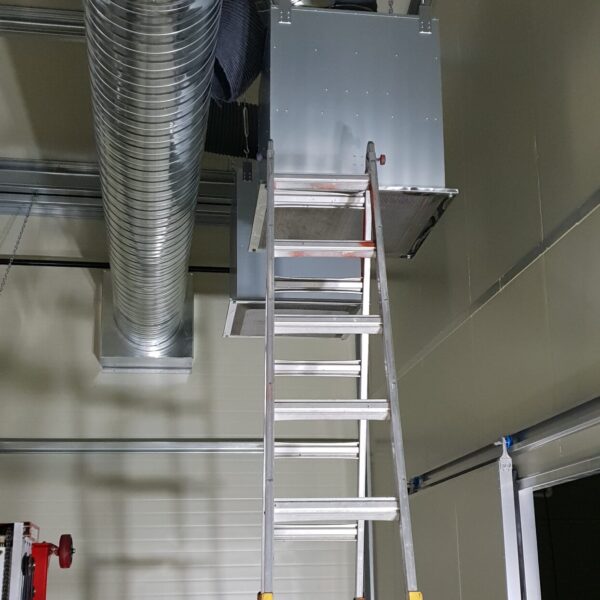
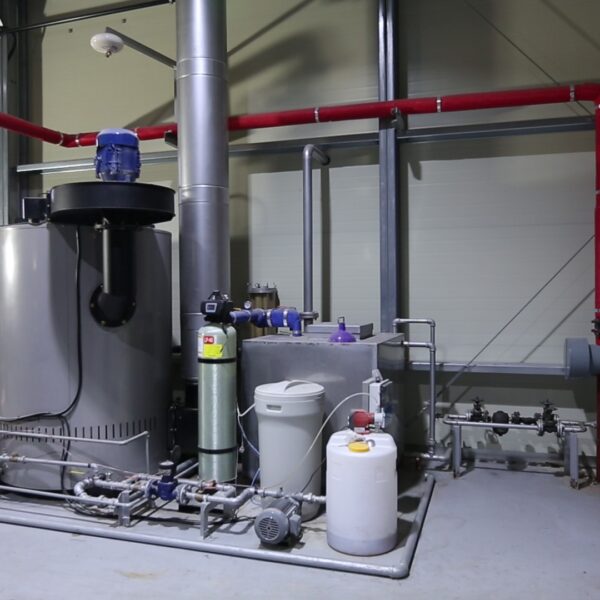
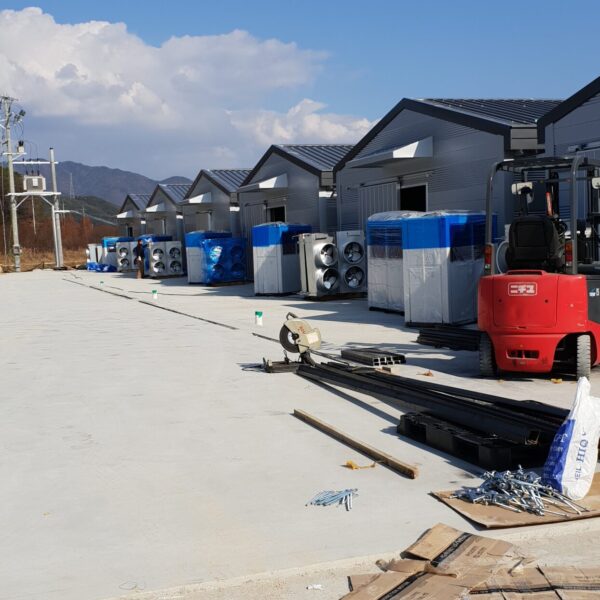
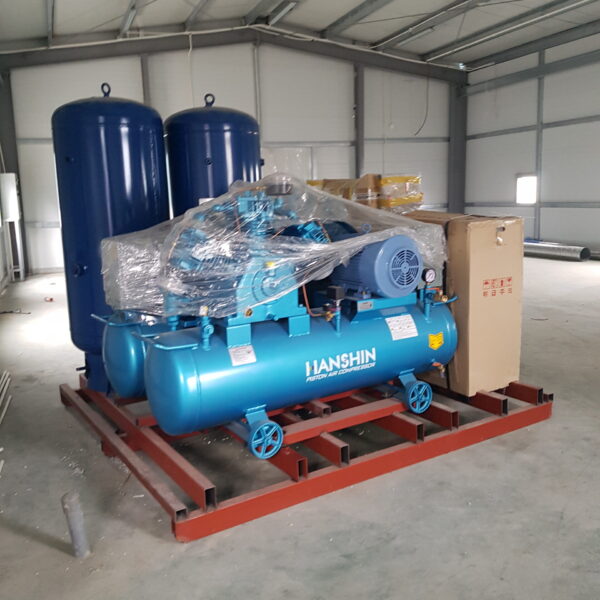
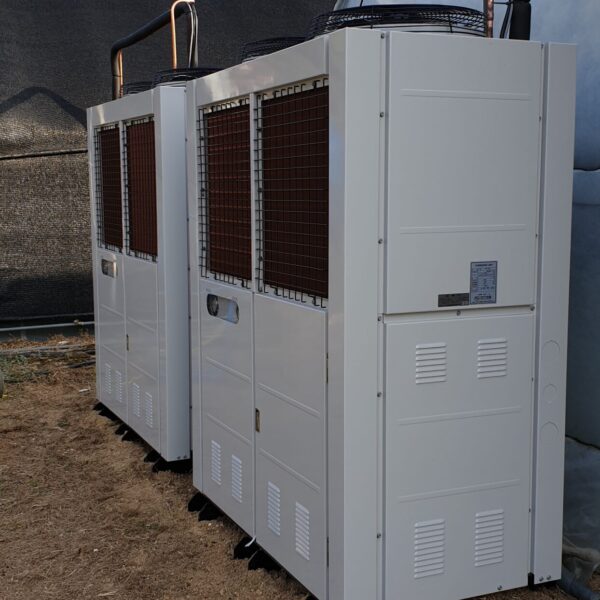
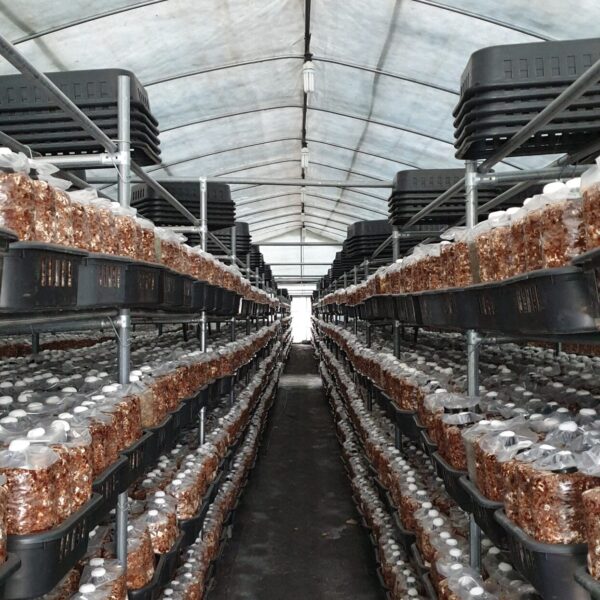
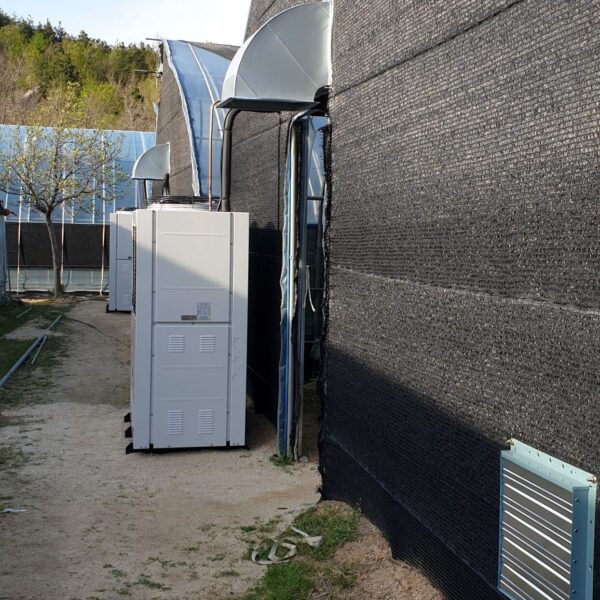
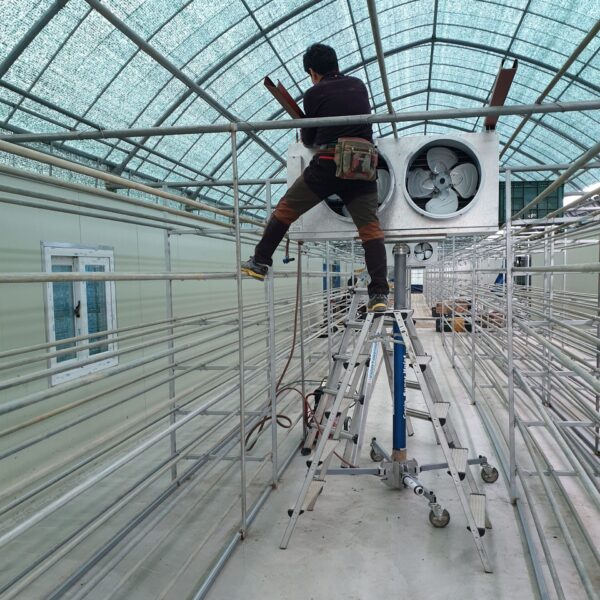
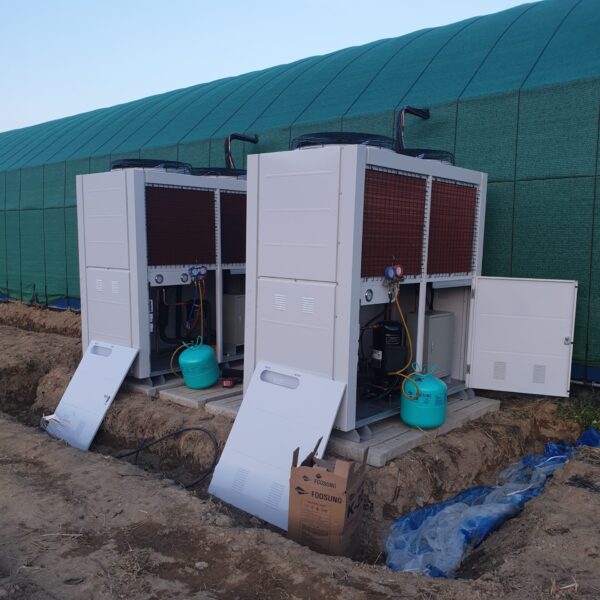
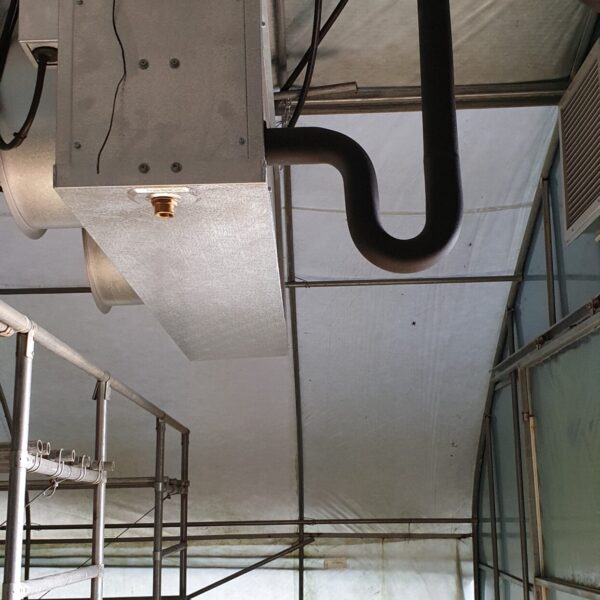
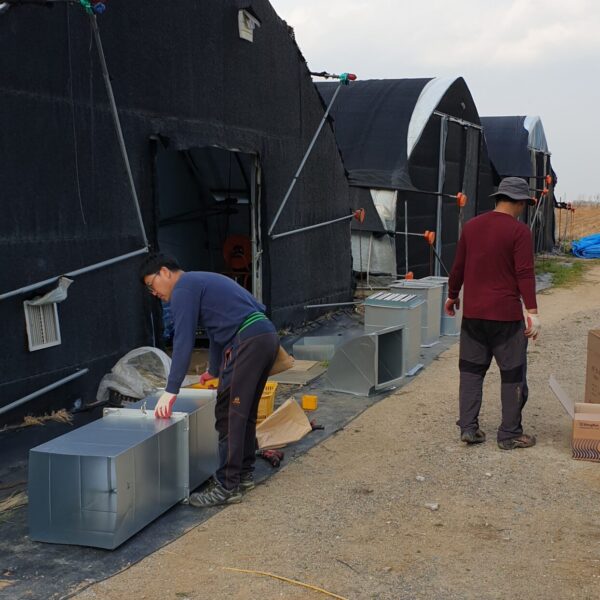
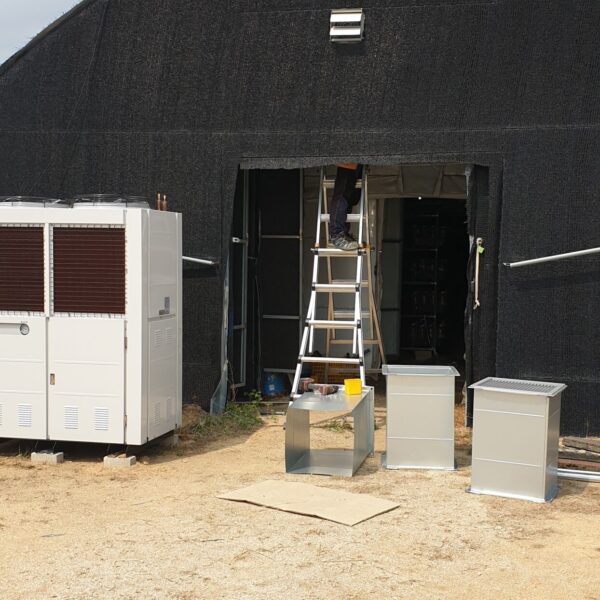
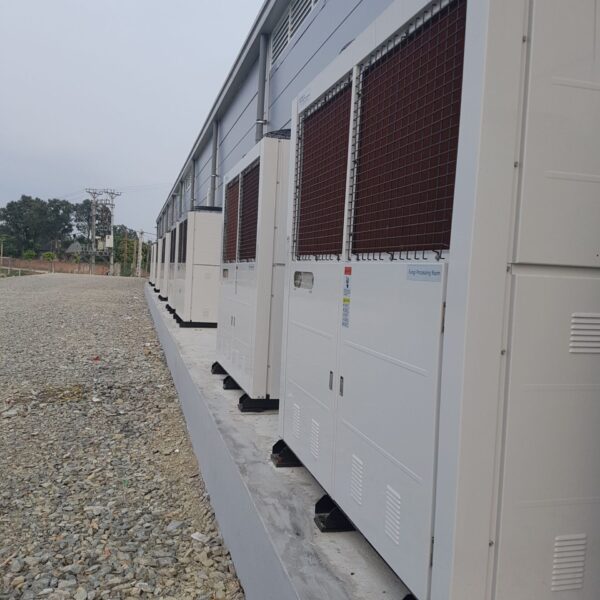
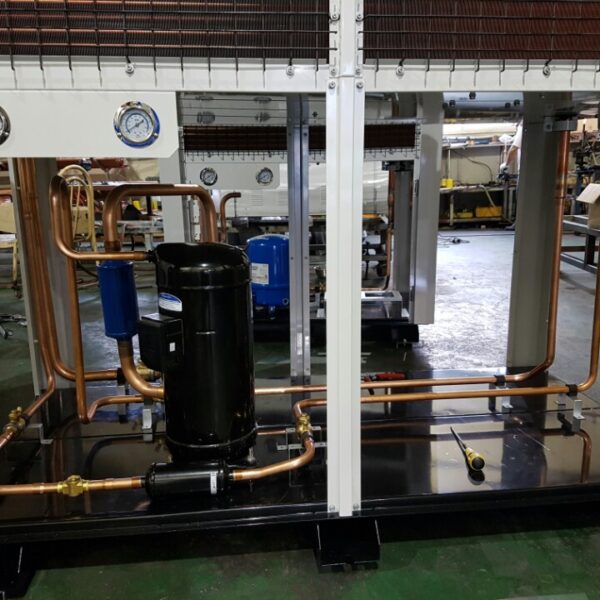
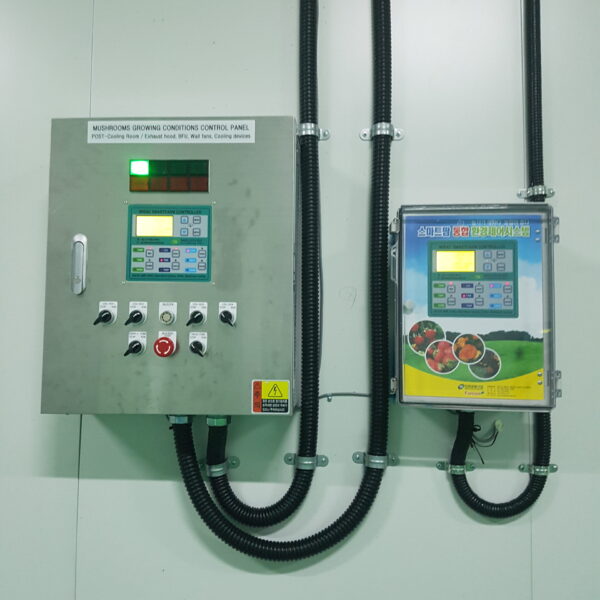
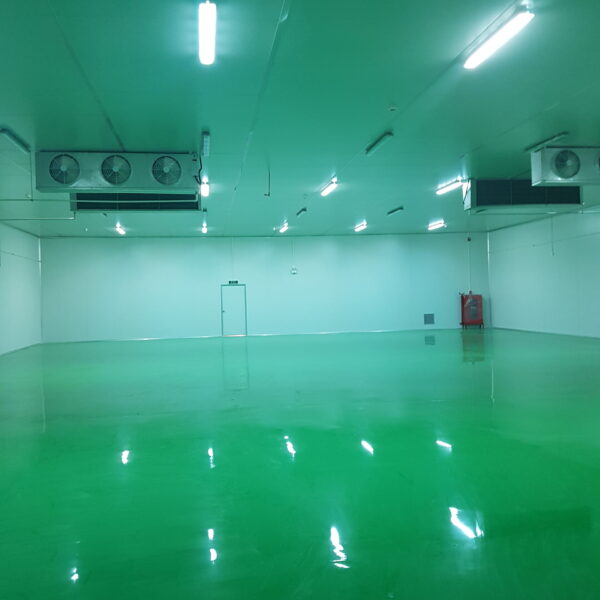
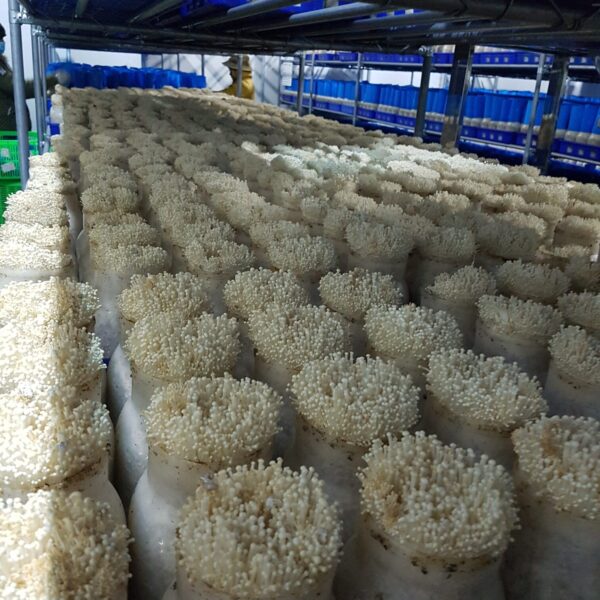
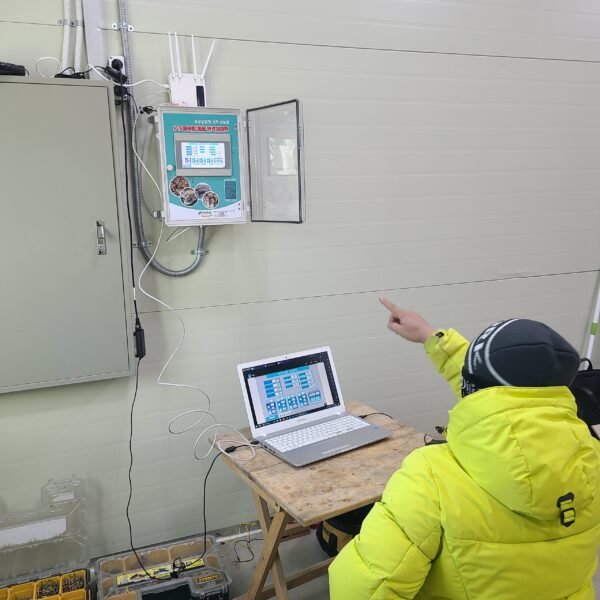
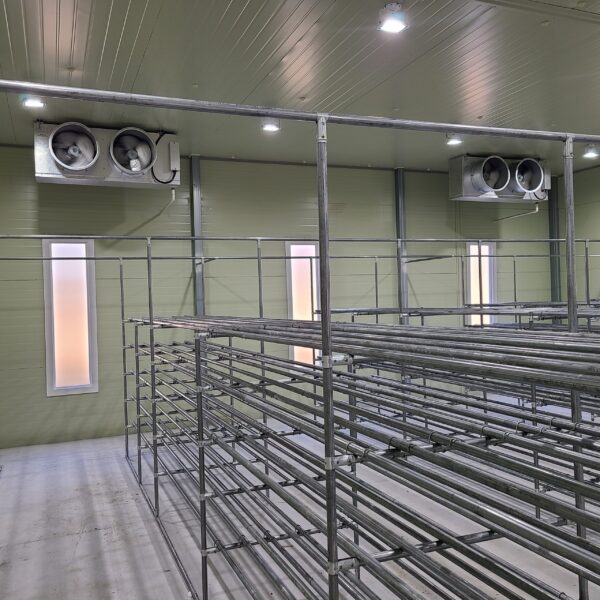
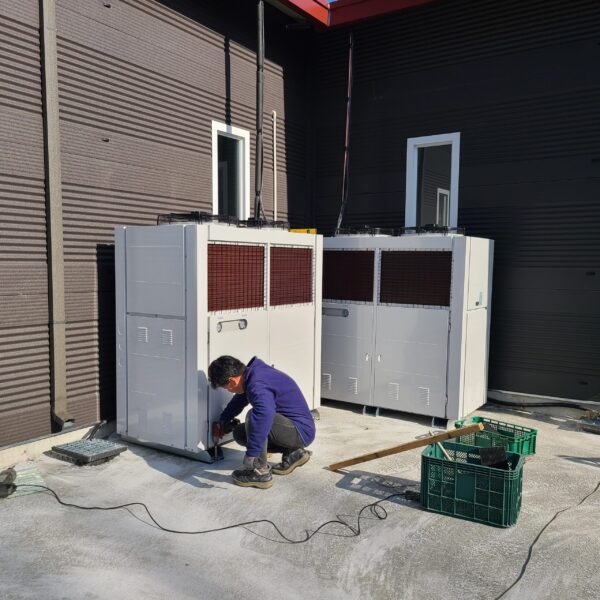
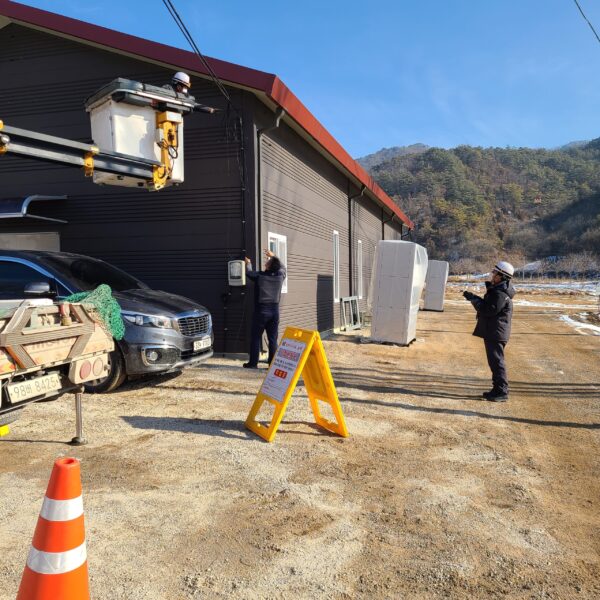
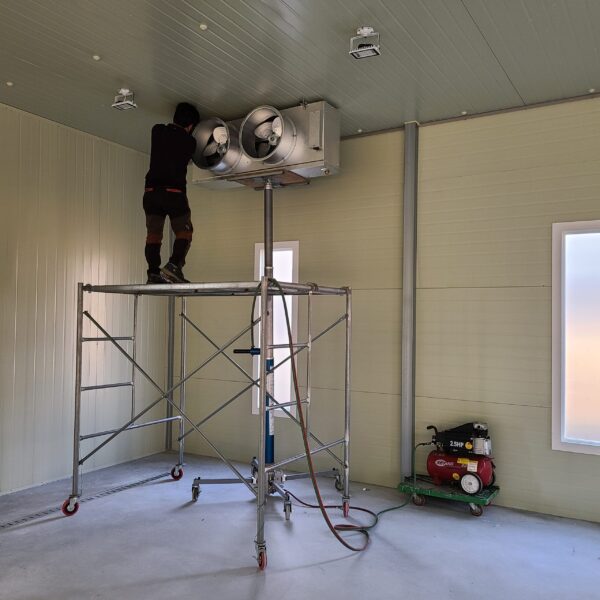
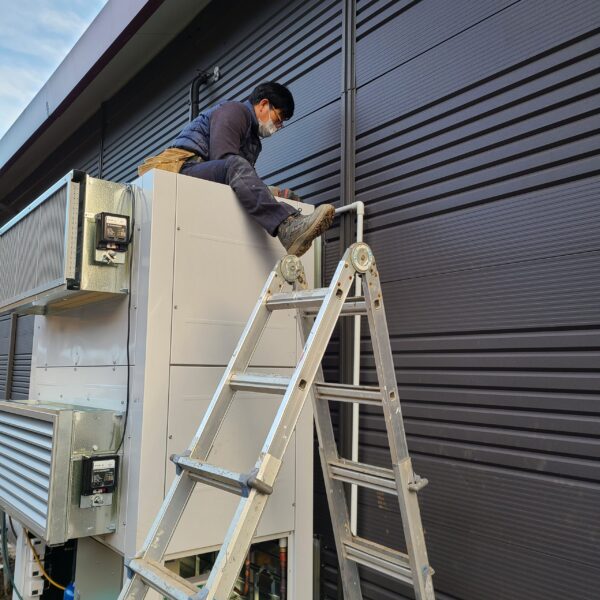
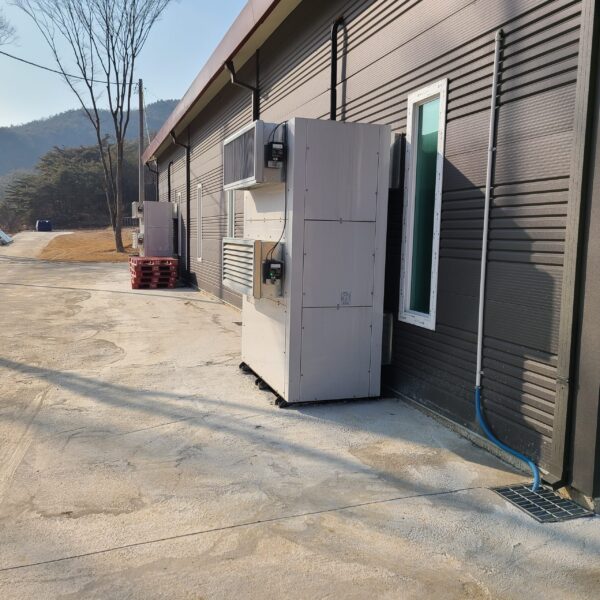
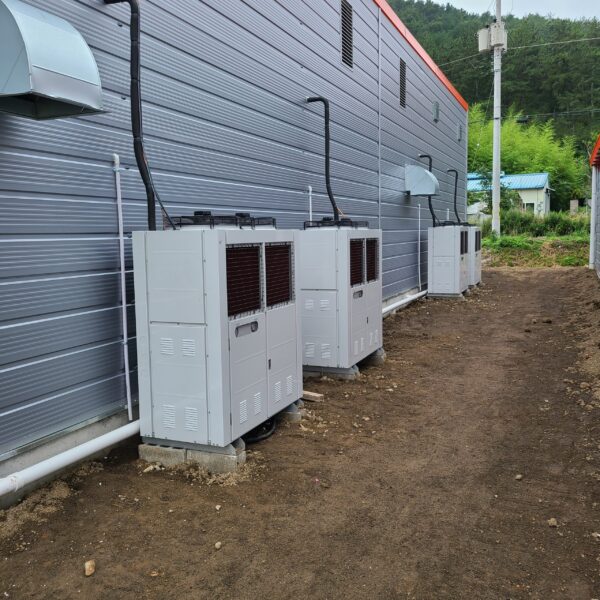
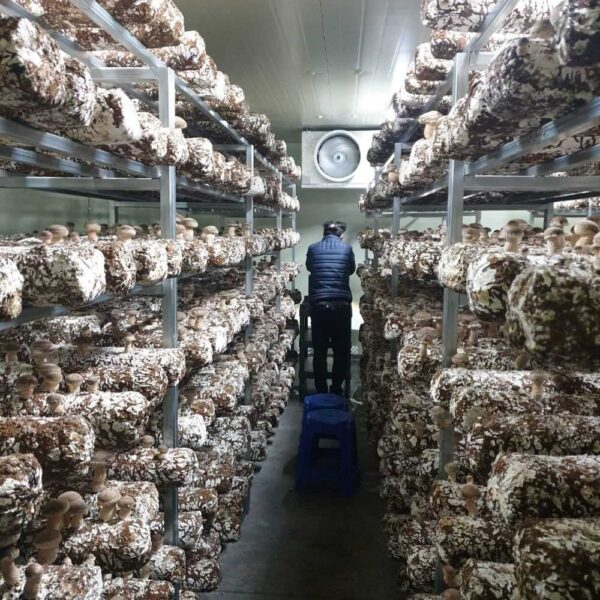
Greenhouse heating is mostly concentrated in winter, and fuel costs account for about 35% of facility horticultural production costs. In the heating design of the greenhouse, the target area, cultivated crops, greenhouse structure, insulation status, heating load, heating method, heat source and thermal efficiency should be considered.
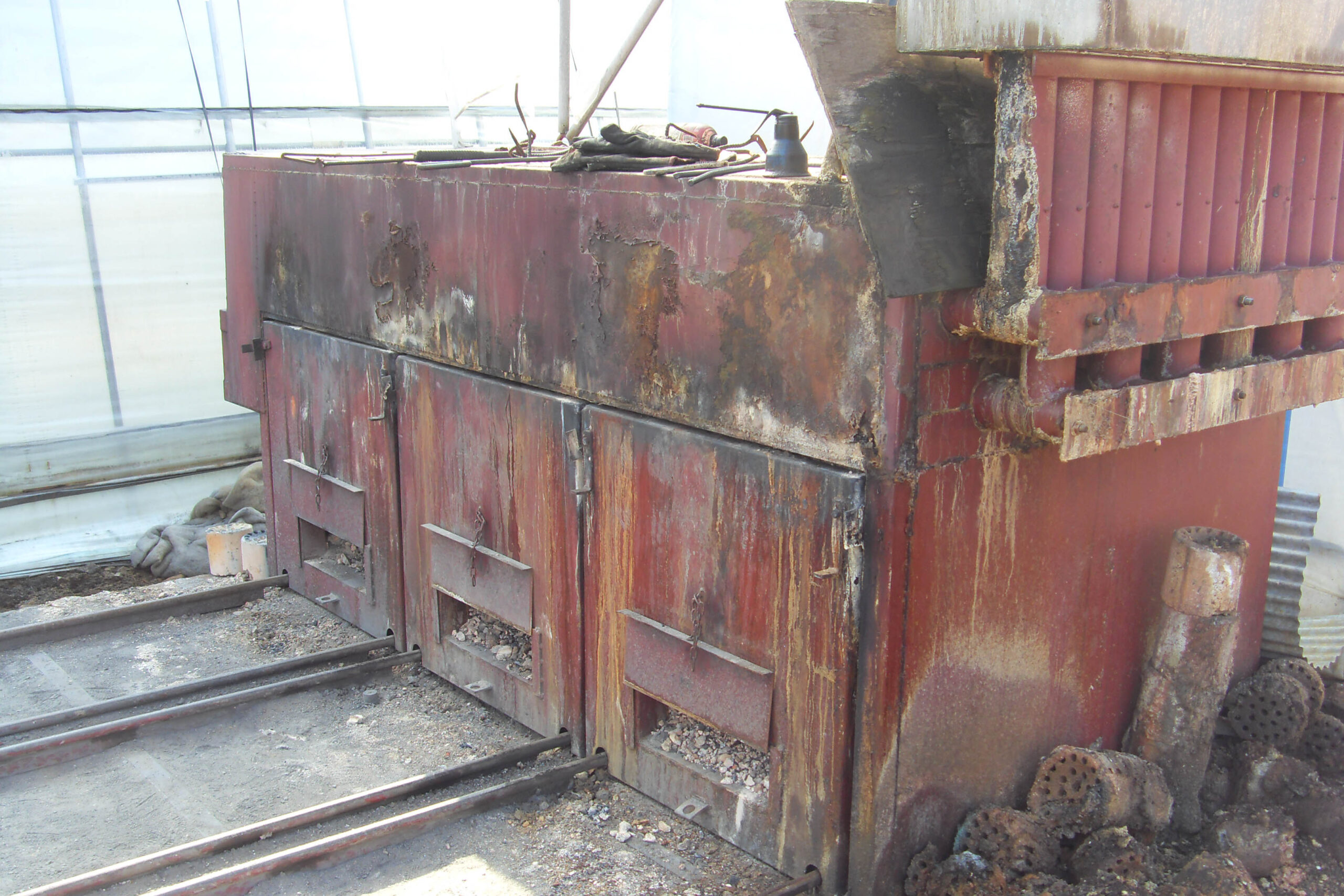
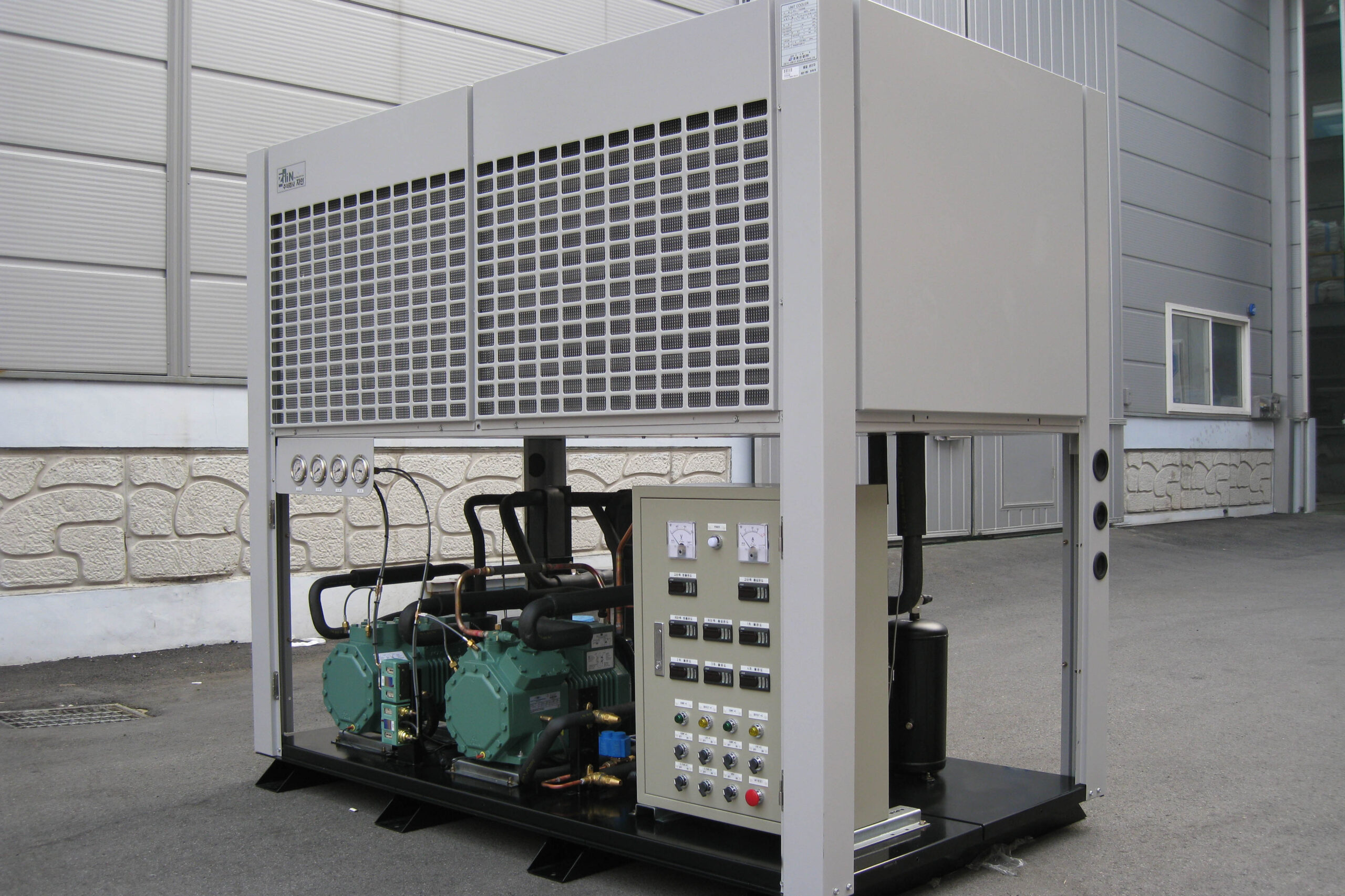
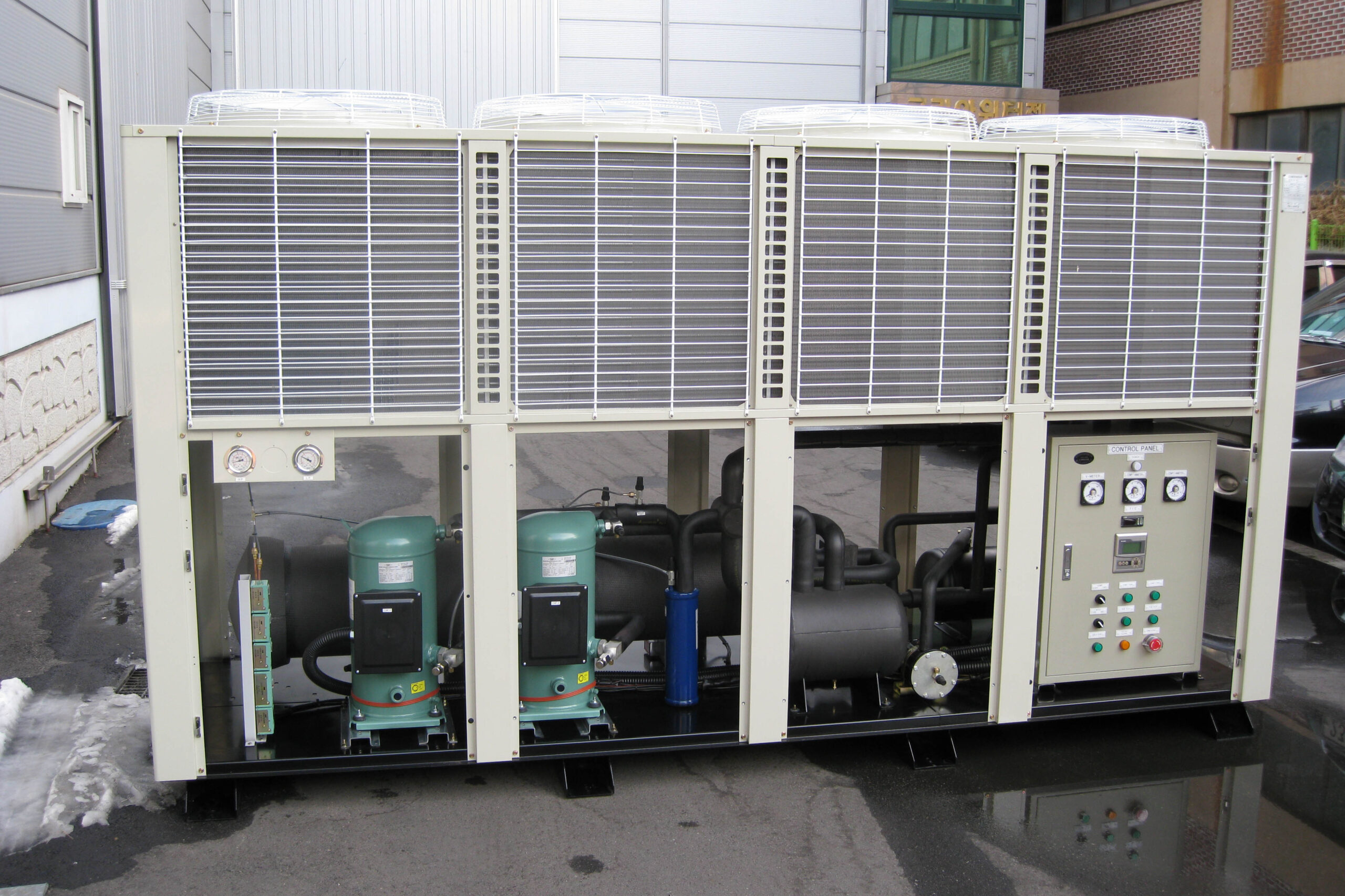
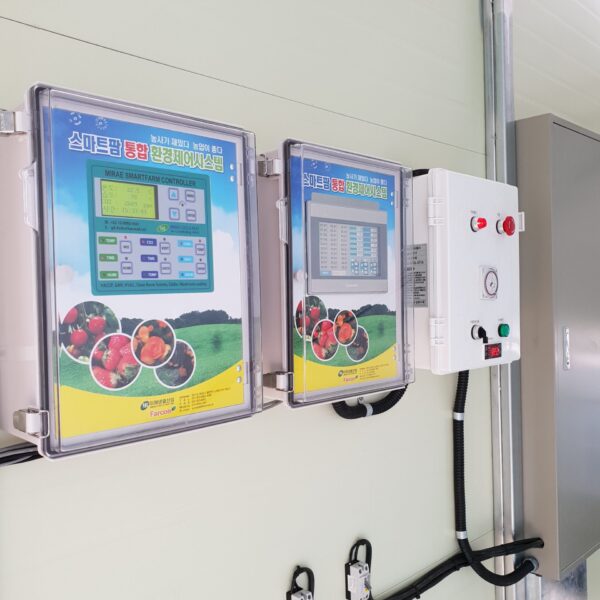
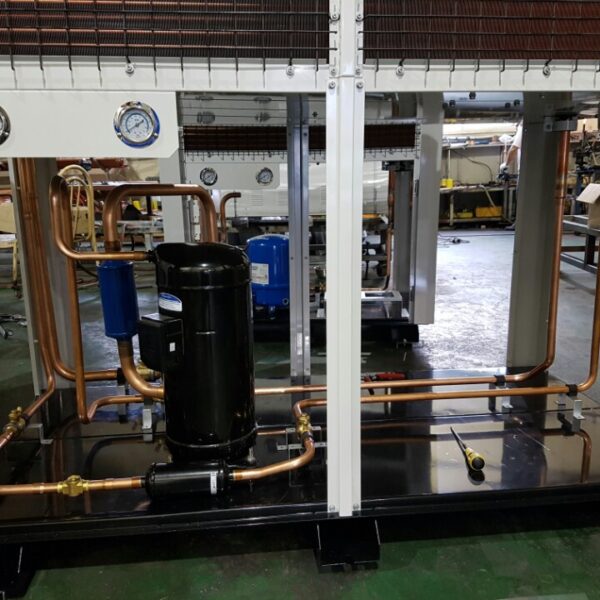
Most of the heating methods used in most greenhouses are hot air heating and hot water heating using coal, diesel, kerosene, and gas as heat sources. Heat pump heating method is also used, but its use is limited if cooling is not included due to high facility cost. On the other hand, electric hot air heating using electricity is convenient to use, and automation facilities using smart farms are easy and safe, so it is necessary to review and use heat sources that are good for use, electricity supply and demand by country, and charge system.