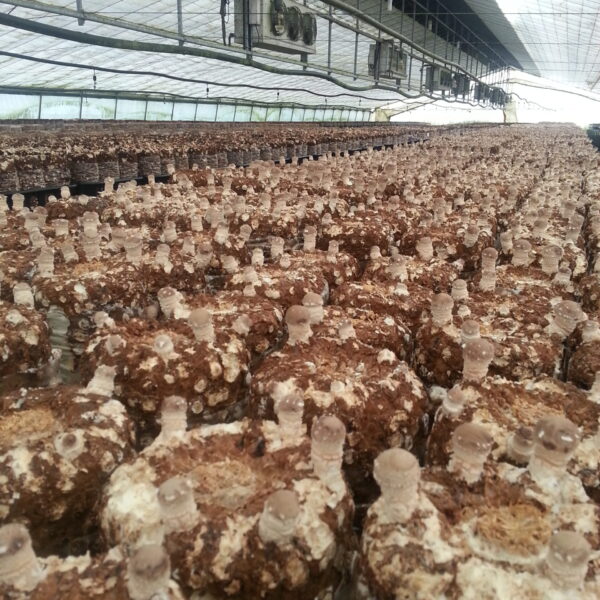
Shiitake mushrooms are a type of fungus and have strong metabolism even after harvest, so post-harvest product temperature management is important to maintain freshness. Even in winter, if the product is stored in boxes after harvest, the internal product temperature will rise continuously, so pre-cooling should be done immediately after harvest. Because shiitake mushrooms are difficult to distribute in refrigeration, most of them are dried and used. However, dried mushrooms are inconvenient to use for cooking and taste and flavor are inferior to those of fresh shiitake. Therefore, consumption of fresh shiitake is increasing day by day. Technology development for storage is required. The cultivation of shiitake mushrooms is mainly cultivated in China and Japan, including Korea, and there are two types of cultivation: wood cultivation and sawdust medium cultivation, and there are some differences in taste and nutrition depending on the cultivation conditions.

The moisture content of the shiitake mushroom cap differs depending on the characteristics of the mushrooms during the harvest season. Depending on the shape of the cap, the moisture content at the time the cap is fully deployed is higher than that of the less developed hyanggo or bundling, but there is no difference in the moisture content depending on the growth status of the mushrooms. Mushrooms that appear dry at the time of harvest have a lower moisture content than those that look humid, and it is advantageous for mushrooms that are suitable for sub-freezing storage to be somewhat dry at the time of harvest, even if they are low-temperature properties. Mushrooms for export are low-temperature mushrooms, so those with a moisture content of around 80% of Hwago or Donggo produced in spring are suitable.
Among the low-temperature shiitake, Hwago harvested in spring has good storability, and Donggo harvested in autumn has poorer storability than Hwago.
Among bundling, mushrooms produced in humid conditions have a high moisture content, so it is not desirable for long-term storage.
storage
Since shiitake mushrooms have a very high respiration rate, respiration resumes if the product temperature cannot be removed promptly after harvest. Metabolism continues even during partial freezing at a storage temperature of -3°C to generate heat of respiration. is lowered
The storage limit temperature of shiitake is -3℃, and mushrooms with low or medium temperature and moisture content of less than 80% are the limit temperature of -3℃, and water mushrooms with high moisture content are between -3℃ and 0℃ It is determined according to the degree of moisture content. When stored at -3℃, it appears to be frozen, but the tissue is not damaged. When performing forced ventilation pre-cooling, the temperature of the pre-cooling room should be set to -3℃, and the temperature should be cooled to the center of the mushroom in a short time to stop breathing. At this time, set the pre-cooling room size freezer capacity so that the cooling rate to 0°C is within 2 hours, the cooling rate to -3°C is within 3 hours, and the pre-cooling time is not more than 5 hours.

As a long-term storage method of low-temperature shiitake, it is stored frozen below the freezing point. In this case, the internal tissue is not affected by freezing, so it is an effective method for long-term storage. The cooling capacity of the pre-cooling room is designed with sufficient capacity, and the mushroom container is kept at about 12 kg per box, and when loading, it secures a flow space for cold air, and wraps it with a plastic tent to prevent transpiration. However, for short-term storage, sub-freezing storage is not desirable.
In the case of low-temperature shiitake, if stored at -3℃ below freezing point, it can be stored for up to 60 days.
If the storage temperature is below -3℃, tissue destruction occurs due to freezing and the function of cell membrane is destroyed, but thermophilic mushrooms are more damaged. Therefore, for high-temperature shiitake, pre-cooling at -3℃ or higher and below 0℃ can prevent quality change, and short-term storage also refers to the moisture content between -3℃ and 0℃, and long-term storage is not recommended. .
design
In refrigerated storage at low temperature altitude, the calorific value by respiration at the set temperature of 10℃ is 740kcal/hr per ton, and the calorific value at -3℃ after freezing is 323kcal/hr, which is reduced to less than half. There is a difference in calorific value depending on the shape of the mushrooms at the time of harvest. The calorific value of the bundled mushroom was the lowest, and the calorific value increased in the order of the slightly open cap and the fully unfolded state. The height of shiitake was much higher than that of oyster mushroom and somewhat lower than that of oyster mushroom, indicating the calorific value due to breathing. The product temperature at the time of harvest of high-temperature shiitake in July was 25℃. At this time, the calorific value per ton was about 4,000kcal/hr, which is much higher than that of low-temperature shiitake. decreased significantly to about 10% of If the respiratory heat is not removed immediately after harvest, growth continues, the cap develops, and it turns brown and turns into a low-quality mushroom, resulting in poor marketability. Insufficient amount of cooling heat in the low-temperature storage can cause the temperature of the storage to rise because it cannot handle the temperature of the mushrooms during storage. . In this case, it is stored in small portions and shipped immediately after pre-cooling to control the storage load within the storage capacity.
The design of the warehouse calculates the cooling load based on the maximum daily production in summer. The pre-cooling room and the defrosting room are divided into a low-temperature storage room, and the pre-cooling room is designed with three times the amount of time produced as the maximum pre-cooling capacity.
Freezing 20% of the mushroom weight within 4 hours at -3℃ set temperature The selection of the freezer per ton is 20hp/ton. When designing for fresh distribution, that is, for domestic distribution, it is designed at 10hp/ton when the temperature is 0℃ for up to 2 hours based on pre-cooling. In the design of the low-temperature storage room, the cooling capacity is sufficient to maintain the temperature by moving from the pre-cooling room to the pre-cooling room, so the storage room size is designed based on the maximum yield for 5 days, and the capacity of the freezer is 5hp per 10 pyeong.
thaw
Mushrooms stored at -3℃ freezing temperature must be thawed before shipping because the mycelium and moisture are frozen. Defrosting is carried out slowly at 10℃, and after thawing is completed, a humidifier is used to supply moisture so that the moisture in the body that has decreased during storage can be recovered. At this time, excessive humidification may cause dew condensation on the mushroom surface, which may cause water mushrooms, and there is a risk of browning and water immersion in the distribution process.
distribution
After thawing the frozen and stored mushrooms, as a distribution condition, they must be sold at low temperature through cold chain and refrigerated display through showcase. According to the study, during the distribution and sale process after thawing, low-temperature shiitake maintained marketability for 8 days under refrigeration conditions below 10℃, but maintained marketability for only 4 days when distributed at room temperature. When selling at room temperature, the commercial properties were maintained for only 2 days. Drying and browning are the most common causes of loss of marketability, and excessive humidification during the thawing process causes tissue to collapse due to plastic packaging in the state of water mushrooms. In this case, small packaging is not recommended.

Export
Shiitake mushrooms are rich in fiber, mineral, vitamin D, and amino acids, and are particularly good for preventing hypertension and osteoporosis, and have strong medicinal properties. The cultivated area in Korea is steadily increasing, and K-food is popular in South America, the United States, Southeast Asia and Europe due to the recent influence on the Hallyu wave.
As the technical aspects of export of fresh shiitake are being studied continuously, mushrooms exported after maintaining the frozen state maintained 95% or more quality when sold at retail stores in a refrigerated showcase under 10℃ for 2 days, and 84% when distributed at room temperature. If the commercialization rate is 92% when selling through the normal distribution process through the cold chain after harvesting at domestic farms, the export of fresh shiitake is expected.
For export packaging, bulk packaging can prevent condensation and browning caused by excessive moisture that occurs during small packaging rather than small packaging. 90% of the shiitake distributed overseas is from China, and most of it is distributed in the form of dried shiitake. However, the use of dried shiitake is limited for soup dishes and for broth, and consumption is concentrated mostly in Asian countries including local Koreans. In this urgent situation, when fresh shiitake can be distributed locally, local consumption is expected to increase explosively beyond that of dried shiitake. Tax benefits of exporting farms When exports are actively carried out through diversification of export markets, etc., it not only increases the income of domestic farms who are suffering from poor prices due to increased production, but also informs the world of K-food, which is rich in taste and nutrition, and earns foreign currency. It can also contribute to the global market, so it is a time for shiitake farmers to actively plan overseas markets.

Considerations when designing
a low-temperature warehouse
Considerations when designing
a low-temperature warehouse